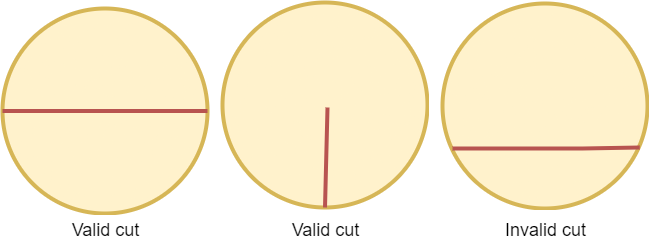
A valid cut in a circle can be:
- A cut that is represented by a straight line that touches two points on the edge of the circle and passes through its center, or
- A cut that is represented by a straight line that touches one point on the edge of the circle and its center.
Some valid and invalid cuts are shown in the figures below.
Given the integer n, return the minimum number of cuts needed to divide a circle into n equal slices.
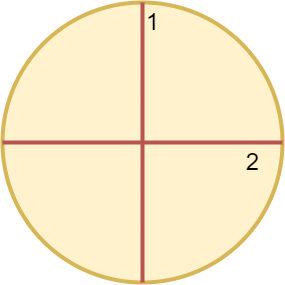
Example 1:
Input: n = 4 Output: 2 Explanation: The above figure shows how cutting the circle twice through the middle divides it into 4 equal slices.
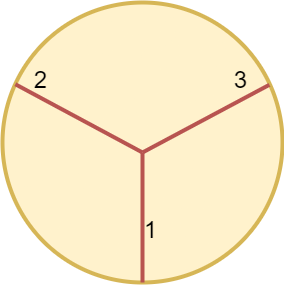
Example 2:
Input: n = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: At least 3 cuts are needed to divide the circle into 3 equal slices. It can be shown that less than 3 cuts cannot result in 3 slices of equal size and shape. Also note that the first cut will not divide the circle into distinct parts.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 100
class Solution:
def numberOfCuts(self, n: int) -> int:
return n if (n > 1 and n & 1) else n >> 1class Solution {
public int numberOfCuts(int n) {
return n > 1 && n % 2 == 1 ? n : n >> 1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numberOfCuts(int n) {
return n > 1 && n % 2 == 1 ? n : n >> 1;
}
};func numberOfCuts(n int) int {
if n > 1 && n%2 == 1 {
return n
}
return n >> 1
}function numberOfCuts(n: number): number {
return n > 1 && n & 1 ? n : n >> 1;
}impl Solution {
pub fn number_of_cuts(n: i32) -> i32 {
if n > 1 && n % 2 == 1 {
return n;
}
n >> 1
}
}public class Solution {
public int NumberOfCuts(int n) {
return n > 1 && n % 2 == 1 ? n : n >> 1;
}
}