It should be quite obvious to GitHub users why our team likes git - we branch, diff, merge and rebase heavily, work offline, stash, amend commits and do other git-specific things that make git so fun and useful.
However, our corporate standard is Subversion. It is simple and reliable, the history is immutable and Project managers can use TortoiseSVN to access the project repository as well, keeping project documents neatly organized alongside source repositories; administrators have easy tools for managing authorization and authentication etc. Everyone is generally happy with it.
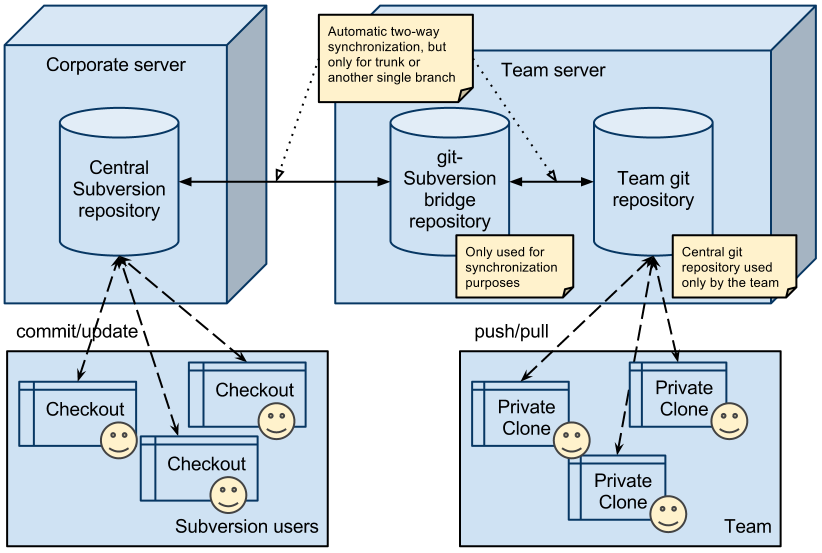
To reap the best of both worlds, we have setup a git-Subversion bridge that synchronizes changes between our team git repository and the corporate Subversion repository. The obvious requirement is that our git usage has to be transparent to other Subversion users, not interfere with their work or damage the corporate repository.
The setup looks like this:
This document gives an overview of the setup.
If you have administrator access to the Subversion repository (we don't), be sure to check out SubGit. It may (or may not) make the setup simpler.
-
Each update of a branch in the central git repository will trigger synchronization with Subversion. Additionally, there is a cron job that runs the synchronization every n minutes (so that the repository is updated even if there are no commits at git side). Concurrent synchronization is properly guarded with a lock.
-
There is no synchronization of branches created in git. New branches can be created in Subversion only.
-
As Subversion history is linear, git merge commits will be squashed into a single commit (see examples below).
-
To properly set author information in commits between git and Subversion, Subversion user passwords need to be available at the synchronization process. This bridge utility keeps passwords in an encrypted database and uses that for synchronization (see description below).
-
git history is duplicated as commits first go up to and then come back down again with a
git-svn-idfrom Subversion. This is the most confusing limitation, although Subversion history remains clean (see examples below; note that--no-ffis used to record the merges). -
Rewriting history on branch will probably mess up the git-Subversion synchronization, so it is disabled with the update hook in the central git repository (we haven't tried though, this just seems a sane precaution).
-
If the project is Windows-only then the git bridge repo must be configured to retain Windows line endings. (TODO: describe how.)
Squashed branch merge commit to master from git (see dave.sh below):
$ svn log trunk@r9 -l 1
------------------------------------------------------------------------
r9 | dave | 2012-08-26 13:22:39 +0300 (Sun, 26 Aug 2012) | 10 lines
2012-08-26 13:22:36 +0300 | Merge branch 'payment-support'
[Dave]
2012-08-26 13:22:36 +0300 | Add storage encryption for payments
[Dave]
2012-08-26 13:22:36 +0300 | Implement credit card payments
[Dave]
2012-08-26 13:22:36 +0300 | Implement PayPal payments
[Dave]
2012-08-26 13:22:36 +0300 | Add payment processing interface
[Dave]
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Single commit to master from git (see carol.sh below):
$ svn log trunk@r8 -l 1
------------------------------------------------------------------------
r8 | carol | 2012-08-26 13:22:36 +0300 (Sun, 26 Aug 2012) | 2 lines
2012-08-26 13:22:35 +0300 | Use template filters to represent amounts in localized format
[Carol]
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Single commit before synchronization:
$ git log a165c -1
commit a165c9857eebb168e44b22278950cd930259394c
Author: Carol <[email protected]>
Date: Sun Aug 26 13:22:35 2012 +0300
Use template filters to represent amounts in localized format
After synchronization, it will be duplicated with another commit that has come down from Subversion:
$ git log
...
commit 10fb01c123851b02f2105c98cb7c9adc47a1bb39
Merge: fc656d9 a165c98
Author: Carol <[email protected]>
Date: Sun Aug 26 13:22:36 2012 +0300
2012-08-26 13:22:35 +0300 | Use template filters to represent amounts in localized format
[Carol]
git-svn-id: svn://localhost/trunk@8 49763079-ba47-4a7b-95a0-4af80b88d9d8
...
commit a165c9857eebb168e44b22278950cd930259394c
Author: Carol <[email protected]>
Date: Sun Aug 26 13:22:35 2012 +0300
Use template filters to represent amounts in localized format
...
