JMXProxy exposes all available MBean attributes on a given JVM via simple HTTP request. The results are in easily-parsable JSON format. The server component is built using Dropwizard.
- Downloading
- Compiling
- Configuration
- Execution
- Usage
- Limitation
- Load Balancing
- Example Clients
- Web Interface
- Libraries
- License
- Latest version compiled artifact: jmxproxy-3.4.0.jar
- Latest version source code archive: jmxproxy.3.4.0.tar.gz
The build is a simple maven invocation. To compile, test, and package JMXProxy execute the following.
$ mvn clean package
The resulting package is a self-executable "fat jar" file located at target/jmxproxy-3.4.0.jar.
Configuration is handled entirely by Dropwizard. Create a yaml file and point to it at startup by adding it to the command-line as the last parameter.
$ java -jar target/jmxproxy-3.4.0.jar server config.yaml
For example, to configure the listening port for both application and admin servlets:
server:
type: simple
applicationContextPath: /
connector:
type: http
port: 8000Note, it is important to specify the applicationContextPath, otherwise all requests will have to be prefixed with /application in the URI. Once this entry is in the configuration file, any part of it may be overriden on the command-line, i.e.:
$ java -Ddw.server.connector.port=9000 target/jmxproxy-3.4.0.jar server config.yaml
For more built-in configuration options, please see the Dropwizard Configuration Reference
JMXProxy itself has the following configuration parameters, which are added to the same file:
jmxproxy:
# how often for the cleaner thread to
# wake up to purge unaccessed hosts
# Time units: ns, us, ms, s, m, h, d
clean_interval: 1m
# how long to keep unaccessed hosts before purging
# by the cleaner thread
access_duration: 5m
# how long to cache JMX attribute values before
# reconnecting to the agent and pulling new data
cache_duration: 5m
# how long to wait on a new JMX connection before
# giving up with a not found error to the client
connect_timeout: 3s
# white list of allowed endpoints in host or host:port
# format for this agent to connect to, defaulting
# to allowing all when empty or missing
allowed_endpoints:
- 'localhost'
- 'host1:1234'
- 'host1:4321'
- 'host2:5678'
# maximum number of historical attribute values to
# retain and provide when the history query parameter
# is specified to the attribute request call
history_size: 1The self-executing fat jar file contains all the bits necessary to start and run the server.
$ java -jar target/jmxproxy-3.4.0.jar server
A more complex example that enables the JMX agent and limits heap may look something like this:
$ java -Xmx100m -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=1123 -jar target/jmxproxy-3.4.0.jar server
An example startup script exists that will launch the server listening on port 8080 and enable authenticated JMX agent in the jvm on port 1123:
$ scripts/server/start.sh
INFO [2014-11-25 17:41:41,312] io.dropwizard.assets.AssetsBundle: Registering AssetBundle with name: assets for path /*
INFO [2014-11-25 17:41:41,544] io.dropwizard.server.ServerFactory: Starting jmxproxy
__ __ __ __ __ ______ ______ ______ __ __ __ __
/\ \ /\ "-./ \ /\_\_\_\ /\ == \ /\ == \ /\ __ \ /\_\_\_\ /\ \_\ \
_\_\ \ \ \ \-./\ \ \/_/\_\/_ \ \ _-/ \ \ __< \ \ \/\ \ \/_/\_\/_ \ \____ \
/\_____\ \ \_\ \ \_\ /\_\/\_\ \ \_\ \ \_\ \_\ \ \_____\ /\_\/\_\ \/\_____\
\/_____/ \/_/ \/_/ \/_/\/_/ \/_/ \/_/ /_/ \/_____/ \/_/\/_/ \/_____/
...
JMXProxy provides fine-grained access to MBeans exposed by a target JVM. Clients can request anything from a whole dictionary of all the attributes down to specific attribute values. Clients can also supply JMX authentication credentials for JMXProxy to pass to the target JVM. Here are examples of how to access JMXProxy, using the JVM running the server as the target.
