Linux auto tiling manager with hot corner support for Openbox, Fluxbox, IceWM, Xfwm, KWin, Marco, Muffin, Mutter and other EWMH compliant window managers using the X11 window system. Therefore, this project provides dynamic tiling for XFCE, LXDE, LXQt, KDE and GNOME (Mate, Deepin, Cinnamon, Budgie) based desktop environments.
Simply keep your current window manager and install cortile on top of it.
Once enabled, the tiling manager will handle resizing and positioning of existing and new windows.
- Workspace based tiling.
- Auto detection of panels.
- Toggle window decorations.
- User interface for tiling mode.
- Systray icon indicator and menu.
- Custom addons via python bindings.
- Keyboard, hot corner and systray bindings.
- Vertical, horizontal, maximized and fullscreen mode.
- Remember layout proportions.
- Floating and sticky windows.
- Drag & drop window swap.
- Workplace aware layouts.
- Multi monitor support.
Support for keyboard and mouse events sets cortile apart from other tiling solutions. The go implementation ensures a fast and responsive system, where multiple layouts, keyboard shortcuts, drag & drop and hot corner events simplify and speed up your daily work.
Manually download the latest binary file from releases or use wget:
wget -qO- $(wget -qO- https://api.github.com/repos/leukipp/cortile/releases/latest | \
jq -r '.assets[] | select(.name | contains ("linux_amd64.tar.gz")) | .browser_download_url') | \
tar -xvzExecute the binary file and cortile will automatically begin tiling windows until you choose to stop it:
./cortileAnother installation method can be found in the development section. The latest official release is published on GitHub. Versions distributed via package managers are community supported and may be outdated.
To enable auto tiling on startup, you can run cortile as a service after the graphical user interface has been loaded.
A template to run cortile as a systemd service is provided in the services folder.
You may have to adjust the filepath/symlink under ExecStart and enable the user service:
# copy systemd service file
cp cortile.service ~/.config/systemd/user/
# reload systemd configuration
systemctl --user daemon-reload
# enable systemd service
systemctl --user enable cortile.service
# start systemd service
systemctl --user start cortile.serviceThe layouts are based on the master-slave concept, where one side of the screen is considered to be the master area and the other side is considered to be the slave area:
vertical-right:split the screen vertically, master area on the right.vertical-left:split the screen vertically, master area on the left.horizontal-top:split the screen horizontally, master area on the top.horizontal-bottom:split the screen horizontally, master area on the bottom.maximized:single window that fills the entire tiling area.fullscreen:single window that fills the entire screen.
The number of windows per side and the occupied space can be changed dynamically. Adjustments to window sizes are considered to be proportion changes of the underlying layout.
Windows placed on the master side are static and the layout will only change as long the space is not fully occupied. Once the master area is full, the slave area is used, where the layout changes dynamically based on available space and configuration settings.
