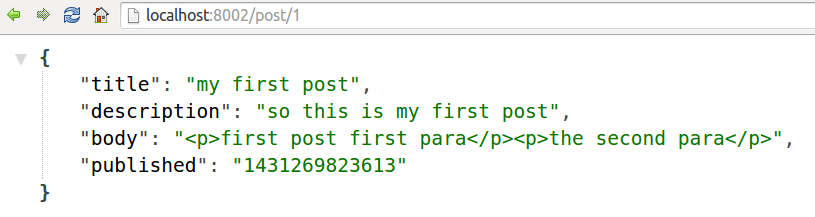
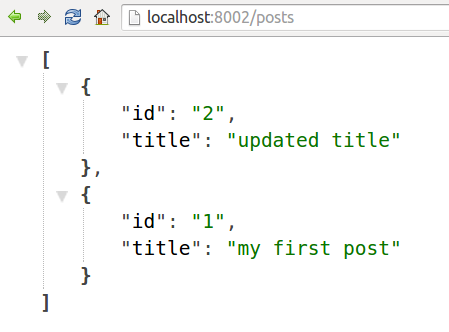
We demonstrate the use of Redis as a data store for blog posts, and implement a trivial "API server" to serve our JSON content using ExpressJS.
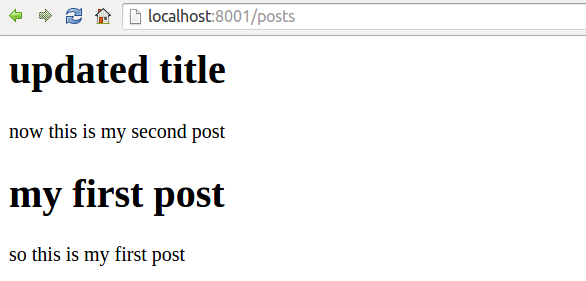
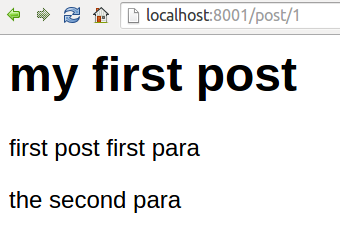
Furthermore, we implement a web server to use ReactJS to render the content as HTML on NodeJS, served by ExpressJS.
The following code snippet demonstrates retrieving data from Redis.
function retrievePosts(ids, callback) {
log.info('posts', ids);
async.map(ids, function(id, cb) {
redisClient.hgetall('post:table:' + id, (err, post) => {
log.info('posts hgetall', {id, err, post});
cb(err, post);
});
}, (err, posts) => {
log.info('posts', {ids, err, posts});
if (err) {
callback(err);
} else {
callback(null, lodash.map(posts, (post, index) => {
return {
id: ids[index],/.1/
title: post.title,
description: post.description
}
}));
}
});
}The following code snippet demonstrates rendering using ReactJS.
function getPostId(req, res) {
postService.find(req.params.id, (err, post) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send(err);
} else {
var html = React.renderToString(
React.createElement(PostPage, {post}));
res.set('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.send(html);
}
});
}where we render a PostPage React component into HTML.
The PostPage component is composed using the following Post component.
import React from 'react';
const Post = React.createClass({
render: function () {
let post = this.props.post;
return (
<div className="postContainer">
<h1 style={{marginTop: 4}}>{post.title}</h1>
<p dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{__html: post.body}}></p>
</div>
);
}
});