This document is meant to be a Swiss Army Knife for entry level Cybersecurity jobs and to learn hacking skills. A work in progress, so if you see mistakes, please mention it in the "Issues" section.
NOTE: I DO NOT OWN ANY OF THIS INFORMATION. THIS IS JUST MEANT TO BE A COMPILATION OF VARIOUS RESOURCES. SOURCES ON THE BOTTOM.
DISCLAIMER: The information below is for eduational purposes ONLY. You are responsible for your own actions. (Don't hack your friend for not hanging out with you!)
- Foothold Job Titles
- Entry-Level Job Titles
- Mid-Level Job Titles
- Advanced-Level Jobs Titles
- Career Websites
- Learning Hacking Skills
- Subreddits
- Blogs
- Podcasts
- Certifications
- OWASP
- Cheat Sheets
- Sources for this Document
- Acknowledgements
IT Support Technician - Using a ticketing system for internal support requests and installing programs on computers.
IT Helpdesk Tier 1 - Using a ticketing system to provide support, as well as providing technical support over the phone.
Junior Network Technician - Assisting in adding users to the network, modifying user access, and performing basic network maintenance tasks.
System Administrator - Responsible for the configuration, upkeep and reliable operation of a company’s network and computer systems.
Data Administrator - Use specialized software to store and organize data.
Network Administrator - Manage an organization's computer networks.
IT Technician - Provide general desktop and printer support for a company and/or its clients, or they provide network support.
Security Administrator - Installs, administers, and troubleshoots an organization's security solutions.
Network Engineer - Design, build, implement and maintain the computer networks businesses and organizations use.
Information Security Analyst - Plan, implement, upgrade, or monitor security measures for the protection of computer networks and information.
Junior Penetration Tester - Hired by a client to bypass or defeat security controls.
Cybersecurity (Security) Technician / Specialist - Protects computer assets by establishing and documenting access; maintaining files.
Cyber Crime Analyst/Investigator - Information security professionals who use their skills and background knowledge in areas like network administration or network engineering to help counter the activities of cyber criminals such as hackers and developers of malicious software.
Incident Analyst/Responder - Require an understanding of security operations, a solid foundation of technical skills related to information and network security, and strong communication skills.
IT Auditor - Responsible for analyzing and assessing a company’s technological infrastructure to ensure processes and systems run accurately and efficiently, while remaining secure and meeting compliance regulations.
Cybersecurity Engineer (systems): ensures memory is handled safely, ensures interfaces are implemented securely, etc
Cybersecurity Engineer (Web): ensures web apps utilize frameworks or architecture paradigms that are resistant to CSRF/XSS/SQL injection attacks (using tokens, MVC frameworks, input validation, etc.), ensures imported libs are trustworthy, etc.
DevSecOps Engineer: largely operates in the IT security space, automates security tasks and functions in a security orchestration position
Cybersecurity Analyst - Information technology professional whose primary function is to protect organizations from cyber attacks and respond swiftly to restore protection if compromised.
Cybersecurity Consultant - Responsible for keeping a client’s data suitably protected and free from the risk of cyber attacks and related problems
Penetration & Vulnerability Tester - Highly skilled security specialists that spend their days attempting to breach computer and network security systems.
Cybersecurity Architect - Combines hardware and software knowledge with programming proficiency, research skills, and policy development.
Cybersecurity Manager / Admininstrator - Require an advanced understanding of information security concepts, security operations and information assurance, as well as risk management and project management skills.