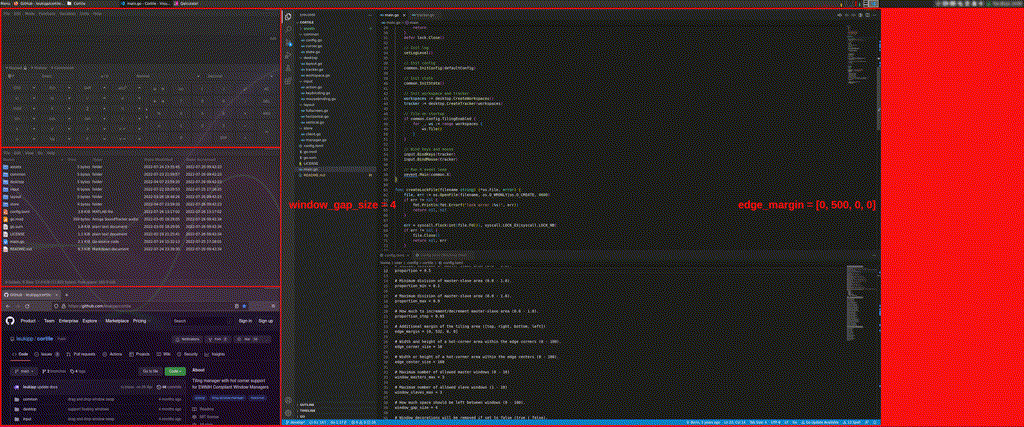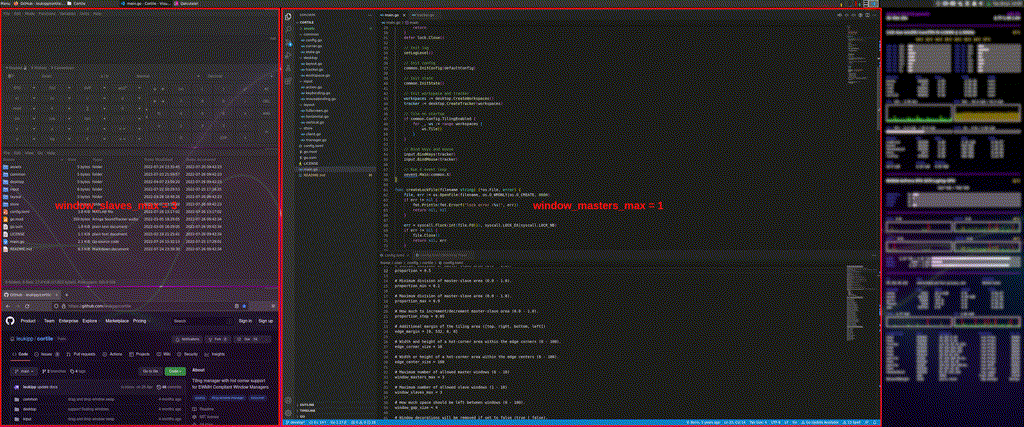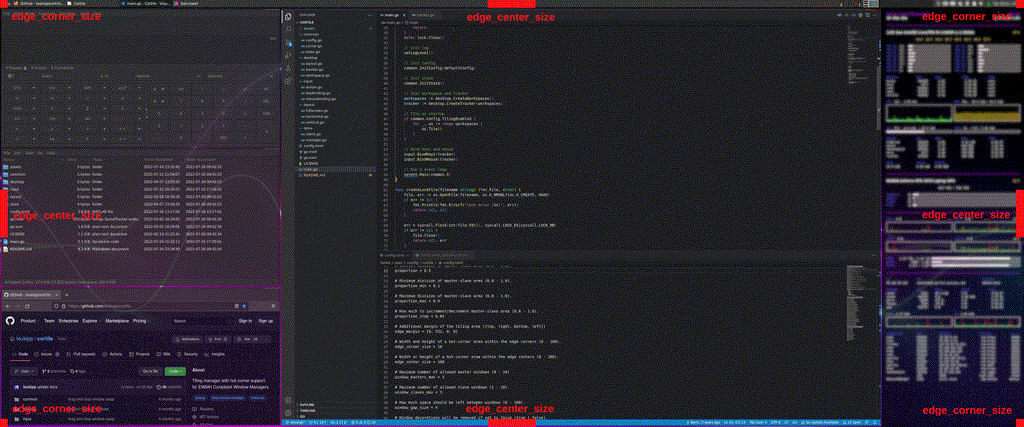
The configuration file is located at ~/.config/cortile/config.toml (or XDG_CONFIG_HOME) and is created with default values during the first startup.
Additional information about individual entries can be found in the comments section of the config.toml file.
The default keyboard shortcuts are assigned as shown below.
If some of them are already in use by your system, update the default values in the [keys] section of the configuration file:
| Keys | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Shift+Home | Enable tiling on the current screen |
| Ctrl+Shift+End | Disable tiling on the current screen |
| Ctrl+Shift+T | Toggle between enable and disable |
| Ctrl+Shift+D | Toggle window decoration on and off |
| Ctrl+Shift+R | Disable tiling and restore windows |
| Ctrl+Shift+BackSpace | Reset layouts to default proportions |
| Ctrl+Shift+Next | Cycle through next layouts |
| Ctrl+Shift+Prior | Cycle through previous layouts |
| Ctrl+Shift+Left | Activate vertical-left layout |
| Ctrl+Shift+Right | Activate vertical-right layout |
| Ctrl+Shift+Up | Activate horizontal-top layout |
| Ctrl+Shift+Down | Activate horizontal-bottom layout |
| Ctrl+Shift+Space | Activate maximized layout |
| Ctrl+Shift+Return | Activate fullscreen layout |
| Ctrl+Shift+Plus | Increase number of maximum slave windows |
| Ctrl+Shift+Minus | Decrease number of maximum slave windows |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_Add | Increase number of master windows |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_Subtract | Decrease number of master windows |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_2 | Move focus to the next window |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_8 | Move focus to the previous window |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_9 | Move the active window to the next screen |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_7 | Move the active window to the previous screen |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_5 | Make the active window master |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_6 | Make the next window master |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_4 | Make the previous window master |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_3 | Increase proportion of master-slave area |
| Ctrl+Shift+KP_1 | Decrease proportion of master-slave area |
Hot corner events are defined under the [corners] section and are triggered when the pointer enters one of the target areas:
| Corners | Description |
|---|---|
| Top-Left | Focus previous window |
| Top-Right | Make the active window master |
| Bottom-Right | Increase proportion of master-slave area |
| Bottom-Left | Decrease proportion of master-slave area |
Systray events are defined under the [systray] section and are triggered when the pointer keys are pressed while hovering the icon:
| Pointer | Description |
|---|---|
| Middle-Click | Toggle between enable and disable |
| Scroll-Up | Cycle through previous layouts |
| Scroll-Down | Cycle through next layouts |
| Scroll-Right | Increase proportion of master-slave area |
| Scroll-Left | Decrease proportion of master-slave area |
Common pointer shortcuts used in some environments:
- Move window: Alt+Left-Click.