-
Get the list of mbeans available on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123' ["java.lang:type=OperatingSystem", ... -
Get the dictionary of all mbeans, attributes, and values available on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123?full=true' {"java.lang:type=OperatingSystem": {"name": "Mac OS X", ... -
Get the dictionary of all mbeans, and full history of associated attribute values in reverse chronological order on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123?full=true&limit=0' {"java.lang:type=OperatingSystem": {"name": ["Mac OS X", ... -
Get the dictionary of all mbeans, and partial history of associated attribute values in reverse chronological order on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123?full=true&limit=3' {"java.lang:type=OperatingSystem": {"name": ["Mac OS X", ... -
Get the list of attributes available for a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=OperatingSystem' ["Name","Arch", ... -
Get the dictionary of all attributes and values available for a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=OperatingSystem?full=true' {"name": "Mac OS X", "arch": "x86_64" ... -
Get the dictionary of all attributes and full history of associated attribute values in reverse chronological order for a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=OperatingSystem?full=true&limit=0' {"name": ["Mac OS X", ... -
Get the dictionary of all attributes and partial history of associated attribute values in reverse chronological order for a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=OperatingSystem?full=true&limit=3' {"name": ["Mac OS X", ... -
Get an attribute value available for an attribute of a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=OperatingSystem/Name' "Mac OS X" -
Get a full history of attribute values in reverse chronological order of an attribute of a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=ClassLoading/LoadedClassCount?limit=0' [5176,5155,5136,5119,5016] -
Get a partial history of attribute values in reverse chronological order of an attribute of a specific mbean on a target JVM
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123/java.lang:type=ClassLoading/LoadedClassCount?limit=3' [5176,5155,5136]
For JMX agents that require authentication, JMXProxy allows clients to submit credentials via HTTP POST as either application/json or application/x-www-form-urlencoded content-type:
-
Get the list of mbeans available on a target JVM with form-urlencoded credentials
$ curl -s -d'username=ro&password=public' 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123' ["java.lang:type=OperatingSystem", ... -
Get the list of mbeans available on a target JVM with JSON credentials
$ curl -s -d'{"username":"ro","password":"public"}' -H'Content-Type: application/json' 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123' ["java.lang:type=OperatingSystem", ...
JMXProxy service has the following miscelleneous APIs for convinience and UI building:
-
Get the list of currently cached endpoints:
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy' ["localhost:1123"] -
Delete the requested endpoint to purge its history:
$ curl -s -XDELETE 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/localhost:1123' true -
Get the current service configuration:
$ curl -s 'http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy/config' {"clean_interval":60000,"cache_duration":20000,"access_duration":1800000,"history_size":20,"allowed_endpoints":[]}
- SSL agent connections are currently not supported. Remote JVM must be started with
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false.
Because JMXProxy caches results for a configurable amount of time to quickly service consecutive requests, load balancers should be configured to balance traffic based on the first component of the request path. Below is an example haproxy configuration snippet. It shows how to balance traffic between five JMXProxy servers as well as check each instance's health.
listen SRV_JMXPROXY:8080 :8080
balance uri depth 2
cookie SRVID insert indirect
option httplog
option httpchk GET /healthcheck
server srv001:8080 srv001:8080 cookie srv001:8080 check port 8081 observe layer7
server srv002:8080 srv002:8080 cookie srv002:8080 check port 8081 observe layer7
server srv003:8080 srv003:8080 cookie srv003:8080 check port 8081 observe layer7
server srv004:8080 srv004:8080 cookie srv004:8080 check port 8081 observe layer7
server srv005:8080 srv005:8080 cookie srv005:8080 check port 8081 observe layer7
Nagios Health Plugin
scripts/nagios/check_jmxproxy.py [-h] -a HOST -p PORT [-c AUTH] -e EXPR [-j PROXY]
[-i] [-f FORMAT] {textual,metrics} ...
The script supports two modes of operation: textual string match of an attribute value and metrics calculation based on a RPN expression. In metrics mode, if any specified expression component yields an attribute that has a list value, the result will be the count of items in the list for that position. The script defaults to using http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy as the JMXProxy address. Some practical usage examples are provided below.
