_
| |_ _ __ ___ __ ___ __
| __| '_ ` _ \ / _` \ \/ /
| |_| | | | | | (_| |> <
\__|_| |_| |_|\__,_/_/\_\
The positioning of tmax is a command line tool with a little artificial intelligence.
If you frequently deal with the terminal daily, tmax will greatly improve your work efficiency.
- Have a local storage as a knowledge base
- Efficient search algorithm and accurate feedback
- Full command line interaction
- Make your very long cmd short
For linux and macos you can install tmax as follows.
Use make build and you will get tmax in the directory.
chmod +x tmax && cp tmax /usr/local/bin
- go get
If you have golang environment, use
go getto install tmax
go get -u github.com/hantmac/tmax- brew install
For mac os, you can use
brew:
brew tap hantmac/tap && brew install --build-from-source tmax- binary file If you use unix, you can download binary file to use tmax:
wget https://github.com/hantmac/tmax/releases/download/v0.1.0/tmax_v0.1.0_linux_x86_64.tar.gz && \
tar -zxvf tmax_v0.1.0_linux_x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin && chmod +x /usr/local/bin/tmaxThen, you need to tmax generate to generate a config file in $HOME/.tmax.yaml and the file look like as follows:
custom:
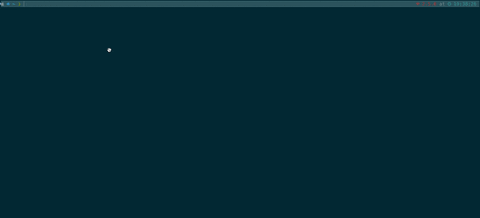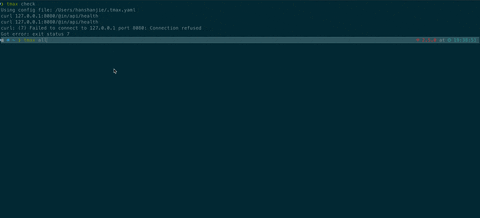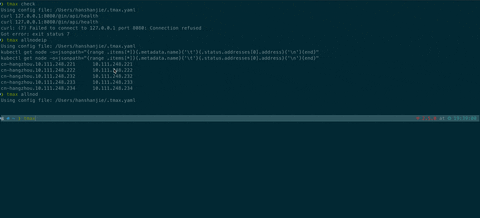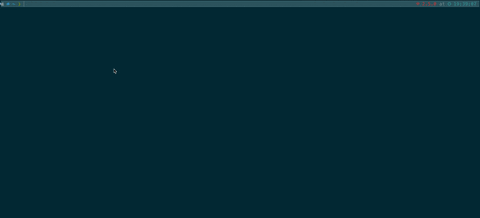
check: curl 127.0.0.1:8080/health
k8s:
filternodecpu: kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{'\t'}{.status.capacity.cpu}{'\t'}{.status.capacity.memory}{'\n'}{end}"
filternodetaint: kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{'\t'}{.spec.taints[*].key}{'\n'}{end}"
corednsedit: kubectl edit cm coredns -nkube-system
allnode: kubectl get no
alldeploy: kubectl get deploy
allpod: kubectl get pod -A
busyboxrun: kubectl run busybox --rm -ti --image=busybox /bin/sh
allnodeip: kubectl get node -o=jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{'\t'}{.status.addresses[0].address}{'\n'}{end}"
podResource: kubectl get pod -o custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,podIP:status.podIP,hostIp:spec.containers[0].resources
getns: kubectl get ns
createdemo: kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
exposedemo: kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80
getnetwork: kubectl get networkpolicy
runbox: kubectl run busybox --rm -ti --image=busybox /bin/sh
unix:
"tar": "tar -xjvf test.tar.bz2"As you can see, there are many long commands those hard to keep in your mind. If you want to quickly get a long command, even if you have memorized it, it takes a long time to type it into the console, not to mention that sometimes you can't remember such a long command.
At this moment, tmax appeared, it will solve the problem just mentioned.
tmax has 3 modes: directly mode, search mode and interactive mode. And tmax will make your very long terminal cmd short, improve your operation efficiency.
If you clearly know the key you want to execute the command, you can use directly mode.
Use 'tmax somekey' , example: tmax check will execute curl 127.0.0.1:8080/health
First, suppose we define the following short command in the configuration file ~/.tmax.yaml:

tmax getpod myapp-deploymyapp-deploy is a custom parameter, you can even add parameters later:
tmax getpod myapp-deploy -n YOUR_NAMESPACEYou can freely customize your own tmax configuration file according to the required custom parameters.
You should notice that custom parameters can only be appended after the tmax command.
If you want to add a variable parameter in the middle, you can't use it.
For example, if you want to make a taint for a k8s node, and this taint is commonly used by your company,
you must execute kubectl taint node node-1.1.1.1 reserved=mynode:NoSchedule,
and the name of the node will become a variable The parameters and the taint name are fixed, so the good way is to enter the node name to complete the command.
Don't panic, tmax supports template parameters. For the above command we can add in ~/.tmax.yaml:
taintnode: kubectl taint node {{.n}} reserved=cd-staging:NoScheduleJust execute the following content to complete the taint command:
tmax taintnode -n YOUR_NODE_NAMEor you have an exec cmd like:
exec: kubectl exec -it {{.p}} -- shJust execute the following cmd to exec into a pod:
tmax exec -p YOUR_POD_NAMEIf you know the general content of the command you want to execute, you can use the search mode to find and execute it.
Use tmax s CONTENTOFCMD, example: tmax s pod or tmax search pod.
If you don't want to search, tmax has interactive mode.
Just type tmax and enter to interactive mode.