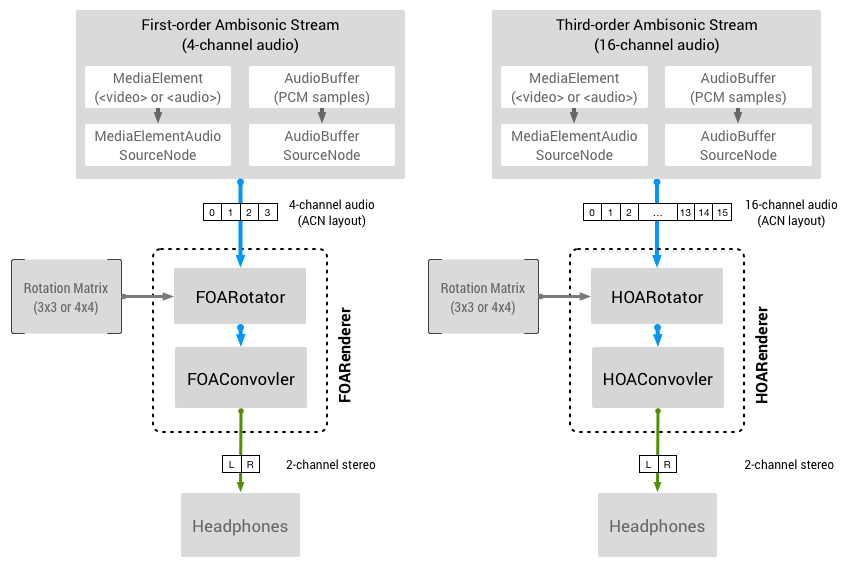
Omnitone is a robust implementation of FOA (first-order-ambisonic) decoder with binaural rendering written in Web Audio API. Its decoding process is based on multiple gain nodes for ambisonic gain matrix and convolutions for HRTF binaural rendering, ensuring the optimum performance.
The implementation of Omnitone is based on the Google spatial media specification. The input audio stream must be configured to ACN channel layout with SN3D normalization.
Omnitone is designed to be used for the web-facing projects, so the installation via Bower or NPM is recommended. Alternatively, you can clone or download this repository and use the library script file as usual.
bower install omnitone
// Or
npm install omnitoneOmnitone is a high-level library that abstracts various technical layers of the spatial audio processing. The input audio stream can be either a media element (video or audio tags) or a multichannel web audio source. The rotation of the sound field also can be easily linked to the mobile phone's sensor or the on-screen user interaction.
The first step is to include the library file in an HTML document.
<script src="omnitone.min.js"></script>The decoder requires an <audio> or <video> element and AudioContext. The following is an example of how to set up the context and the element for Omnitone.
// Prepare audio element to feed the ambisonic source audio feed.
var audioElement = document.createElement('audio');
audioElement.src = 'resources/4ch-spatial-audio-file.wav';
// Create an AudioContext and an Omnitone decoder.
var audioContext = new AudioContext();
var decoder = Omnitone.createFOADecoder(audioContext, audioElement);
// Initialize and then start playing the audio element.
decoder.initialize().then(function () {
audioElement.play();
}, function (onInitializationError) {
console.error(onInitializationError);
});The decoder constructor accepts the context and the element as arguments. Omnitone uses HRTFs from Google spatial media repository, but you can use a custom set of HRTF files as well. The initialization of a decoder instance returns a promise which resolves when the resources (i.e. impulse responses) are fully loaded.
The rotation matrix (3x3, row-major) in the decoder can be updated inside of the graphics render loop. This operation rotates the entire sound field. The rotation matrix is commonly derived from the quaternion of the orientation sensor on the VR headset or the smartphone. Also Omnitone converts the coordinate system from the WebGL space to the audio space internally, so you need not to transform the matrix manually.
// Rotate the sound field.
decoder.setRotationMatrix(rotationMatrix);Use setMode method to change the setting of the decoder. This is useful when the media source does not have spatially encoded (e.g. stereo or mono) or when you want to reduce the CPU usage or the power consumption by disabling the decoder.