Check JVM memory thresholds:
scripts/nagios/check_jmxproxy.py -a localhost -p 1123 -c ro:public -e 'java.lang:type=Memory//HeapMemoryUsage//max java.lang:type=Memory//HeapMemoryUsage//used / 100 *' -f 'JVM heap memory {result:.02f}% used' metrics -c 95 -w 90
JVM heap memory 19.40% used
Check a Hadoop namenode active state:
scripts/nagios/check_jmxproxy.py -a namenode001 -p 8001 -e 'Hadoop:service=NameNode,name=FSNamesystem//tag.HAState' -f 'HA State: {result}' textual active
HA State: active
Check a Hadoop datanode failed volume count:
scripts/nagios/check_jmxproxy.py -a datanode001 -p 8003 -e 'Hadoop:service=DataNode,name=FSDatasetState.*//NumFailedVolumes' -f '{result:.0f} volume failures' metrics -c 0 -w 0
0 volume failures
Cacti ScriptServer Plugin
scripts/cacti/ss_jmxproxy.php <host:port> [username:password] [jmxproxy-host:port]
The script defaults to using http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy as the JMXProxy address. For example, to request basic stats from the JVM running JMXProxy itself:
$ php -q scripts/cacti/ss_jmxproxy.php localhost:1123
thread_count:35 thread_peak:35 memory_heap_used:6763352 memory_heap_max:101384192 gc_count:19 classes_loaded:3679 classes_total:3679 classes_unloaded:0
It is also possible to supply JMX credentials and a remote JMXProxy to use:
$ php -q scripts/cacti/ss_jmxproxy.php localhost:1123 ro:public http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy
thread_count:35 thread_peak:35 memory_heap_used:6763352 memory_heap_max:101384192 gc_count:19 classes_loaded:3679 classes_total:3679 classes_unloaded:0
This plugin allows easy extensions by creating another PHP file that includes ss_jmxproxy.php, sets up an array of desired beans to fetch, and passes it to the ss_jmxproxy() function. One such extension, ss_hadoop.php, exists to demonstrate this behavior and usage:
$ php -q scripts/cacti/ss_hadoop.php datanode001:8003 datanode
thread_count:165 thread_peak:593 memory_heap_used:158213848 memory_heap_max:1908932608 gc_count:27465 classes_loaded:2717 classes_total:2775 classes_unloaded:58 ds_capacity:2869079572480 ds_remaining:1665482752 ds_used:2750974428881 ds_failed:0 blocks_read:1230 blocks_removed:167 blocks_replicated:0 blocks_verified:28 blocks_written:133 bytes_read:222298772 bytes_written:8175757632 reads_from_local_client:1165 writes_from_local_client:36 reads_from_remote_client:65 writes_from_remote_client:97 ops_block_copy:0 ops_block_read:1230 ops_block_write:133 ops_block_replace:0 ops_block_checksum:0 ops_block_reports:0 ops_heartbeat:100
Likewise, JMX credentials and remote JMXProxy address are also supported:
$ php -q scripts/cacti/ss_hadoop.php datanode001:8003 datanode ro:public http://localhost:8080/jmxproxy
thread_count:165 thread_peak:593 memory_heap_used:158213848 memory_heap_max:1908932608 gc_count:27465 classes_loaded:2717 classes_total:2775 classes_unloaded:58 ds_capacity:2869079572480 ds_remaining:1665482752 ds_used:2750974428881 ds_failed:0 blocks_read:1230 blocks_removed:167 blocks_replicated:0 blocks_verified:28 blocks_written:133 bytes_read:222298772 bytes_written:8175757632 reads_from_local_client:1165 writes_from_local_client:36 reads_from_remote_client:65 writes_from_remote_client:97 ops_block_copy:0 ops_block_read:1230 ops_block_write:133 ops_block_replace:0 ops_block_checksum:0 ops_block_reports:0 ops_heartbeat:100
Graphite Poller Script
scripts/graphite/jmxproxy.py [-h] [--service-host SERVICE_HOST] --service-port
SERVICE_PORT [--service-auth SERVICE_AUTH]
[--graphite-key GRAPHITE_KEY]
[--graphite-host GRAPHITE_HOST]
[--graphite-port GRAPHITE_PORT]
[--jmxproxy-host JMXPROXY_HOST]
[--jmxproxy-port JMXPROXY_PORT] [-n]
