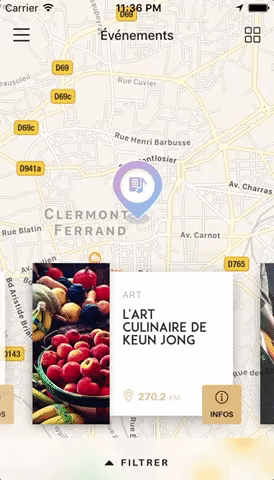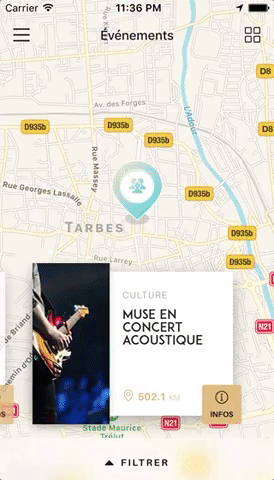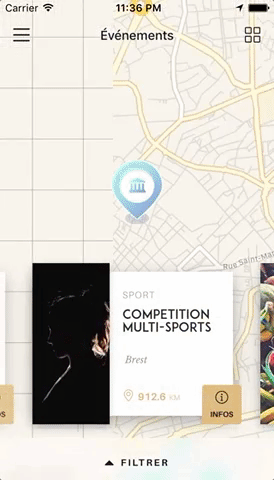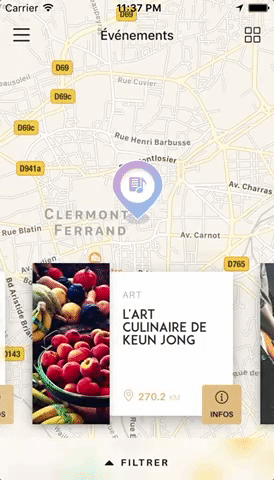
Swiper component for React Native with previews and snapping effect. Compatible with Android & iOS. Pull requests are very welcome!
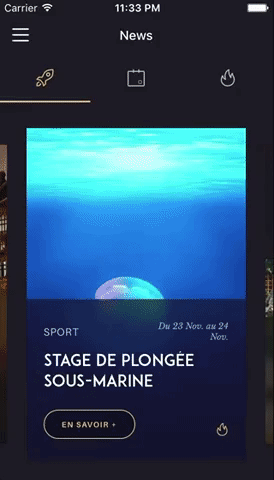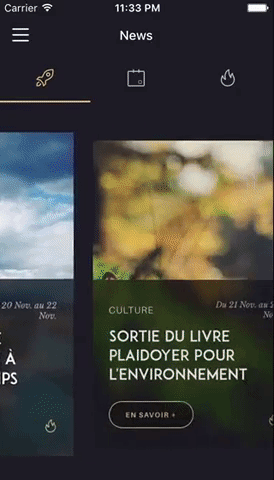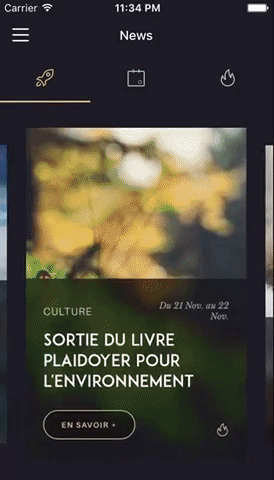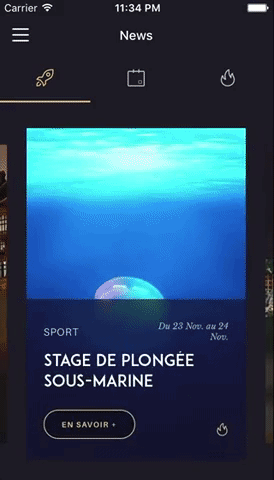
You can try these examples live in Archriss' showcase app on Android and iOS. This app is going to be updated on a regular basis.
Since it has been asked multiple times, please note that we do not plan on Open-Sourcing the code of our showcase app. Still, we've put together an example for you to play with, and you can find some insight about our map implementation in this comment.
Since version 2.0.0, items are now direct children of the component. As a result, props items and renderItem have been removed.
