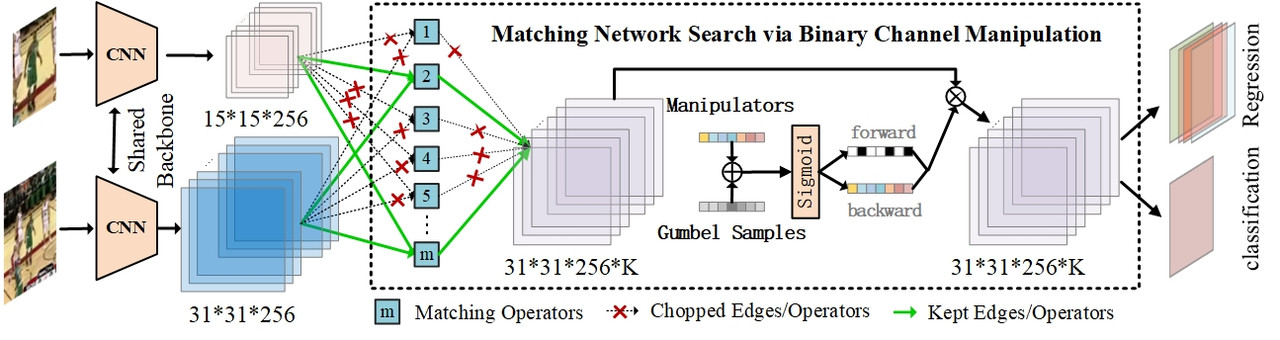
💥 The paper AutoMacth has been accepted by ICCV2021. Code and models will be released later (The main author is looking for job recently, so it may take a while.)
💥 The improved version of CSTrack_panda has been released, containing the end-to-end tranining codes on PANDA. It is a strong baseline for Gigavison MOT tracking. Our tracker takes the 5th place in Tianchi Global AI Competition (天池—全球人工智能技术创新大赛[赛道二]), with the score of A-0.6712/B-0.6251 (AB榜), which surprisingly outperforms the baseline tracker JDE with score of A-0.32/B-0.34. More details about CSTrack_panda can be found here.
[Paper] [Raw Results] [Training and Testing Tutorial] [Demo]
AutoMatch replaces the essence of Siamese tracking, i.e. the cross-correlation and its variants, to a learnable matching network. The underlying motivation is that heuristic matching network design relies heavily on expert experience. Moreover, we experimentally find that one sole matching operator is difficult to guarantee stable tracking in all challenging environments. In this work, we introduce six novel matching operators from the perspective of feature fusion instead of explicit similarity learning, namely Concatenation, Pointwise-Addition, Pairwise-Relation, FiLM, Simple-Transformer and Transductive-Guidance, to explore more feasibility on matching operator selection. The analyses reveal these operators' selective adaptability on different environment degradation types, which inspires us to combine them to explore complementary features. We propose binary channel manipulation (BCM) to search for the optimal combination of these operators.
[Paper] [Raw Results] [Training and Testing Tutorial] [Demo]
Ocean proposes a general anchor-free based tracking framework. It includes a pixel-based anchor-free regression network to solve the weak rectification problem of RPN, and an object-aware classification network to learn robust target-related representation. Moreover, we introduce an effective multi-scale feature combination module to replace heavy result fusion mechanism in recent Siamese trackers. This work also serves as the baseline model of OceanPlus. An additional TensorRT toy demo is provided in this repo.
[Paper] [Raw Results] [Training and Testing Tutorial] [Demo]
SiamDW is one of the pioneering work using deep backbone networks for Siamese tracking framework. Based on sufficient analysis on network depth, output size, receptive field and padding mode, we propose guidelines to build backbone networks for Siamese tracker. Several deeper and wider networks are built following the guidelines with the proposed CIR module.
[Paper] [Raw Results] [Training and Testing Tutorial] [Demo]
Official implementation of the OceanPlus tracker. It proposes an attention retrieval network (ARN) to perform soft spatial constraints on backbone features. Concretely, we first build a look-up-table (LUT) with the ground-truth mask in the starting frame, and then retrieve the LUT to obtain a target-aware attention map for suppressing the negative influence of background clutter. Furthermore, we introduce a multi-resolution multi-stage segmentation network (MMS) to ulteriorly weaken responses of background clutter by reusing the predicted mask to filter backbone features.
[Paper] [Training and Testing Tutorial] [Demo]
CSTrack proposes a strong ReID based one-shot MOT framework. It includes a novel cross-correlation network that can effectively impel the separate branches to learn task-dependent representations, and a scale-aware attention network that learns discriminative embeddings to improve the ReID capability. This work also provides an analysis of the weak data association ability in one-shot MOT methods. Our improvements make the data association ability of our one-shot model is comparable to two-stage methods while running more faster.
This version can achieve the performance described in the paper (70.7 MOTA on MOT16, 70.6 MOTA on MOT17). The new version will be released soon. If you are interested in our work or have any questions, please contact me at [email protected].
Other trackers, coming soon ...
☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️
experiments:training and testing settingsdemo:figures for readmedataset:testing datasetdata:training datasetlib:core scripts for all trackerssnapshot:pre-trained modelspretrain:models trained on ImageNet (for training)tutorials:guidelines for training and testingtracking:training and testing interface
$TrackSeg
|—— experimnets
|—— lib
|—— snapshot
|—— xxx.model/xxx.pth
|—— dataset
|—— VOT2019.json
|—— VOT2019
|—— ants1...
|—— VOT2020
|—— ants1...
|—— ...
[1] Bhat G, Danelljan M, et al. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking. ICCV2019.
[2] Chen, Kai and Wang, et.al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark.
...