- Resize window: Alt+Right-Click.
- Maximize window: Alt+Double-Click.
External processes may communicate with cortile by using dbus directly or via the cortile-addons python bindings.
Running cortile starts a dbus server instance that makes internal properties and method calls available.
Since using dbus communication directly with an external process, bash script, etc. is possible, the development requires some knowledge of dbus and is quite messy.
Therefore, there is a built-in dbus client incorporated in the same cortile binary that can be started via cortile dbus -... as a secondary process.
This client instance communicates with the running server instance and allows to listen for events and to execute remote procedure calls.
The documentation of available properties and method calls can be found via cortile dbus -help.
Additional python bindings are available to further simplify communication with cortile and to build a community-based library of useful snippets and examples.
For simplicity, the python bindings just spawn another cortile instance via cortile dbus -... running in the background and wrapping all available interfaces in easy-to-use python methods.
Example scripts and detailed information's on how to get started can be found in the cortile-addons repository.
You need go >= 1.22 to compile cortile.
Install - go
Use a package manager supported on your system:
# apt
sudo apt install golang
# yum
sudo yum install golang
# dnf
sudo dnf install golang
# pacman
sudo pacman -S goDownload a binary release suitable for your system:
cd /tmp/ && wget https://dl.google.com/go/go1.22.8.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo tar -xvf go1.22.8.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv -fi go /usr/localSet required environment variables:
echo "export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin" >> ~/.profile
echo "export GOPATH=~/.go" >> ~/.profile
source ~/.profileVerify the installed go version:
go env | grep "GOPATH\|GOVERSION"Install - cortile
Install directly from develop branch:
go install github.com/leukipp/cortile/v2@developClone source code from develop branch:
git clone https://github.com/leukipp/cortile.git -b develop
cd cortileIf necessary you can make local changes, then execute:
go install -ldflags="-X 'main.date=$(date --iso-8601=seconds)'"Start cortile in verbose mode:
$GOPATH/bin/cortile -vSpecial use cases:
- Use the
window_slaves_maxproperty to limit the number of windows.- e.g. with one active master and
window_slaves_max = 2, all windows following the third window are stacked behind the two slaves.
- e.g. with one active master and
- Use the
edge_marginproperty to account for additional spaces.- e.g. for deskbar panels or conky infographics.
- Use
tiling_enabled = falseif you prefer to enable tiling only when needed.- e.g. or to mainly utilize the hot corner functionalities.
- Use cortile-addons if you need any other specific logic. This repository offers a range of extensions and enhancements specifically designed for cortile.
Security concerns:
- Since the dbus api exposes internal cortile properties to the outside, malicious code running on the same host could easily access them.
However, the information cortile holds (e.g. about open windows) can also be accessed using other tools interfacing with the X11 window system.
Therefore the decision was made that direct access to cortile provides greater flexibility for running custom logic without compromising security.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
cortile disable-dbus-interface.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
- Any scripts placed in the
~/.config/cortile/addons/folder will be executed when the application starts. This provides the possibility to run custom cortile-addons scripts without worrying much about startup behavior and dependency issues. However, it also creates a potential security risk, as malicious code could place files in this folder to be executed by cortile.- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
cortile disable-addons-folder.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
- Newly pinned issues appear as menu entries in a submenu within the systray.
This feature requires a network request to the GitHub API.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
cortile disable-issue-info.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
- Cortile checks for new releases and provides the option for an in-place upgrade of the current binary.
Similar to the GitHub issue information, this feature also requires a network request.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
cortile disable-release-info.
- If you want to disable this feature run cortile with
- The binary file runs perfectly fine with user permissions.
- Do not run cortile as root!
Cortile works best with Xfwm and Openbox window systems. However, it`s still possible that you may encounter problems during usage.
Windows:
- It's recommended to disable all build-in window snapping features (e.g. snap to other windows, snap to screen borders).
- It's recommended to disable any logic that changes the window focus other than by clicking or opening a window (e.g. focus follow mouse, scroll wheel focus).
- Automatic panel detection may not work under some window managers, use the
edge_marginproperty to adjust for additional margins. - Particularly in GNOME based desktop environments, window displacements or resizing issues may occur.
- Sticky windows may cause unwanted layout modifications during workspace changes.
- Toggling window decoration may cause unwanted layout modifications.
Systray:
- Adjust the bindings in the
[systray]section, as some pointer events may not fire across different desktop environments. - Window managers not supporting StatusNotifierItem for displaying systray icons will need to install snixembed.
Debugging:
- If you encounter problems start the process with
cortile -vv, which provides additional debug outputs. - A log file is created by default under
/tmp/cortile.log.
Based on zentile (Berin Larson) and pytyle3 (Andrew Gallant).
The main libraries used in this project are xgbutil, toml, dbus, systray, gopsutil, fsnotify, selfupdate and logrus.