$ npm install --save react-native-snap-carousel
import Carousel from 'react-native-snap-carousel';
// Example with different children
render () {
<Carousel
ref={'carousel'}
sliderWidth={sliderWidth}
itemWidth={itemWidth}
>
<View style={styles.slide1} />
<ListView style={styles.slide2} />
<Image style={styles.slide3} />
</Carousel>
}
// Example of appending the same component multiple times while looping through an array of data
render () {
const slides = this.state.entries.map((entry, index) => {
return (
<View key={`entry-${index}`} style={styles.slide}>
<Text style={styles.title}>{ entry.title }</Text>
</View>
);
});
<Carousel
ref={'carousel'}
sliderWidth={sliderWidth}
itemWidth={itemWidth}
>
{ slides }
</Carousel>
}In addition to these props, you can provide any prop from the ScrollView component.
| Prop | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| itemWidth | Width in pixels of your items | Number | Required |
| sliderWidth | The width in pixels of your slider | Number | Required |
| animationFunc | Animated animation to use. Provide the name of the method | String | timing |
| animationOptions | Animation options to be merged with the default ones. Can be used w/ animationFunc | Object | { easing: Easing.elastic(1) } |
| autoplay | Trigger autoplay on mount | Boolean | false |
| autoplayDelay | Delay before enabling autoplay on startup & after releasing the touch | Number | 5000 |
| autoplayInterval | Delay in ms until navigating to the next item | 3000 |
|
| containerCustomStyle | Optional styles for Scrollview's global wrapper | ScrollView Style Object | {} |
| contentContainerCustomStyle | Optional styles for Scrollview's items container | ScrollView Style Object | {} |
| enableMomentum | See momentum | Boolean | false |
| enableSnap | If enabled, releasing the touch will scroll to the center of the nearest/active item | Number | true |
| firstItem | Index of the first item to display | Number | 0 |
| inactiveSlideOpacity | Value of the opacity effect applied to inactive slides | Number | 1 |
| inactiveSlideScale | Value of the 'scale' transform applied to inactive slides | Number | 0.9 |
| shouldOptimizeUpdates | whether to implement a shouldComponentUpdate strategy to minimize updates |
Boolean | true |
| slideStyle | Optional style for each item's container (the one whose scale and opacity are animated) | Animated View Style Object | {} |
| snapOnAndroid | Snapping on android is kinda choppy, especially when swiping quickly so you can disable it | Boolean | true |
| swipeThreshold | Delta x when swiping to trigger the snap | Number | 20 |
| onSnapToItem(slideIndex) | Callback fired when navigating to an item | Function | undefined |
In order to use the following methods, you need to create a reference to the carousel's instance. There are two ways of doing it.
<Carousel
// other props
ref={(carousel) => { this._carousel = carousel; } }
/>
// methods can then be called this way
onPress={() => { this._carousel.snapToNext(); }}ref as a string attribute (legacy)
<Carousel
// other props
ref={'carousel'}
/>
// methods can then be called this way
onPress={() => { this.refs.carousel.snapToNext(); }}startAutoplay (instantly = false)Start the autoplay manuallystopAutoplay ()Stop the autoplay manuallysnapToItem (index, animated = true)Snap to an item manuallysnapToNext (animated = true)Snap to next item manuallysnapToPrev (animated = true)Snap to previous item manually
currentIndexCurrent active item (int, starts at 0)
You can find the following example in the /example folder.
Since 1.5.0, the snapping effect can now be based on momentum instead of when you're releasing your finger. It means that the component will wait until the ScrollView isn't moving anymore to snap. By default, the inertia isn't too high on Android. However, we had to tweak the default iOS value a bit to make sure the snapping isn't delayed for too long.
You can adjust this value to your needs thanks to this prop.
As a rule of thumb, we recommend setting
enableMomentumtofalse(default) anddecelerationRateto'fast'when you are displaying only one main slide (as in the showcase above), and to usetrueand'normal'(default) otherwise. This should help providing a better snap feeling.
If you need some extra horizontal margin between slides (besides the one resulting from the scale effect), you should add it as paddingHorizontal on the slide container. Make sure to take this into account when calculating item's width.
const sliderWidth = Dimensions.get('window').width * 0.75;
const slideWidth = 250;
const horizontalMargin = 20;
const itemWidth = slideWidth + horizontalMargin * 2;
const styles = Stylesheet.create({
slide: {
width: itemWidth
// other styles for your item's container
}
};
<Carousel
sliderWidth={sliderWidth}
itemWidth={itemWidth}
>
...
</Carousel>- Handle autoplay properly when updating children's length
- Implement 'loop' mode
- Implement 'preload' mode
- Handle changing props on-the-fly
- Handle device orientation event
- Add vertical implementation
- Improve momemtum handling
- Improve snap on Android
- Handle passing 1 item only
- Fix centering
Written by Maxime Bertonnier and Benoît Delmaire at Archriss.