// Mono or regular multi-channel layouts.
decoder.setMode('bypass');
// Ambisonically decoded audio stream.
decoder.setMode('ambisonic');
// Disable encoding completely. (audio processing disabled)
decoder.setMode('off');Omnitone also provides various building blocks for the first-order-ambisonic decoding and the binaural rendering. The FOADecoder is just a ready-made object built with those components. You can create them and connect together build your own decoding mechanism.
FOADecoder is a ready-made FOA decoder and binaural renderer. If you need to use the spatialization without any custom configuration, this is the simplest way of using Omnitone.
var decoder = Omnitone.createFOADecoder(context, element, {
HRTFSetUrl: 'YOUR_HRTF_SET_URL',
postGainDB: 30,
channelMap: [0, 1, 2, 3]
});- context (AudioContext): an AudioContext object.
- element (MediaElement): A target video or audio element for streaming.
- options (Object): options for decoder.
- HRTFSetUrl (String): Base URL for the cube HRTF sets.
- postGainDB (Number): Post-decoding gain compensation in dB.
- channelMap (Array): A custom channel map.
FOARouter is useful when you need to change the channel layout of the incoming multichannel audio stream. This is necessary because the channel layout changes depending on the audio codec in the browser.
var router = Omnitone.createFOARouter(context, channelMap);- context (AudioContext): an AudioContext object.
- channelMap (Array): an array represents the target channel layout.
router.setChannelMap([0, 1, 2, 3]); // 4-ch AAC in Chrome (default).
router.setChannelMap([1, 2, 0, 3]); // 4-ch AAC in Safari.FOARotator is a sound field rotator for the first-order-ambisonic decoding. It also performs the coordinate transformation between the world space and the audio space.
var rotator = Omnitone.createFOARotator(context);- context (AudioContext): an AudioContext object.
rotator.setRotationMatrix([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]); // 3x3 row-major matrix.FOAPhaseMatchedFilter is a pair of pass filters (LP/HP) with a crossover frequency to compensate the gain of high frequency contents without a phase difference.
var filter = Omnitone.createFOAPhaseMatchedFilter(context);- context (AudioContext): an AudioContext object.
FOAVirtualSpeaker is a virtual speaker abstraction with the decoding gain coefficients and HRTF convolution for the first-order-ambisonic audio stream. Note that the speaker instance directly connects to the destination node of AudioContext. So you cannot apply additional audio processing after this component.
var speaker = Omnitone.createFOAVirtualSpeaker(context, options);- context (AudioContext): an AudioContext object.
- options (Object): options for speaker.
- coefficients: decoding coefficients for (W,X,Y,Z).
- IR: stereo IR buffer for HRTF convolution.
- gain: post-gain for the speaker.
speaker.enable(); // activate the speaker.
speaker.disable(); // deactivate the speaker.Deactivating a virtual speaker can save CPU powers. Running multiple HRTF convolution can be computationally expensive, so disabling a speaker might be helpful when the binaural rendering is not necessary.
Omnitone uses WebPack to build the minified library and to manage dependencies.
npm run install # install dependencies.
npm run build # build a non-minified library.
npm run watch # recompile whenever any source file changes.
npm run build-all # build a minified library and copy static resources.Omnitone is designed to run any browser that supports Web Audio API, however, it does not address the incompatibility issue around various media codec in the browsers. At the time of writing, the decoding of compressed multichannel audio via <video> or <audio> elements is not fully supported by the majority of mobile browsers.
Special thanks to Julius Kammerl, Dillon Cower, Boris Smus and Brandon Jones for their help on this project. We are also grateful to Tim Fain and Jaunt VR for their permission to use beautiful VR contents in the demo.
If you have found an error in this library, please file an issue at: https://github.com/GoogleChrome/omnitone/issues.
Patches are encouraged, and may be submitted by forking this project and submitting a pull request through GitHub. See CONTRIBUTING for more detail.
Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.