-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Filter Syntax
This section documents how to write and use Koncorde filters.
Table of Contents
Matches attributes using strict equality.
The tested attribute must be a scalar (number, string or boolean), and of the same type than the provided filter value.
equals: {
<field name>: <value>
}
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace'
}The following filter validates the first document:
{
equals: { firstName: 'Grace' }
}Test for the existence of a key in an object, or of a scalar in an array.
exists: 'nested.field.path'
(see nested field syntax)
exists: 'nested.array[value]'
(see array value syntax)
The following syntax is deprecated since Koncorde 1.2, and supported for backward compatibility only:
exists: { field: 'nested.field.path' }
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
city: 'NYC',
hobby: ['compiler', 'COBOL'],
alive: false
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
city: 'London',
hobby: ['programming', 'algorithm']
}The following filter validates the first document:
{
exists: 'alive'
}And this filter validates the second document:
{
exists: 'hobby["algorithm"]'
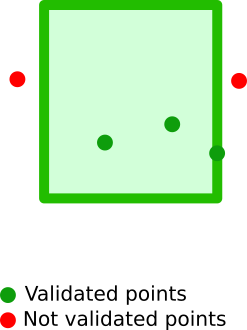
}Filter documents containing a geographical point confined within a provided bounding box:
A bounding box is a 2D box that can be defined using either of the following formats:
- 2 geopoints, defining the top left (
topLeftortop_left) and bottom right (bottomRightorbottom_right) corners of the box - 4 distinct values defining the 4 box corners:
topandbottomare latitudes,leftandrightare longitudes
The bounding box description must be stored in an attribute, named after the geographical point to be tested in future documents.
geoBoundingBox: {
<geopoint field name>: {
<bounding box description>
}
}
All of the following syntaxes below are accepted, and they describe the same bounding box, with the following properties:
- top-left corner of latitude
43.5810609and longitude3.8433703 - bottom-right corner of latitude
43.6331979and longitude3.9282093
{
top: 43.5810609,
left: 3.8433703,
bottom: 43.6331979,
right: 3.9282093
}{
topLeft: { lat: 43.5810609, lon: 3.8433703 },
bottomRight: { lat: 43.6331979, lon: 3.9282093 }
}{
top_left: "43.5810609, 3.8433703",
bottom_right: "43.6331979, 3.9282093"
}Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
location: {
lat: 32.692742,
lon: -97.114127
}
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
location: {
lat: 51.519291,
lon: -0.149817
}
}The following filter will match the second document only:
{
geoBoundingBox: {
location: {
top: -2.939744,
left: 52.394484,
bottom: 1.180129,
right: 51.143628
}
}
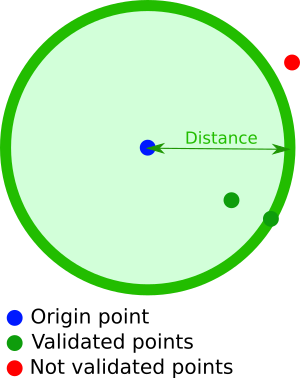
}Filter documents containing a geographical point, whose position is within a distance radius centered around a provided point of origin:
A geoDistance filter contains the following properties:
- a geopoint (accepted formats) defining the point of origin. This geopoint attribute must be named after the geographical point to test in future documents
- a
distanceparameter (accepted formats)
geoDistance: {
<geopoint field name>: {
<geopoint description>
},
distance: <geodistance>
}
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
location: {
lat: 32.692742,
lon: -97.114127
}
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
location: {
lat: 51.519291,
lon: -0.149817
}
}The following filter will match the second document only:
{
geoDistance: {
location: {
lat: 51.5029017,
lon: -0.1606903
},
distance: '10km'
}
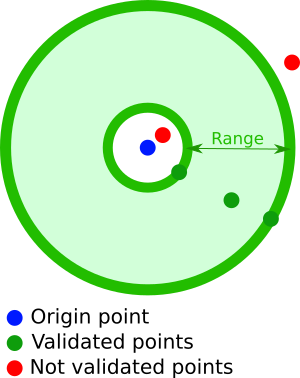
}Filter documents containing a geographical point, whose position is within a distance range from a given point of origin:
A geoDistanceRange filter contains the following properties:
- a geopoint(accepted formats) defining the center point of the distance range. This geopoint attribute must be named after the geographical point to test in future documents
- a
fromattribute, describing the minimum distance from the center point, using a geodistance (accepted formats) - a
toattribute, describing the maximum distance from the center point, using a geodistance (accepted formats)
geoDistanceRange: {
<geopoint field name>: {
<geopoint description>
},
from: <geodistance>,
to: <geodistance>
}
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
location: {
lat: 32.692742,
lon: -97.114127
}
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
location: {
lat: 51.519291,
lon: -0.149817
}
}The following filter will match the second document only:
{
geoDistanceRange: {
location: [51.5029017, -0.1606903],
from: '1km',
to: '10 kilometers'
}
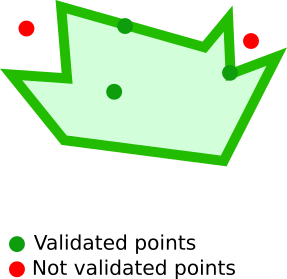
}Filter documents containing a geographical point, confined within a polygon of an arbitrary number of sides:
A geoPolygon filter is described using an array of geopoints (accepted formats). At least 3 points are needed.
