xmark is a PHP7 extension that provides the following features:
- It can mark string variables
- It can hook most functions/classes
- It can Hook parts of the opcodes
- linux:
phpize
./configure
make
- windows
example:
<?php
function var_dump(...$args) {
echo "in custom var_dump\n";
_var_dump(...$args);
}
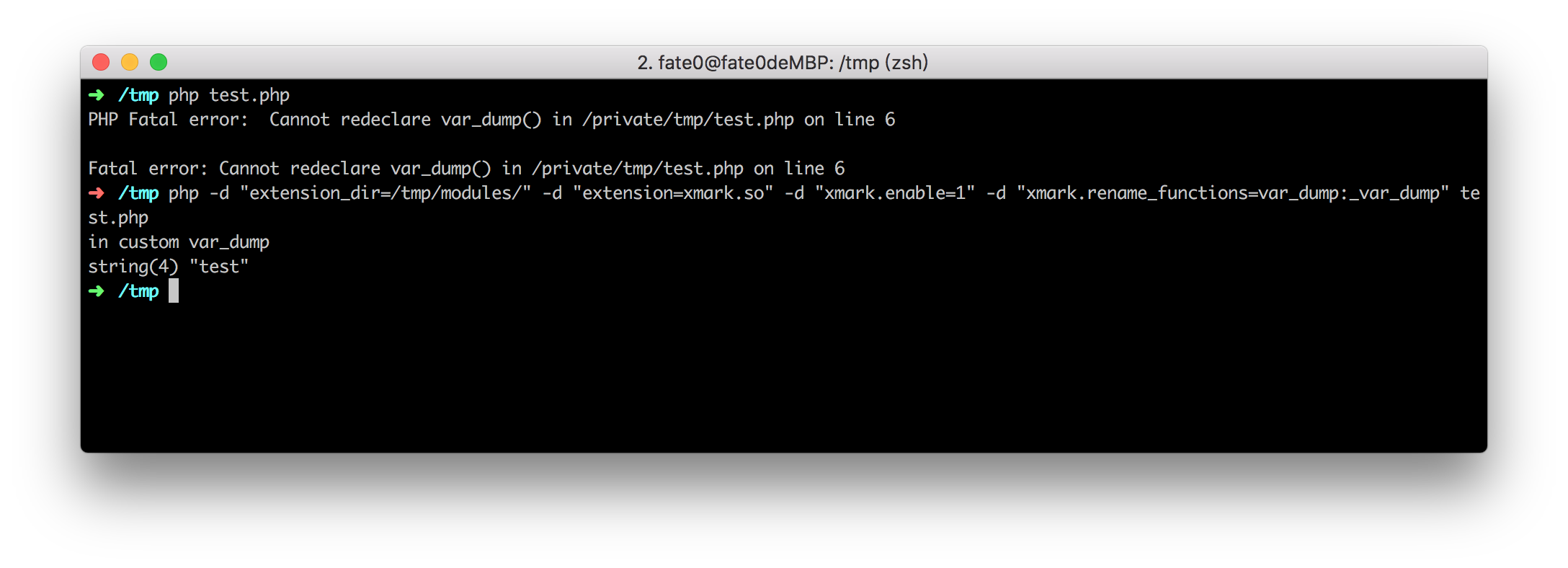
var_dump("test");run:
php -d "extension_dir=/tmp/modules/" -d "extension=xmark.so" -d "xmark.enable=1" -d "xmark.rename_functions=var_dump:_var_dump" test.php
result:
- mark string variables
bool xmark(string &$str);
- check if the string variable is marked
bool xcheck(string &$str);
- clear tag on string variables
bool xclear(string &$str);
- change the name of the user function
bool xrename_function(string $old_name, string $new_name);
- change the name of the user class
bool xrename_class(string $old_name, string $new_name);
- register opcode callback
bool xregister_opcode_callback(int $opcode, string $callback);
$callback must be a function name, not a class method, or any other callable。
each opcode callback has a different function description, so let's explain it one by one。
XMARK_ECHO
void echo_handler(string $string)
XMARK_EXIT
void exit_handler(string $string)
XMARK_INIT_METHOD_CALL
void init_method_call_handler(string $funcname)
XMARK_INIT_USER_CALL
void init_user_call_handler(string $funcname)
XMARK_INIT_DYNAMIC_CALL
void init_dynamic_call_handler(string $funcname)
XMARK_INCLUDE_OR_EVAL
void include_or_eval_handler(string $code_or_file)
XMARK_CONCAT
string concat_handler(string $param1, string $param2)
XMARK_FAST_CONCAT
string fast_concat_handler(string $param1, string $param2)
XMARK_ASSIGN_CONCAT
string assign_concat_handler(string $param1, string $param2)
XMARK_ROPE_END
void rope_end_handler(array $params)
XMARK_DO_FCALL
void do_fcall(string $call, array $params)
XMARK_DO_ICALL
void do_icall(string $call, array $params)
XMARK_DO_UCALL
void do_ucall(string $call, array $params)
XMARK_DO_FCALL_BY_NAME
void do_fcall_by_name(string $call, array $params)
enable xmark extension:
xmark.enable = 1
enable rename PHP user functions/classes (do not enable this in production envri)
xmark.enable_rename = 1
rename PHP internal functions:
xmark.rename_functions="
phpinfo:my_phpinfo,
system:my_system
"
rename PHP internal classes:
xmark.rename_classes="
PDO:my_POD,
yyy:_yyy
"
str_replace
str_replace function description:
mixed str_replace ( mixed $search , mixed $replace , mixed $subject [, int &$count ] )
$count is a reference parameter,so the correct way to hook str_replace is as follows:
function str_replace($search, $replace, $subject, &$count=NULL) {
return call_user_func_array("origin_str_replace", array($search, $replace, $subject, &$count));
}
str_replace("a", "e", "hallo world", $count);
var_dump($count);hook other function with reference parameters are also done as above.
strval
xmark can not hook strval function. because strval is optimized directly in the compile stage,
and does not need to be searched by EG(function_table),
other similar functions zend_compile.c
getallheaders
xmark can not hook getallheaders function. because getallheaders function is inside the sapi_module,
sapi_module initialization time is later than php_extension and zend_extension,
so the functions in sapi_module can not be hooked with xmark,fortunately, there are only a few functions in sapi_module.
extract
xmark can hook extract function, but it will affect the original function of extract.
because extract will change its own variable scope,
extract will look up the last user function int the call stack and then modify its variable scope,
when we rename extract to another name and write another extract function in PHP,
the extract function we wrote becomes the last user function in the call stack, so extract won't work properly.
other similar functions: Forbid dynamic calls to scope introspection functions
if you just need to monitor the calls to these functions, then I recommend using opcode callback.
array_map
xmark can also hook array_map function,but it may also affect the original function of array_map.
because when array_map calls the callback, it will determine whether the function calling array_map has permission to call the corresponding callback.
example:
<?php
function test($callable, $arr) {
array_map($callable, $arr);
}
class A {
public function hi() {
test(array($this, 'hello'), array(1, 2));
}
private function hello() {
echo "hello\n";
}
}
$a = new A();
$a->hi();when array_map is called, zend_get_executed_scope will look up the last use function in the call stack and then
determine if the user function has permission to call the callback. so it may cause the the call to array_map to fail.
the same problem occurs in other internal functions that accept callback parameter.
in summary, if a function depends on or will change the scope of the caller, then you should carefully determine whether the function can still be hooked.