For each branch merge, an additional squashed merge commit will come down from Subversion as shown in the previous section.
The following walkthrough is provided both for documentation and for hands-on testing (Example script can be found in scripts/test-sync.sh).
Start by creating the bridge user (use your actual email address instead of [email protected], it is used later during setup and testing):
$ sudo adduser git-svn-bridge
$ sudo su git-svn-bridge
$ set -u
$ [email protected]
$ git config --global user.name "Git-SVN Bridge (GIT SIDE)"
$ git config --global user.email "$YOUR_EMAIL"
$ cd
$ mkdir {bin,git,svn,test}
Assure that Subversion caches passwords:
$ echo 'store-plaintext-passwords = yes' >> ~/.subversion/servers
Create the Subversion repository (in real life you would simply use the existing central Subversion repository):
$ cd ~/svn
$ svnadmin create svn-repo
$ svn co file://`pwd`/svn-repo svn-checkout
Checked out revision 0.
Commit a test revision to Subversion:
$ cd svn-checkout
$ mkdir -p trunk/src
$ echo 'int main() { return 0; }' > trunk/src/main.cpp
$ svn add trunk
A trunk
A trunk/src
A trunk/src/main.cpp
$ svn ci -m "First commit."
Adding trunk
Adding trunk/src
Adding trunk/src/main.cpp
Transmitting file data .
Committed revision 1.
Setup svnserve to serve the repository:
$ cd ~/svn
$ SVNSERVE_PIDFILE="$HOME/svn/svnserve.pid"
$ SVNSERVE_LOGFILE="$HOME/svn/svnserve.log"
$ SVNSERVE_CONFFILE="$HOME/svn/svnserve.conf"
$ SVNSERVE_USERSFILE="$HOME/svn/svnserve.users"
$ >> $SVNSERVE_LOGFILE
$ cat > "$SVNSERVE_CONFFILE" << EOT
[general]
realm = git-SVN test
anon-access = none
password-db = $SVNSERVE_USERSFILE
EOT
$ cat > "$SVNSERVE_USERSFILE" << EOT
[users]
git-svn-bridge = git-svn-bridge
alice = alice
bob = bob
carol = carol
dave = dave
EOT
$ TAB="`printf '\t'`"
$ cat > ~/svn/Makefile << EOT
svnserve-start:
${TAB}svnserve -d \\
${TAB}${TAB}--pid-file "$SVNSERVE_PIDFILE" \\
${TAB}${TAB}--log-file "$SVNSERVE_LOGFILE" \\
${TAB}${TAB}--config-file "$SVNSERVE_CONFFILE" \\
${TAB}${TAB}-r ~/svn/svn-repo
svnserve-stop:
${TAB}kill \`cat "$SVNSERVE_PIDFILE"\`
EOT
Start svnserve:
$ make svnserve-start
Setup the central repository that git users will use:
$ cd ~/git
$ git init --bare git-central-repo-trunk.git
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/git-svn-bridge/git/git-central-repo-trunk.git/
$ cd git-central-repo-trunk.git
$ git remote add svn-bridge ../git-svn-bridge-trunk
Setup the git-Subversion bridge repository:
$ cd ~/git
$ SVN_REPO_URL="svn://localhost/trunk"
$ git svn init --prefix=svn/ $SVN_REPO_URL git-svn-bridge-trunk
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/git-svn-bridge/git/git-svn-bridge-trunk/.git/
Fetch changes from Subversion:
$ cd git-svn-bridge-trunk
$ AUTHORS='/tmp/git-svn-bridge-authors'
$ echo "git-svn-bridge = Git SVN Bridge <${YOUR_EMAIL}>" > $AUTHORS
$ git svn fetch --authors-file="$AUTHORS" --log-window-size 10000
Authentication realm: <svn://localhost:3690> git-SVN test
Password for 'git-svn-bridge': git-svn-bridge
A src/main.cpp
r1 = 061725282bdccf7f4a8efa66ee34b195ca7070fc (refs/remotes/svn/git-svn)
Checked out HEAD:
file:///home/git-svn-bridge/svn/svn-repo/trunk r1
Verify that the result is OK:
$ git branch -a -v
* master 0617252 First commit.
remotes/svn/git-svn 0617252 First commit.
Add the central repository as a remote to the bridge repository and push changes from Subversion to the central repository:
$ git remote add git-central-repo ../git-central-repo-trunk.git
$ git push --all git-central-repo
Counting objects: 4, done.
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 332 bytes, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Unpacking objects: 100% (4/4), done.
To ../git-central-repo-trunk.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Clone the central repository and verify that the Subversion test commit is there:
$ cd ~/git
$ git clone git-central-repo-trunk.git git-central-repo-clone
Cloning into 'git-central-repo-clone'...
done.
$ cd git-central-repo-clone
$ git log
commit 061725282bdccf7f4a8efa66ee34b195ca7070fc
Author: git-svn-bridge <git-svn-bridge>
Date: Wed Aug 15 11:38:57 2012 +0000
First commit.
git-svn-id: file:///home/git-svn-bridge/svn/svn-repo/trunk@1 b4f7b086-5416-...
Create the git hook that blocks non-fast-forward commits in the central repository:
$ cd ~/git/git-central-repo-trunk.git
$ cat > hooks/update << 'EOT'
#!/bin/bash
set -u
refname=$1
shaold=$2
shanew=$3
# don't allow non-fast-forward commits
if [[ $(git merge-base "$shanew" "$shaold") != "$shaold" ]]; then
echo "Non-fast-forward commits to master are not allowed"
exit 1
fi
EOT
$ chmod 755 hooks/update
Create the git hook that triggers synchronization:
$ cat > hooks/post-update << 'EOT'
#!/bin/bash
# trigger synchronization only on commit to master
for arg in "$@"; do
if [[ "$arg" = "refs/heads/master" ]]; then
/home/git-svn-bridge/bin/synchronize-git-svn.sh GIT_HOOK
exit $?
fi
done
EOT
$ chmod 755 hooks/post-update
$ cat > ~/bin/synchronize-git-svn.sh << 'EOT'
# test script to verify that the git hook works properly
echo "Commit from $1 to master" > /tmp/test-synchronize-git-svn
exit 1 # test that error exit does not abort the update
EOT
$ chmod 755 ~/bin/synchronize-git-svn.sh
Test that the hook works:
$ cd ~/git/git-central-repo-clone
$ echo "void do_nothing() { }" >> src/main.cpp
$ git commit -am "Update main.cpp"
[master 2c833e2] Update main.cpp
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
$ git push
Counting objects: 7, done.
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 341 bytes, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Unpacking objects: 100% (4/4), done.
To /home/git-svn-bridge/git/git-central-repo-trunk.git
5b73892..2c833e2 master -> master
$ cat /tmp/test-synchronize-git-svn
Commit from GIT_HOOK to master
Verify that non-fast-forward commits to master are not allowed:
$ echo "void do_nothing() { }" >> src/main.cpp
$ git add src/
$ git commit --amend
[master d2f9a16] Update main.cpp
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
$ git push --force
Counting objects: 7, done.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (4/4), 345 bytes, done.
Total 4 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Unpacking objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Non-fast-forward commits to master are not allowed
remote: error: hook declined to update refs/heads/master
To /home/git-svn-bridge/git/git-central-repo-trunk.git
! [remote rejected] master -> master (hook declined)
error: failed to push some refs to '/home/git-svn-bridge/git/git-central-repo-trunk.git'
$ git reset --hard origin/master
So far, so good. Let's wire in the real synchronization utilities now.
Real synchronization relies on the git-svn-bridge utility written in GoLang (TODO: describe encrypt passwords mechanism in crypt/crypt.go, SECRET constant).
First, create main bridge directory, for example (complete script can be found here: TODO):
$ sudo mkdir /opt/git-bridge
Copy to main directory files and folders:
$ sudo cp ./git-svn-bridge /opt/git-bridge
$ sudo cp ./config.yml /opt/git-bridge
$ sudo cp ./deploy/sync-all.sh /opt/git-bridge
$ sudo cp -r ./gitHookTemplates /opt/git-bridge
Verify that it works:
$ cd /opt/git-bridge
$ sudo chmod 770 ./git-svn-bridge
$ ./git-svn-bridge
A bi-directional bridge that allows work with SVN repo like it is a (almost) orginal GIT repo
Usage:
git-svn-bridge [command]
Available Commands:
add-user Add user information for the repo
completion Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell
create Create repository configuration
help Help about any command
init Initialize repo
pre-sync Checks if sync SVN and GIT repositories is available
sync Sync SVN and GIT repositories
Flags:
-h, --help help for git-svn-bridge
Use "git-svn-bridge [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Create repo for synchronization:
$ ./git-svn-bridge create "https://svn-repo-path" --name TestRepo
Add the git-svn-bridge user for testing (as before, use your actual email address instead of [email protected] and 'git-svn-bridge' as password):
$ ./git-svn-bridge add-user TestRepo "git-svn-bridge"
Adding/overwriting SVN usr: git-svn-bridge
SVN password: passw0rd
SVN password (confirm): passw0rd
e-mail: [email protected]
Git user name: Git-SVN Bridge
Initialized created repo (Utility will create git repo, checkout Subversion repo to bridge, etc. It may take a long time for large repos):
$ ./git-svn-bridge init TestRepo
We are done with the setup now (TODO: cron).