For example, to request basic stats from the JVM running jmxproxy itself:
$ scripts/graphite/jmxproxy.py --service-port 1123 --service-host localhost --jmxproxy-host localhost --jmxproxy-port 8080 --jmxproxy-path jmxproxy -n # dry-run output
localhost.jvm.classes_loaded 3804 1363021890
localhost.jvm.classes_total 3917 1363021890
localhost.jvm.classes_unloaded 113 1363021890
localhost.jvm.gc_count 43 1363021890
localhost.jvm.memory_heap_max 101384192 1363021890
localhost.jvm.memory_heap_used 5893816 1363021890
localhost.jvm.thread_count 36 1363021890
localhost.jvm.thread_peak 36 1363021890
This script allows easy extensions by creating another script that imports jmxproxy, sets up a dictionary of desired beans, and passes it to the jmxproxy.main() function. One such extension, hadoopy.py, exists to demonstrate this behavior and usage:
$ scripts/graphite/hadoop.py --service-port 8003 --service-host datanode001 --jmxproxy-host localhost --jmxproxy-port 8080 --jmxproxy-path jmxproxy --service-name datanode -n # dry-run output
datanode001.datanode.blocks_read 1839 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.blocks_removed 1584 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.blocks_replicated 0 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.blocks_verified 25 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.blocks_written 192 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.bytes_read 6320489641 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.bytes_written 9864394003 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ds_capacity 2869079572480 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ds_failed 0 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ds_remaining 145051308032 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ds_used 2607723919940 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.classes_loaded 2717 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.classes_total 2805 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.classes_unloaded 88 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.gc_count 32970 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.memory_heap_max 1908932608 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.memory_heap_used 146242304 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.thread_count 214 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.jvm.thread_peak 593 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_block_checksum 0 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_block_copy 187 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_block_read 1652 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_block_replace 0 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_block_reports 0 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_block_write 192 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.ops_heartbeat 100 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.reads_from_local_client 1370 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.reads_from_remote_client 282 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.writes_from_local_client 50 1363022233
datanode001.datanode.writes_from_remote_client 142 1363022233
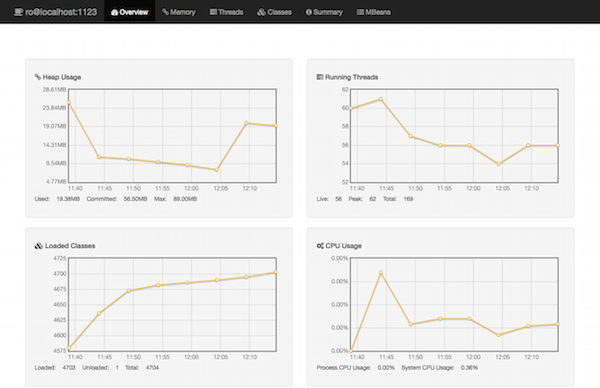
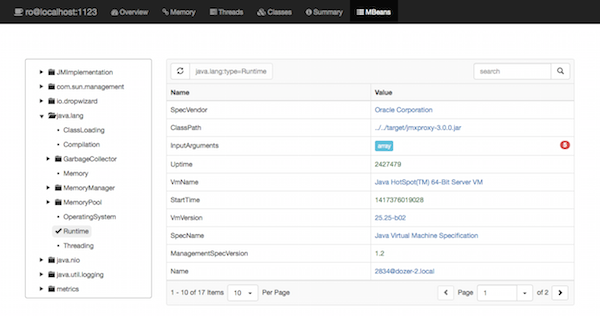
JMXProxy comes with an interactive web interface available by pointing a browser at the root URL.
| Name | Version | License |
|---|---|---|
| dropwizard | 1.2.4 | Apache 2.0 |
| jquery | 3.3.1 | MIT |
| underscore | 1.8.3 | MIT |
| flot | 0.8.3 | MIT |
| bootstrap | 3.3.7 | MIT |
| fuelux | 3.16.5 | BSD3 |
| fontawesome | 5.0.6 | MIT, SIL OFL 1.1, CC BY 4.0 |