Reverse Engineer(RE)/Malware Analyst: decompiles software and uses this information to determine the function or security flaws of target software. Often participates as a member of an Incident Response Team or sometimes even a red team. Probably has a background in OS or embedded/systems development, and in-depth knowledge of assembly code for the target processor architecture
Penetration Tester/Red Team Developer (SWE): May participate on a red team, building utilities and chaining tools that are configured for a specific target. Builds out software for C2 infrastructure. (example, chains a browser exploit, image parser exploit, and OS exploit, then executes code that maintains persistence and elevates privileges)
Google job search (etc. cybersecurity jobs [city name])
Job search on company websites
Learn About Vulnerabilities:
Learn About Kali Linux (Pen-testing OS):
Learn About Parrot (Pen-testing OS):
Learn About BlackArch (Hacking OS):
uthena BlackArch Linux Course (Paid)
Practice Linux Skills:
Practice CTF (Capture The Flag) Skills:
picoCTF (Free)
Cyber Skyline / National Cyber League (Paid)
CTFlearn (Free)
Hacker101 (Free)
Practice Penetration Testing:
HACKTHEBOX (Free/Paid)
TryHackMe (Free/Paid)
PentesterAcademy (Paid)
Watch Videos Related To Hacking:
Youtube - BLACK ARCH LINUX TUTORIAL PLAYLIST
Watch Hackthebox Write-Ups:
Learn MITRE ATT&CK
Learn Reverse Engineering
Practice Reverse Engineering
Learn PowerShell
Microsoft Documentation - PowerShell
Learn Shell-Script
Shell Scripting Tutorial by Steve Parker
SANS Internet Storm Center, InfoCON: green
ToolsWatch.org – The Hackers Arsenal Tools Portal
SANS Internet Stormcenter Daily Network/Cyber Security and Information Security Stormcast
Down the Security Rabbithole Podcast
Recorded Future - Inside Security Intelligence
Certifications are a way to get HR's eye. From my understanding, it DOES NOT replace a College/University Degree.
(Source: https://www.pauljerimy.com/OC/Security%20Certification%20Progression%20Chart%20v7.0.png)
The OWASP® Foundation works to improve the security of software through its community-led open source software projects, hundreds of chapters worldwide, tens of thousands of members, and by hosting local and global conferences.
- OWASP Web Security Testing Guide : The Web Security Testing Guide (WSTG) Project produces the premier cybersecurity testing resource for web application developers and security professionals. The WSTG is a comprehensive guide to testing the security of web applications and web services. Created by the collaborative efforts of cybersecurity professionals and dedicated volunteers, the WSTG provides a framework of best practices used by penetration testers and organizations all over the world.
- OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide We are writing a security standard for mobile apps and a comprehensive testing guide that covers the processes, techniques, and tools used during a mobile app security test, as well as an exhaustive set of test cases that enables testers to deliver consistent and complete results.
- OWASP Application Security Verification Standard The primary aim of the OWASP Application Security Verification Standard (ASVS) Project is to provide an open application security standard for web apps and web services of all types.
The standard provides a basis for designing, building, and testing technical application security controls, including architectural concerns, secure development lifecycle, threat modelling, agile security including continuous integration / deployment, serverless, and configuration concerns.
