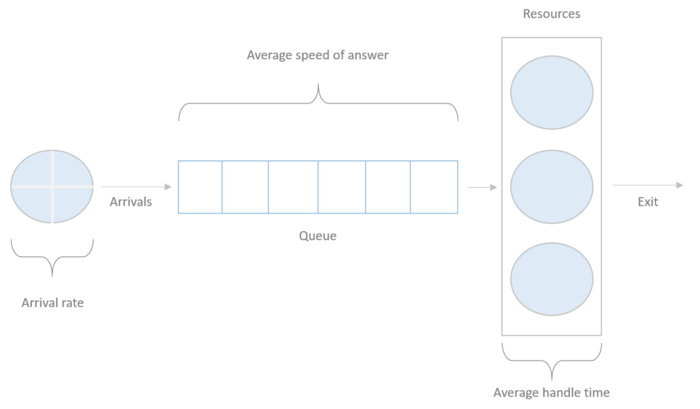
Standard tools for workforce management, queuing, scheduling, rostering and optimization problems.
Make sure to check the documentation, which is available here
Install pyworkforce
It's advised to install pyworkforce using a virtual env, inside the env use:
pip install pyworkforce
If you are having troubles with or-tools installation, check the or-tools guide
For complete list and details of examples go to the examples folder
pyworkforce currently includes:
It solves the following system resource requirements:
- queuing.ErlangC: Find the number of resources required to attend incoming traffic to a constant rate, infinite queue length, and no dropout.
It finds the number of resources to schedule in a shift based on the number of required positions per time interval
(found, for example, using queuing.ErlangC), maximum capacity restrictions and static shifts coverage.
- scheduling.MinAbsDifference: This module finds the "optimal" assignation by minimizing the total absolute differences between required resources per interval against the scheduled resources found by the solver.
- scheduling.MinRequiredResources: This module finds the "optimal" assignation by minimizing the total weighted amount of scheduled resources (optionally weighted by shift cost), it ensures that in all intervals, there are never fewer resources shifted than the ones required per period.
It assigns a list of resources to a list of required positions per day and shifts; it takes into account different restrictions as shift bans, consecutive shifts, resting days, and others. It also introduces soft restrictions like shift preferences.
A brief introduction can be found in this medium post
from pyworkforce.queuing import ErlangC
erlang = ErlangC(transactions=100, asa=20/60, aht=3, interval=30, shrinkage=0.3)
positions_requirements = erlang.required_positions(service_level=0.8, max_occupancy=0.85)
print("positions_requirements: ", positions_requirements)Output:
>> positions_requirements: {'raw_positions': 14,
'positions': 20,
'service_level': 0.8883500191794669,
'occupancy': 0.7142857142857143,
'waiting_probability': 0.1741319335950498}
If you want to run different scenarios at the same time, you can use the MultiErlangC, for example, trying different service levels:
from pyworkforce.queuing import MultiErlangC
param_grid = {"transactions": [100], "aht": [3], "interval": [30], "asa": [20 / 60], "shrinkage": [0.3]}
multi_erlang = MultiErlangC(param_grid=param_grid, n_jobs=-1)
required_positions_scenarios = {"service_level": [0.8, 0.85, 0.9], "max_occupancy": [0.8]}
positions_requirements = multi_erlang.required_positions(required_positions_scenarios)
print("positions_requirements: ", positions_requirements)Output:
>> positions_requirements: [
{
"raw_positions": 13,
"positions": 19,
"service_level": 0.7955947884177831,
"occupancy": 0.7692307692307693,
"waiting_probability": 0.285270453036493
},
{
"raw_positions": 14,
"positions": 20,
"service_level": 0.8883500191794669,
"occupancy": 0.7142857142857143,
"waiting_probability": 0.1741319335950498
},
{
"raw_positions": 15,
"positions": 22,
"service_level": 0.9414528428690223,
"occupancy": 0.6666666666666666,
"waiting_probability": 0.10204236700798798
}
]
A brief introduction can be found in this medium post
from pyworkforce.scheduling import MinAbsDifference, MinRequiredResources
# Rows are the days, each entry of a row, is number of positions required at an hour of the day (24).
required_resources = [
[9, 11, 17, 9, 7, 12, 5, 11, 8, 9, 18, 17, 8, 12, 16, 8, 7, 12, 11, 10, 13, 19, 16, 7],
[13, 13, 12, 15, 18, 20, 13, 16, 17, 8, 13, 11, 6, 19, 11, 20, 19, 17, 10, 13, 14, 23, 16, 8]
]
# Each entry of a shift,an hour of the day (24), 1 if the shift covers that hour, 0 otherwise
shifts_coverage = {"Morning": [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
"Afternoon": [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
"Night": [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1],
"Mixed": [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]}
# Method One
difference_scheduler = MinAbsDifference(num_days=2,
periods=24,
shifts_coverage=shifts_coverage,
required_resources=required_resources,
max_period_concurrency=27,
max_shift_concurrency=25)
difference_solution = difference_scheduler.solve()
# Method Two
requirements_scheduler = MinRequiredResources(num_days=2,
periods=24,
shifts_coverage=shifts_coverage,
required_resources=required_resources,
max_period_concurrency=27,
max_shift_concurrency=25)
requirements_solution = requirements_scheduler.solve()
print("difference_solution :", difference_solution)
print("requirements_solution :", requirements_solution)Output:
>> difference_solution: {'status': 'OPTIMAL',
'cost': 157.0,
'resources_shifts': [{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Morning', 'resources': 8},
{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Afternoon', 'resources': 11},
{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Night', 'resources': 9},
{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Mixed', 'resources': 1},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Morning', 'resources': 13},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Afternoon', 'resources': 17},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Night', 'resources': 13},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Mixed', 'resources': 0}]
}
>> requirements_solution: {'status': 'OPTIMAL',
'cost': 113.0,
'resources_shifts': [{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Morning', 'resources': 15},
{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Afternoon', 'resources': 13},
{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Night', 'resources': 19},
{'day': 0, 'shift': 'Mixed', 'resources': 3},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Morning', 'resources': 20},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Afternoon', 'resources': 20},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Night', 'resources': 23},
{'day': 1, 'shift': 'Mixed', 'resources': 0}]}