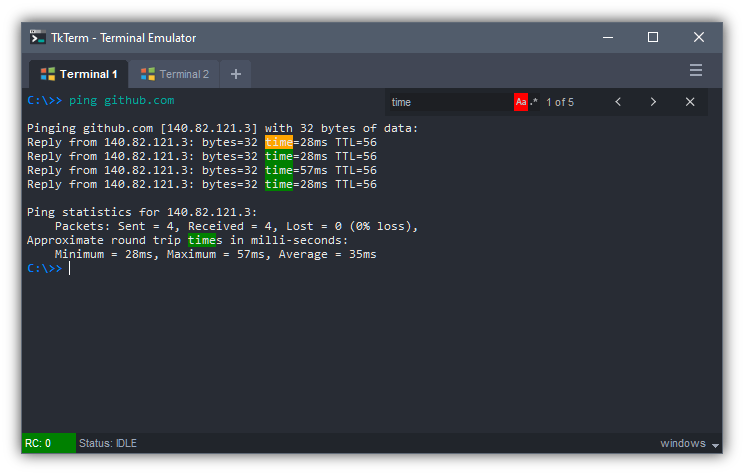
A fully functional terminal emulator built on Tkinter library - perform all basic commands of a terminal
Under the hood it executes commands using Python's subprocess module and spawn as a thread. Pressing Ctrl-C will terminate current running command. Supports Unix shells (sh and bash) and Window's Command Prompt (cmd.exe) commands.
- Compatible with Windows and Unix systems
- Tabbed Terminal -
click & dragto reorder,middle-clickto close tab,double-clickto rename - Return Code (RC) of previous run commands is shown at the bottom status bar
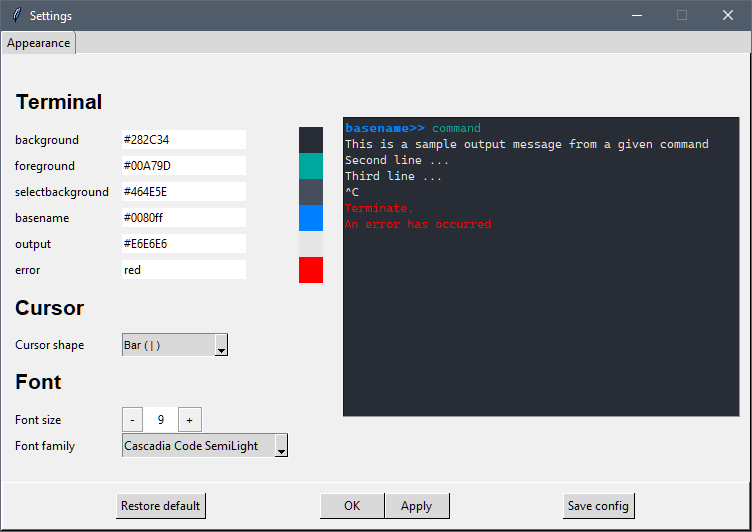
- Settings to customise colours, font and cursor shape
- Ctrl-C to kill current running process
- Ctrl-F to search; supports case sensitivity and regex searches
- UP and DOWN arrow keys to cycle between next and previous commands in history
- Unix-like tab completion on files and directories
- Handles multiline commands using caret character
^or\
The Tkinter GUI library is built into Python, so no 3rd party library is required.
Requires at least Python version 3.x and above.
Get it from Github or PIP package manager
# From github
git clone https://github.com/dhanoosu/TkTerm.git
# From package manager
pip install tktermNavigate to downloaded folder and run script with
cd TkTerm
# Either of these will work
python tkterm
python tkterm/tkterm.pyIf package was installed via pip
python -m tktermThe Terminal is implemented as a Frame widget and can easily be integrated to other Tkinter application by
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from tkterm import Terminal
root = tk.Tk()
terminal = Terminal(root)
terminal.pack(fill=BOTH, expand=True)
root.mainloop()If downloaded via github append to system path before import
import sys sys.path.insert(0, "./TkTerm") from tkterm import Terminal
Customise Terminal interface by Right-click > Settings...
Note:
Clicking Save config saves setting configuration to a file.
Tkterm will automatically load this file the next time it starts up.
Long lines of command can be broken up using a caret. A caret at the line end appends the next line command with the current command.
In Windows the caret is ^, and UNIX is \.
For multiline command to be considered there must be no trailing space after the caret, for example:
$> ping ^is considered$> ping ^is not considered
$>> echo I ^
> have apple ^
> and banana
I have apple and bananaDeveloped by Dhanoo Surasarang
Github: @dhanoosu