Water distribution network modelling, either in the browser or Node. Uses the Open Water Analytics EPANET v2.2 toolkit compiled to Javascript.
Note: All version before 1.0.0 should be considered beta with potential breaking changes between releases, use in production with caution.
Install • Usage • About • Examples • Featured Apps • Build • API • License
To install the stable version with npm:
$ npm install epanet-js
or with yarn:
$ yarn add epanet-js
For those without a module bundler, the epanet-js package will soon be available on unpkg as a precompiled UMD build. This will allow you to drop a UMD build in a <script> tag on your page and access it on the window.epanetJs global variable.
Run this example on CodeSandbox
import { Project, Workspace } from "epanet-js";
import fs from "fs";
// Read an existing inp file from the disk
const net1 = fs.readFileSync("net1.inp");
// Initialise a new Workspace and Project object
const ws = new Workspace();
const model = new Project(ws);
// Write a copy of the inp file to the workspace
ws.writeFile("net1.inp", net1);
// Runs toolkit methods: EN_open, EN_solveH & EN_close
model.open("net1.inp", "report.rpt", "out.bin");
model.solveH();
model.close();More Examples
- Step through the hydraulic simulation
- New model builder API
- Fire Flow Analysis using React
- Float valves using React Code (WIP) - Demo
Engineers use hydraulic modelling software to simulate water networks. A model will represent a network consisting of pipes, pumps, valves and storage tanks. The modelling software tracks the flow of water in each pipe, the pressure at each node, the height of water in each tank throughout the network during a multi-period simulation.
EPANET is an industry-standard program, initially developed by the USEPA, to simulate water distribution networks, its source code was released in the public domain. An open-source fork by the Open Water Analytics (OWA) community has been released extending its original capabilities. Read more about EPANET on Wikipedia and the OWA community on their website.
The EPANET Toolkit is an API written in C that allows developers to embed the EPANET's engine in their own applications. Ports of the toolkit exist in Python and Matlab; however, there are limited options to use the EPANET engine in JavaScript.
Epanet-js is a full port of version 2.2 OWA-EPANET Toolkit in Typescript, providing access to all 122 functions within the toolkit.
The JavaScript library is for engineers, developers and academics to run and share hydraulic analyses or create custom front end or server-side applications.
Reaching version 1.0.0 is the current focus, the first non-beta version will have API stability and have mirrored functions of each method in the EPANET Toolkit.
Also planned are helper classes and an object-oriented wrapper to allow simpler development of applications using the EPANET engine.
See the remaining task on the Version 1.0.0 Project.
The following apps were created using the epanet-js engine, please let us know any apps you've made.
Display models created in EPANET directly in the browser. No data leaves your computer; all data rendered and processed locally using the epanet-js library.
Website: Model View
Source Code: GitHub
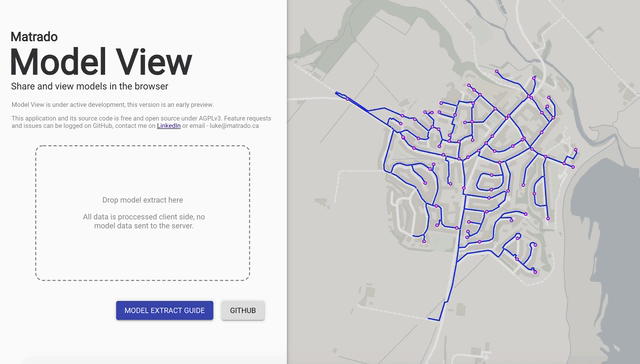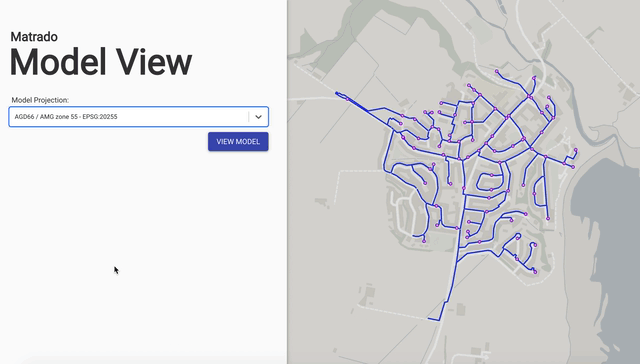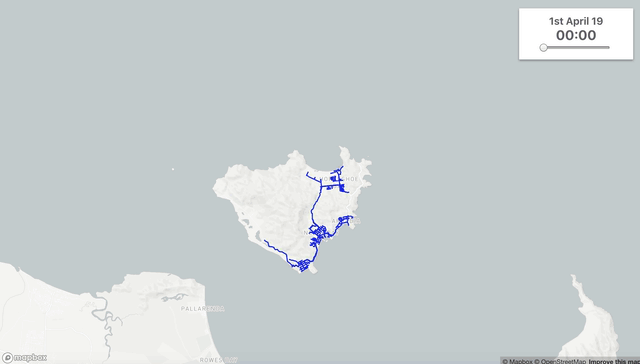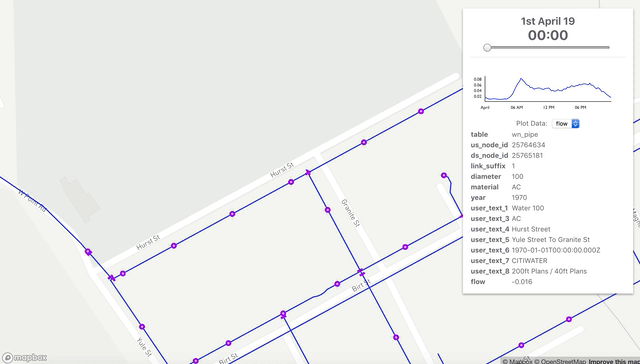
Extract subsections of your InfoWorks WS Pro models and run them in your browser. As you make calibration changes such as modifying roughness or restriction valves the application runs an epanet model and compares the simulated results to those observered in the field.
Website: Model Calibrate
epanet-js is split into two packages, the epanet-engine package which wraps the original C code in C++ and compiles it to JavaScript using Emscripten. And epanet-js is a TypeScript library which wraps over the generated module from Emscripten and manages memory allocation, error handling and returning of varaible.
Building epanet-engine
The first command yarn run build:dockerimage creates a docker container of Emscripten and the compiled OWA-EPANET source code, you can then run yarn run build to compile the C++ wrapper into Javascript.
cd packages/epanet-engine
yarn run build:dockerimage
yarn run buildBuilding epanet-js
You must first build epanet-engine before you can lint, test or build epanet-js.
cd packages/epanet-js
yarn install
yarn run lint
yarn run test
yarn run buildepanet-js contains two classes, Workspace & Project. A Workspace represents a virtual file system where you can store and read files that are consumed by the tool kit, such as INP Files or generated by it, such as RPT files or OUT files.
A Project is a single instance of the EN_Project wrapper object and a singleton with all 122 toolkit methods attached. A full list of all methods can be found on the wiki. All method names have been converted to camelCase to keep with javascript convention.
Create a Project object by instancing the Project class with a Workspace object.
import { Project, Workspace } from `epanet-js`
const ws = new Workspace()
const model = new Project(ws)If you are not familiar with the OWA-EPANET Toolkit API or EPANET it is worthwhile reading the OWA-EPANET Toolkit API documentation and OWA-EPANET wiki.
Both epanet-js and @model-create/epanet-engine are MIT licenced.
The hydraulic engine used within the epanet-js library is OWA-EPANET 2.2, which is MIT licenced, with contributions by the following authors.