Koncorde automatically closes geopolygons.
Different geopoint formats can be used to describe different corners of a polygon.
geoPolygon: {
<geopoint field name>: {
points: <geopoints array>
}
}
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
location: {
lat: 32.692742,
lon: -97.114127
}
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
location: {
lat: 51.519291,
lon: -0.149817
}
}The following filter will match the second document only:
{
geoPolygon: {
location: {
points: [
{ lat: 51.523029, lon: -0.160793 },
[51.522842, -0.145043],
'51.518303, -0.146116',
{ latLon: {lat: 51.516487, lon: -0.162295 }},
'gcpvh6uxh60x1'
]
}
}
}Like equals, but accepts an array of possible scalar values to be tested.
in: { <field name>: <array of values> }
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace'
},
{
firstName: 'Marie',
lastName: 'Curie'
}The following filter validates the first two documents:
{
in: { firstName: ['Grace', 'Ada'] }
}A filter matching documents either with a missing field in an object, or with a missing value in an array.
missing: 'nested.field.path'
(see nested field syntax)
missing: 'nested.array[value]'
(see array value syntax
The following syntax is deprecated since Koncorde 1.2, and supported for backward compatibility only:
missing: { field: 'nested.field.path' }
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
city: 'NYC',
hobbies: ['compiler', 'COBOL'],
alive: false
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
city: 'London',
hobbies: ['algorithm', 'programming'],
}The following filter validates the second document:
{
missing: 'alive'
}And this filter validates the first document:
{
missing: 'hobbies["algorithm"]'
}Filters documents with number attributes within a provided interval.
A range can be defined with at least one of the following arguments:
-
gte: Greater-than or equal to<number> -
gt: Greater-than<number> -
lte: Less-than or equal to -
lt: Less-than
Ranges can be either bounded or half-bounded.
range: {
<field to be tested>: {
[gte]: <number>,
[gt]: <number>,
[lte]: <number>,
[lt]: <number>
}
}
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
age: 85,
city: 'NYC',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
age: 36
city: 'London',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Marie',
lastName: 'Curie',
age: 55,
city: 'Paris',
hobby: 'radium'
}The following filter validates the last two documents:
{
range: {
age: {
lt: 85
}
}
}The regexp filter matches attributes using either RE2 (by default), or PCREs.
See Koncorde's constructor options to know how to choose the regexp engine.
A regexp filter has the following structure, splitting the usual /pattern/flags into two parts:
regexp: {
<field name>: {
value: '<search pattern>',
flags: '<modifier flags>'
}
}If you don't need any modifier flag, then you may also use the following simplified form:
regexp: {
<field name>: '<search pattern>'
}Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace'
}The following filter validates the first document:
{
regexp: {
firstName: {
value: '^g\w+',
flags: 'i'
}
}
}Operands allow to compose complex filters.
The and filter takes an array of filter objects, combining them with AND operands.
and: Object[]
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
city: 'NYC',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
city: 'London',
hobby: 'computer'
}The following filter validates the first document:
{
and: [
{ equals: { city: 'NYC' } },
{ equals: { hobby: 'computer' } }
]
}A filter matching documents matching boolean combinations of other queries.
This operand accepts at least one of the following attributes:
-
must: all listed conditions must betrue -
must_not: all listed conditions must befalse -
should: at least one of the listed condition must betrue -
should_not: at least one of the listed condition must befalse
bool: {
[must]: Object[],
[must_not]: Object[],
[should]: Object[],
[should_not]: Object[]
}
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
age: 85,
city: 'NYC',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
age: 36
city: 'London',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Marie',
lastName: 'Curie',
age: 55,
city: 'Paris',
hobby: 'radium'
}The following filter validates the second document:
{
bool: {
must : [
{ in : { firstName : ['Grace', 'Ada'] } },
{ range: { age: { gte: 36, lt: 85 } } }
],
'must_not' : [
{ equals: { city: 'NYC' } }
],
should : [
{ equals : { hobby : 'computer' } },
{ exists : 'lastName' }
]
}
}The not filter inverts a matching result.
not: Object
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
city: 'NYC',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
city: 'London',
hobby: 'computer'
}The following filter validates the first document:
{
not: { equals: { city: 'London' } }
}The or filter takes an array containing filter objects, combining them using OR operands.
or: <array>
Given the following documents:
{
firstName: 'Grace',
lastName: 'Hopper',
city: 'NYC',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Ada',
lastName: 'Lovelace',
city: 'London',
hobby: 'computer'
},
{
firstName: 'Marie',
lastName: 'Curie',
city: 'Paris',
hobby: 'radium'
}The following filter validates the first two documents:
{
or: [
{ equals: { city: 'NYC' } },
{ equals: { city: 'London' } }
]
}