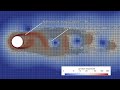
This project shows how to use the gradient of flow variables as a criteria to control Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) for OpenFOAM simulations.
- Run the
prepare.shto generate the mesh and setup the simulation. - Then run the case with
pimpleFoam
The following coded function object in controlDict creates a field which, in each timestep, contains the magnitude of the velocity gradient (which is a tensor):
calcGradient
{
libs ("libutilityFunctionObjects.so");
type coded;
name computeVelocityGradientMag;
executeControl timeStep;
executeInterval 1;
writeControl writeTime;
writeInterval 1;
codeExecute
#{
const volVectorField& U = mesh().lookupObject<volVectorField>("U");
static autoPtr<volScalarField> velocityGradientMagPtr;
if(!velocityGradientMagPtr.valid()) {
Info << "Creating velocityGradientMag" << nl;
velocityGradientMagPtr.set
(
new volScalarField
(
IOobject
(
"velocityGradientMag",
time_.timeName(),
U.mesh(),
IOobject::NO_READ,
IOobject::AUTO_WRITE
),
mag(fvc::grad(U))
)
);
}
volScalarField &velocityGradientMag = velocityGradientMagPtr();
velocityGradientMag.checkIn();
velocityGradientMag = mag(fvc::grad(U));
Info << " max velocityGradientMag " << max(velocityGradientMag) << nl;
#};
}
That field is defined as refinement criteria on dynamicMeshDict:
dynamicFvMesh dynamicRefineFvMesh;
dynamicRefineFvMeshCoeffs
{
// How often to refine
refineInterval 2;
// Field to be refinement on
field velocityGradientMag;
// Refine field inbetween lower..upper
lowerRefineLevel 30;
upperRefineLevel 1e6;
// If value < unrefineLevel unrefine
unrefineLevel 10;
// Refine cells only up to maxRefinement levels
maxRefinement 2;
...
}
The mesh is dynamically refined when the magnitude of the velocity gradient exceeds 30 1/s, and is unrefined when it goes below 10 1/s.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details
Nicolás Diego Badano (https://www.linkedin.com/in/nicolas-diego-badano/)