OWASP.Application.Security.Verification.Standard.4.0.2
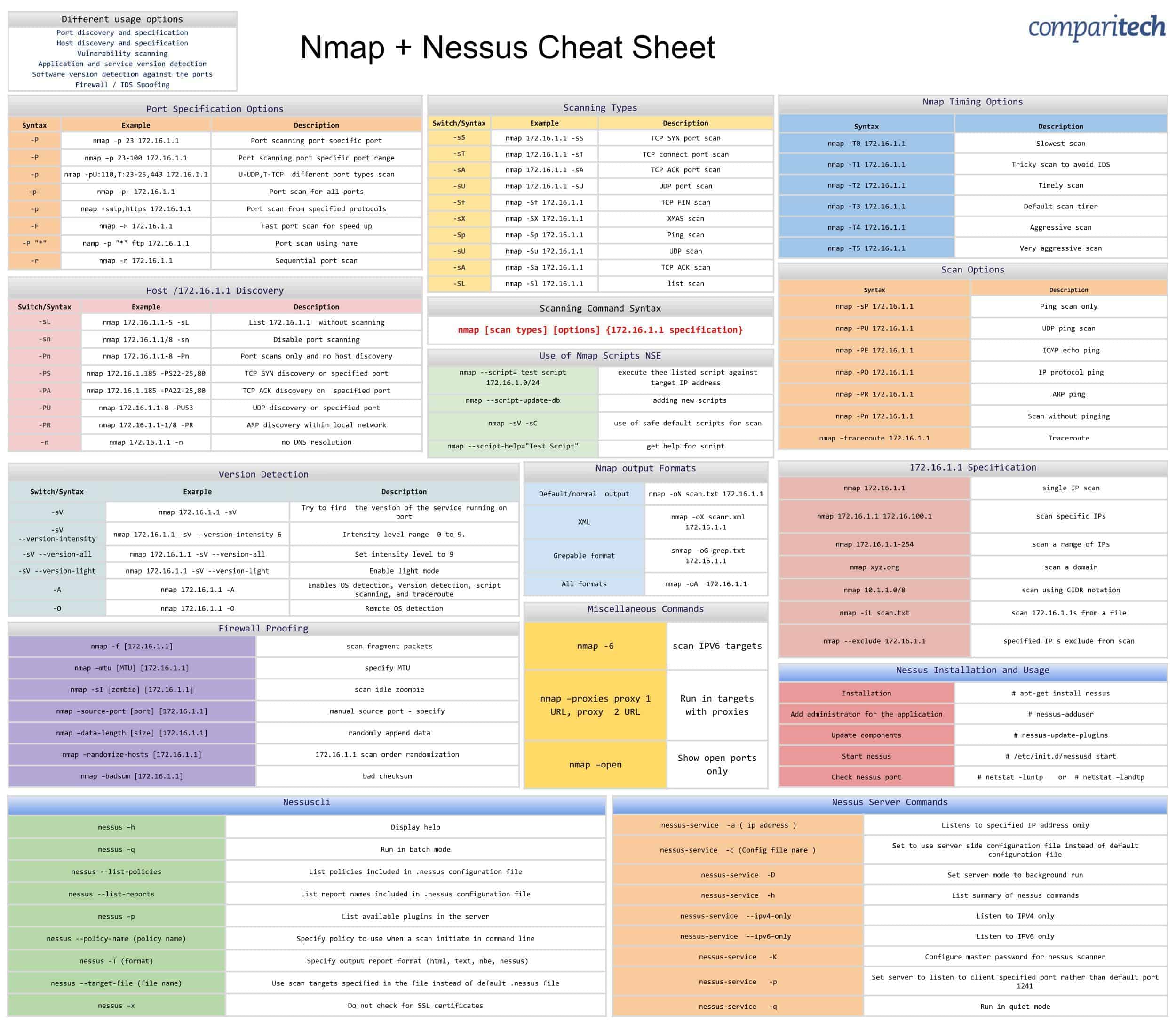
Nmap and Nessus (Source: https://cdn.comparitech.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Nmap-Nessus-Cheat-Sheet.jpg)
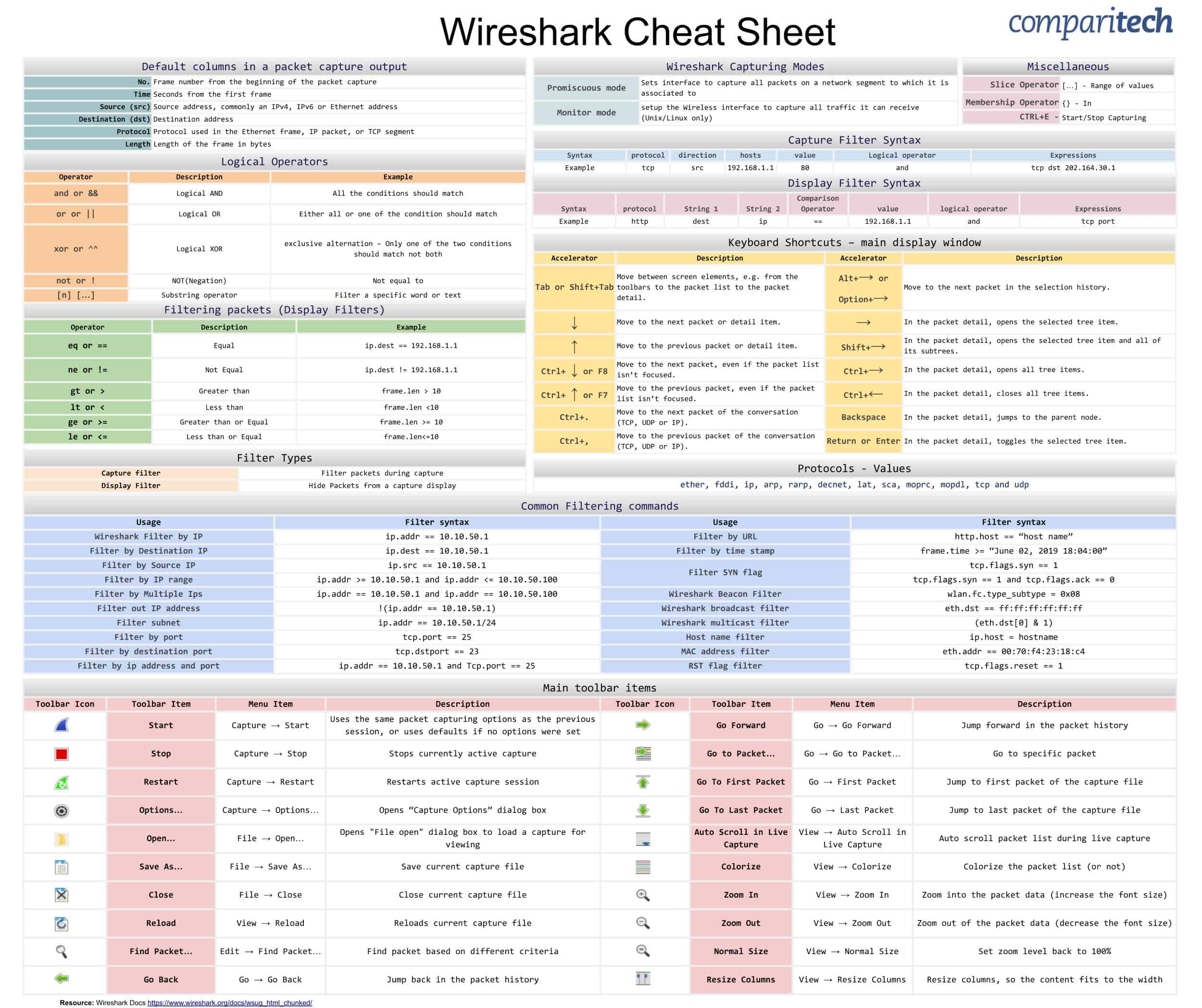
Wireshark (Source: https://cdn.comparitech.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Wireshark-Cheat-Sheet-1.jpg)
Hacking Tools (Source https://blog.compass-security.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/hacking_tools_cheat_sheet_v1.0-0.png)
Hacking Tools P.2 (Source https://blog.compass-security.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/hacking_tools_cheat_sheet_v1.0-1.png)
best entry level cyber security jobs
what does a system administrator do
how to land an entry level cybersecurity job
security-administrator-job-description
system security technician job description
how to become a cyber security analyst
cyber intelligence analyst-2071296
cyber security engineer job description
I want to give a big shoutout to my partner on this document Jalan (JayCruzer17) for assisting me with creating and maintaining this document. I also want to give credit to those on the r/cybersecurity subreddit for giving me feedback on the document. I had made a post on reddit and I would like to thank all the comments for giving feedback in one area or another. In addition, I would like to thank the individuals doing pull requests on this document with additional links/information that I might have overlooked. Without the aforementioned people, this document will not be where it is now.