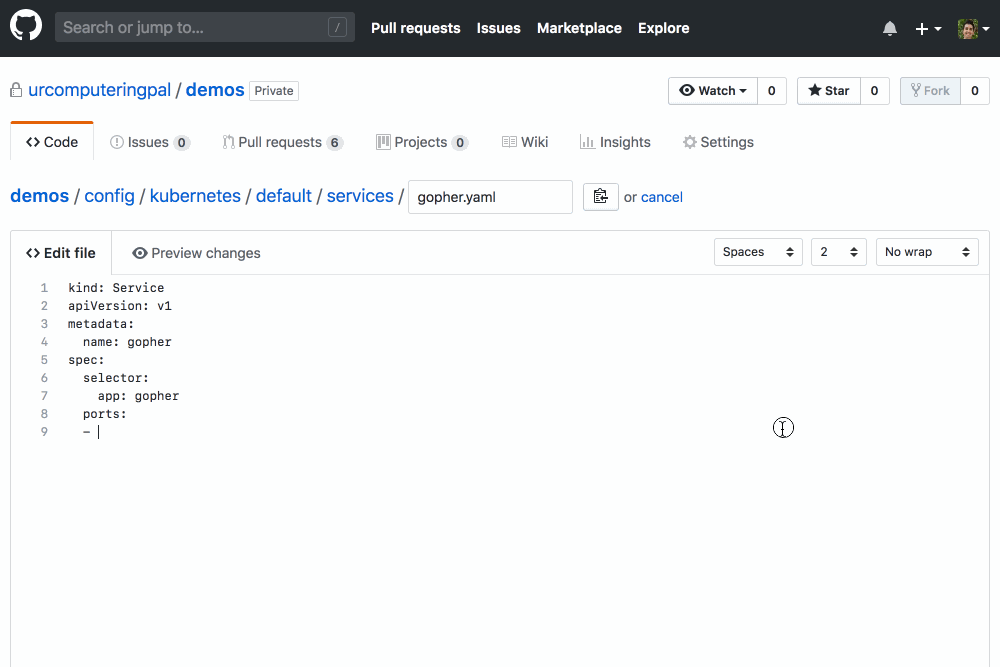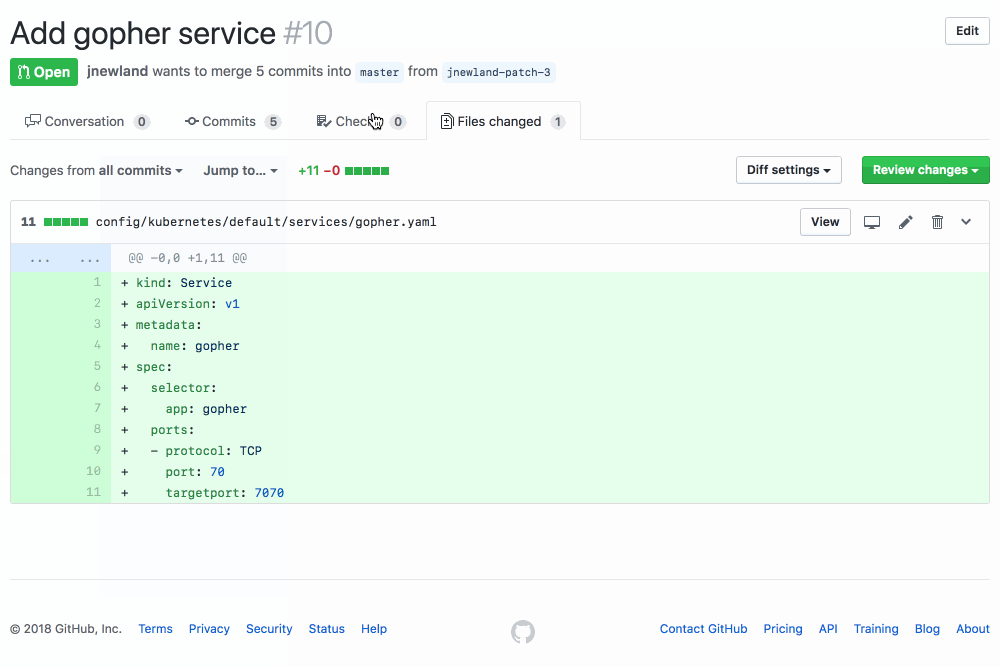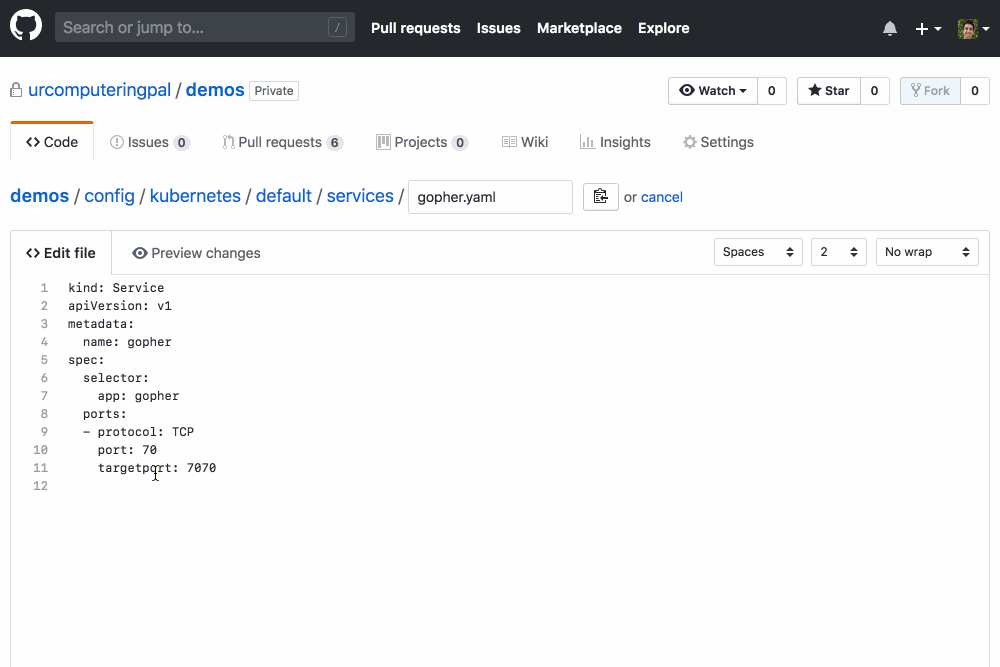