A project on Demonstration of types of cell division, class DSAI, course Object-Oriented Programming, semester 20212.
- Trần Ngọc Khánh 20200326 - @khanhtn2301
- Trần Quốc Khánh 20204881 - @khanha2k46pbc
- Trần Cát Khánh 20204916 - @khanhha1005
- Hồ Minh Khôi 20204917 - @hmkhoi2701
You can watch the demo at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XCg1tfyJsj4
A cell is a basic, structural unit of all life forms.
There are 2 types of cells: Prokaryotic cells (tế bào nhân sơ) and Eukaryotic cells (tế bào nhân thực).
The 2 types differ by the completeness of nuclei (nhân tế bào).
A cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells.
For eukaryotes, a cell cycle includes:
- Resting phase G0: where the cell left the cycle and stop dividing.
- Interphase with 3 phases:
- G1: Collecting materials for DNA replication.
- S: Where DNA replication occurs.
- G2: Cell growth and collecting materials for mitosis.
- Mitosis phase M: the process in which the chromosomes (nhiễm sắc thể) in the cell nucleus were seperated into two identical sets. Immediately, cytokinesis (phân chia tế bào chất) follows, resulting into two identical daughter cells. (Mitosis is one of our study field of this project)
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides, when a mother cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
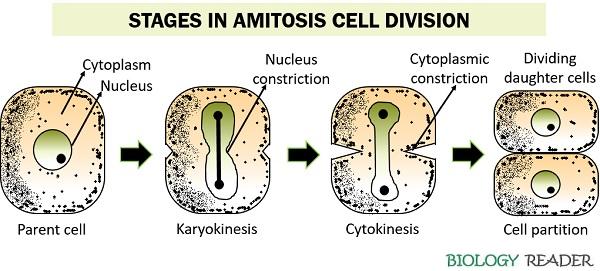
Amitosis occurs in prokaryotic cells, with the stages as below:
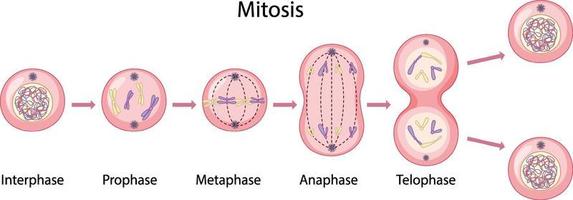
Mitosis occurs in eukaryotic cells, with the stages as below:
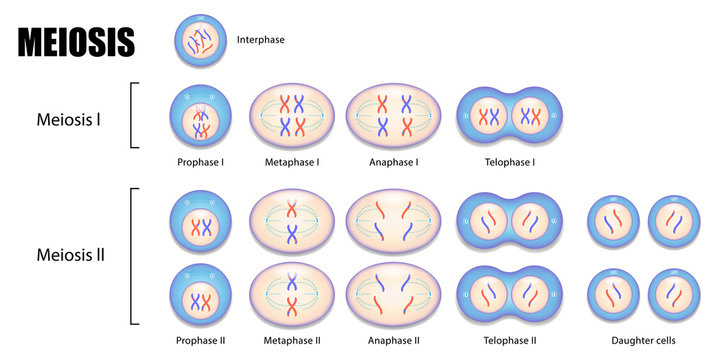
Meiosis is a special type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, specifically reproductive cells (tế bào sinh dục), for example sperm or egg cells. Below are the stages of meiosis: