TrustKit is an open source framework that makes it easy to deploy SSL public key pinning and reporting in any iOS 12+, macOS 10.13+, tvOS 12+ or watchOS 4+ App; it supports both Swift and Objective-C Apps.
If you need SSL pinning/reporting in your Android App. we have also released TrustKit for Android at https://github.com/datatheorem/TrustKit-Android.
TrustKit provides the following features:
- Simple API to configure an SSL pinning policy and enforce it within an App. The policy settings are heavily based on the HTTP Public Key Pinning specification.
- Sane implementation by pinning the certificate's Subject Public Key Info, as opposed to the certificate itself or the public key bits.
- Reporting mechanism to notify a server about pinning validation failures happening within the App, when an unexpected certificate chain is detected. This is similar to the report-uri directive described in the HPKP specification. The reporting mechanism can also be customized within the App by leveraging pin validation notifications sent by TrustKit.
- Auto-pinning functionality by swizzling the App's NSURLConnection and NSURLSession delegates in order to automatically add pinning validation to the App's HTTPS connections; this allows deploying TrustKit without even modifying the App's source code.
- Read the Getting Started guide.
- Check out the API documentation.
- TrustKit was initially released at Black Hat USA 2015 and was also featured on PayPal's engineering blog.
Deploying SSL pinning in the App requires initializing TrustKit with a pinning policy (domains, Subject Public Key Info hashes, and additional settings).
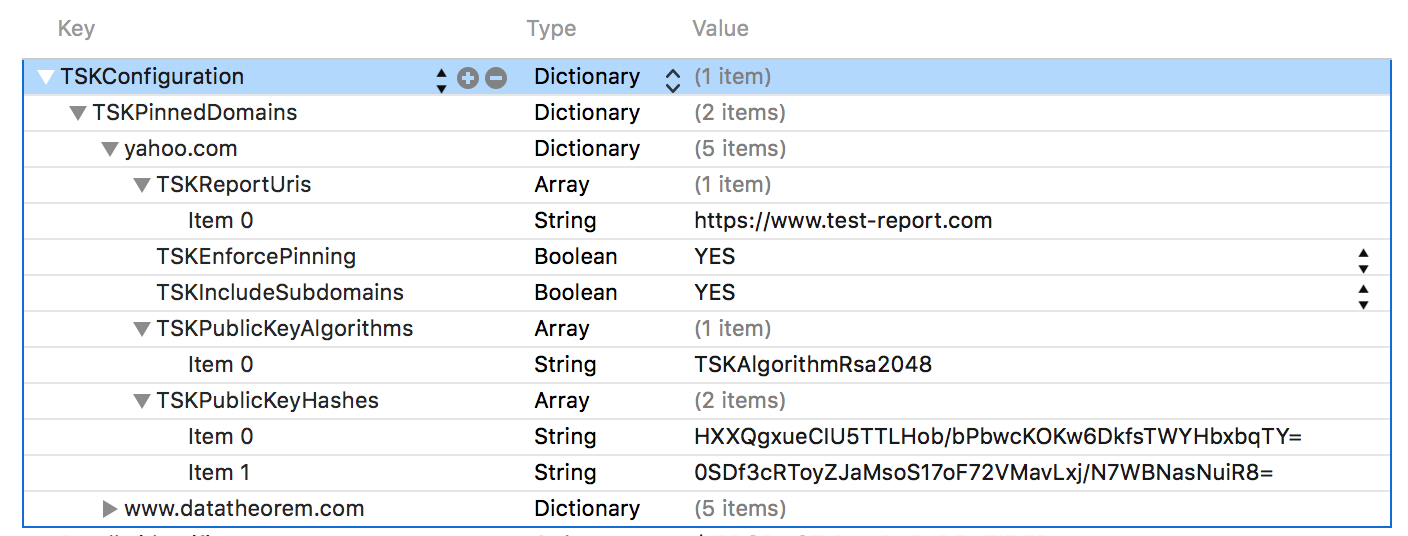
The policy can be configured within the App's Info.plist:
Alternatively, the pinning policy can be set programmatically:
NSDictionary *trustKitConfig =
@{
kTSKSwizzleNetworkDelegates: @NO,
kTSKPinnedDomains : @{
@"www.datatheorem.com" : @{
kTSKExpirationDate: @"2017-12-01",
kTSKPublicKeyHashes : @[
@"HXXQgxueCIU5TTLHob/bPbwcKOKw6DkfsTWYHbxbqTY=",
@"0SDf3cRToyZJaMsoS17oF72VMavLxj/N7WBNasNuiR8="
],
kTSKEnforcePinning : @NO,
},
@"yahoo.com" : @{
kTSKPublicKeyHashes : @[
@"TQEtdMbmwFgYUifM4LDF+xgEtd0z69mPGmkp014d6ZY=",
@"rFjc3wG7lTZe43zeYTvPq8k4xdDEutCmIhI5dn4oCeE=",
],
kTSKIncludeSubdomains : @YES
}
}};
[TrustKit initSharedInstanceWithConfiguration:trustKitConfig];The policy can also be set programmatically in Swift Apps:
let trustKitConfig = [
kTSKSwizzleNetworkDelegates: false,
kTSKPinnedDomains: [
"yahoo.com": [
kTSKExpirationDate: "2017-12-01",
kTSKPublicKeyHashes: [
"JbQbUG5JMJUoI6brnx0x3vZF6jilxsapbXGVfjhN8Fg=",
"WoiWRyIOVNa9ihaBciRSC7XHjliYS9VwUGOIud4PB18="
],]]] as [String : Any]
TrustKit.initSharedInstance(withConfiguration:trustKitConfig)After TrustKit has been initialized, a
TSKPinningValidator instance
can be retrieved from the TrustKit singleton, and can be used to perform SSL pinning validation
in the App's network delegates. For example in an NSURLSessionDelegate:
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *credential))completionHandler {
{
TSKPinningValidator *pinningValidator = [[TrustKit sharedInstance] pinningValidator];
// Pass the authentication challenge to the validator; if the validation fails, the connection will be blocked
if (![pinningValidator handleChallenge:challenge completionHandler:completionHandler])
{
// TrustKit did not handle this challenge: perhaps it was not for server trust
// or the domain was not pinned. Fall back to the default behavior
completionHandler(NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling, nil);
}
}For more information, see the Getting Started guide.
TrustKit is a joint-effort between the mobile teams at Data Theorem and Yahoo. See AUTHORS for details.
TrustKit is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.