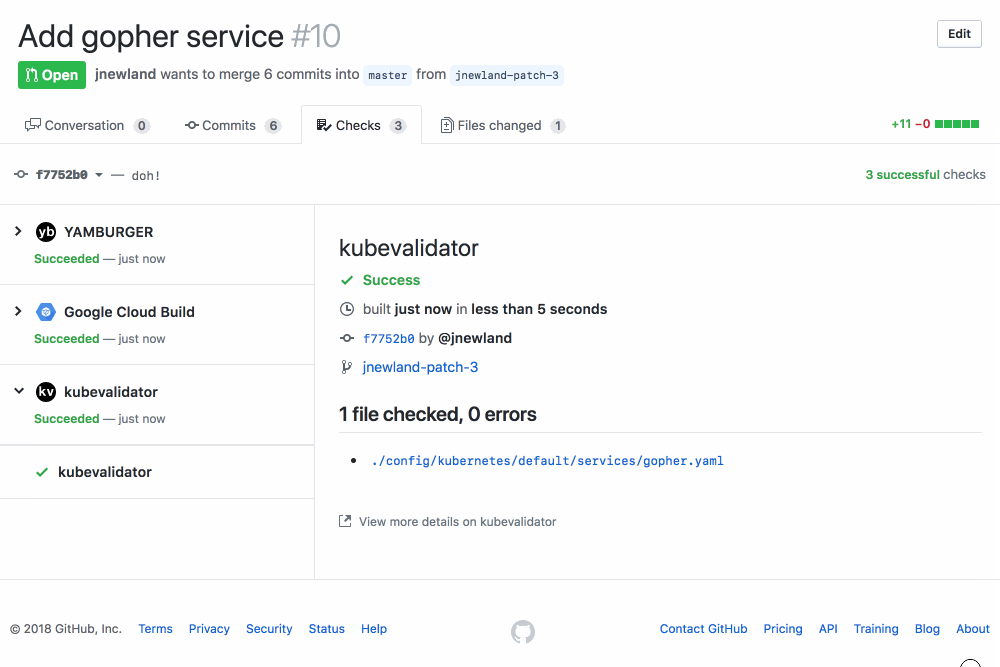
A GitHub App that validates the Kubernetes YAML in your GitHub PRs using kubeval.
