ROS 2 driver of the AR4 robot arm from Annin Robotics. Tested with ROS 2 Iron on Ubuntu 22.04.
Supports:
- AR4 (Original version)
- AR4 MK2
- AR4 MK3
- AR4 servo gripper
Features:
- Moveit control (GUI and Python interface example)
- Gazebo simulation
- Hand-Eye calibration
This is a refresh of ar3_core.
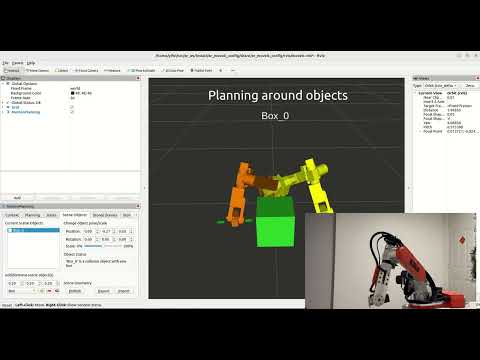
Motion Planning using RViz and Moveit:
Startup, Calibration, and Servo Gripper Demo
- ar_description
- Hardware description of arm & servo gripper urdf.
- ar_hardware_interface
- ROS interfaces for the arm and servo gripper drivers, built on the ros2_control framework.
- Manages joint offsets, limits and conversion between joint and actuator messages.
- Handles communication with the microcontrollers.
- ar_microcontrollers
- Firmware for the microcontrollers, ie. Teensy and Arduino Nano.
- ar_moveit_config
- MoveIt module for motion planning.
- Controlling the arm and servo gripper through Rviz.
- ar_gazebo
- Simulation on Gazebo.
- Install ROS 2 Iron for Ubuntu 22.04
- Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/ycheng517/ar4_ros_driver
- Import required external repos:
vcs import . --input ar_hand_eye/hand_eye_calibration.repos - Install workspace dependencies:
rosdep install --from-paths . --ignore-src -r -y - Build the workspace:
colcon build
- Source the workspace:
source install/setup.bash - Enable serial port access if you haven't already done so:
You will need to log out and back in for changes to take effect.
sudo addgroup $USER dialout
The Teensy and Arduino Nano sketches provided in ar_microcontrollers are compatible with the default hardware. To flash it, follow the same procedure as specified in AR4 Robot Setup.
A docker container and run script has been provided that can be used to run the robot and any GUI programs. It requires an NVIDIA GPU, and the NVIDIA Container Toolkit to be installed. Then you can start the docker container with:
docker build -t ar4_ros_driver .
./run_in_docker.shThere are two modules that you will always need to run:
-
Arm module - this can be for either a real-world or simulated arm
- For controlling the real-world arm, you will need to run the
ar_hardware_interfacemodule - For the simulated arm, you will need to run the
ar_gazebomodule - Either of the modules will load the necessary hardware descriptions for MoveIt
- For controlling the real-world arm, you will need to run the
-
MoveIt module - the
ar_moveit_configmodule provides the MoveIt interface and RViz GUI.
The various use cases of the modules and instructions to run them are described below:
If you are unfamiliar with MoveIt, it is recommended to start with this to explore planning with MoveIt in RViz. This contains neither a real-world nor a simulated arm but just a model loaded within RViz for visualisation.
The robot description, moveit interface and RViz will all be loaded in the single demo launch file
ros2 launch ar_moveit_config demo.launch.pyStart the ar_hardware_interface module, which will load configs and the robot description:
ros2 launch ar_hardware_interface ar_hardware.launch.py \
calibrate:=TrueAvailable Launch Arguments:
ar_model: The model of the AR4. Options arear4(which includes MK2) orar4_mk3. Defaults toar4.calibrate: Whether to calibrate the robot arm (determine the absolute position of each joint).include_gripper: Whether to include the servo gripper. Defaults to:include_gripper:=True.serial_port: Serial port of the Teensy board. Defaults to:serial_port:=/dev/ttyACM0.arduino_serial_port: Serial port of the Arduino Nano board. Defaults toarduino_serial_port:=/dev/ttyUSB0.
calibrate:=False.
Start MoveIt and RViz:
ros2 launch ar_moveit_config ar_moveit.launch.pyAvailable Launch Arguments:
ar_model: The model of the AR4. Options arear4(which includes MK2) orar4_mk3. Defaults toar4.include_gripper: Whether to include the servo gripper. Defaults to:include_gripper:=True.use_sim_time: Make Moveit use simulation time. Should only be enabled when running with Gazebo. Defaults to:use_sim_time:=False.
You can now plan in RViz and control the real-world arm. Joint commands and joint states will be updated through the hardware interface.
Start the ar_gazebo module, which will start the Gazebo simulator and load the robot description:
ros2 launch ar_gazebo ar_gazebo.launch.pyStart Moveit and RViz:
ros2 launch ar_moveit_config ar_moveit.launch.py use_sim_time:=true include_gripper:=TrueYou can now plan in RViz and control the simulated arm.