- Improve the experience of changing and reviewing YAML documents representing Kubernetes resources by detecting and highlighting errors automatically.
- Allow validation against multiple schemas to support applications deployed to multiple Kubernetes clusters with disparate versions.
- Explore the viability of writing a generalized Probot-like GitHub App toolkit in Golang.
- Validate the syntax of your YAML. (Shameless plug: use YAMBURGER for that! It's kinda dope!)
kubevalidator depends on you to tell it which YAML in your repository it should validate using a file at .github/kubevalidator.yaml. This repo's config is a decent example:
apiversion: v1alpha
kind: KubeValidatorConfig
spec:
manifests:
- glob: config/kubernetes/default/*/*.yaml
schemas:
- version: 1.13.0
- version: 1.13.3
#
# Schema options and their defaults. See config.go for more details.
#
# version: 'master'
# name: 'human readable name' # defaults to the value of version
# If the schemas in https://github.com/garethr/kubernetes-json-schema
# don't work for you, fork it and drop your username here! Your schemas
# will be used instead.
#
# schemaFork: garethr
# Set this to openshift to use schemas from
# https://github.com/garethr/openshift-json-schema instead.
#
# type: kubernetes
See CONTRIBUTING.md
These instructions are untested. Please open a new issue or PR if you run into any problems or would prefer to use another deployment tool!
- Fork & clone this repo.
- Edit or delete the included Ingress and/or Service resources to match your target cluster's load balancing requirements.
- Create a new GitHub App with the following settings:
- Homepage URL: the URL to the GitHub repository for your app
- Webhook URL: Use https://example.com/ for now, we'll come back in a minute to update this with the URL of your deployed app.
- Webhook Secret: Generate a unique secret with
openssl rand -base64 32and save it because you'll need it in a minute to configure your deployed app - Permissions:
- Checks: Read & Write
- Repository contents: Read-only
- Repository metadata: Read-only
- Pull requests: Read-only
- Webhooks:
- Check Suite
- Pull Request
- Generate and download a new key for your app. Note the path.
- Create a secret with values to authenticate your instance of kubevalidator as your GitHub app
kubectl create secret generic kubevalidator
--from-file=PRIVATE_KEY=~/Downloads/path-to-kubeval-key.pem \
--from-literal=APP_ID=1234 \
--from-literal=WEBHOOK_SECRET=1234 \
--dry-run=true -o yaml > config/kubernetes/default/secrets/kubeval.yaml
- Configure access to a Kubernetes cluster.
- Create a
kubevalidatornamespace on that cluster. - Install Skaffold.
- Point
build.artifacts[0].imagein skaffold.yaml to an accessible docker image path, and make sure it matches the image specified in thekubernetes/default/deployments/kubevalidator.yamldeployment manifest - Run
skaffold runto deploy this application to your cluster!
- 🙇 to @keavy, @kytrinyx, @lizzhale and many more for your work on GitHub Checks. PRs aren't ever going to be the same.
- 🙇 to @garethr for your work on kubeval. It does all of the heavy lifting here, I've just put some GitHub-flavored window dressing on top.
- 🙇 to @bkeepers for your work on Probot. I've learned a ton building Probot apps in the past few months, and hope that you don't mind that I've poorly re-implemented a small portion of it in Golang in this project. 😉
Please file an issue! If you'd prefer to reach out in private, please send an email to [email protected].