Smart Segment is an optimization-driven segmentation tool designed to enhance business intelligence. It allows for data-driven customer segmentation to improve targeted marketing efforts. By leveraging customer propensities (predicted probabilities with data science) and historical data (actual outcomes), it optimizes segmentation to maximize expected revenue while accounting for costs and penalties. This approach leads to more effective, fine-tuned segments than traditional methods such as naive or percentile-based segmentation.
- Optimized Segmentation: Dynamically adjusts segmentation boundaries to maximize expected revenue, taking into account conversion rates and customer acquisition costs.
- Customizable Functions: Users can define their own revenue and cost functions based on their business needs.
- Data-Driven Adaptation: Automatically adjusts to the actual distribution of customer propensities and conversion behaviors to allocate resources to the most promising segments.
- Merges Small Bins: Merges bins that don't meet a minimum sample size, producing more robust and reliable segments.
Smart Segment is particularly useful for business intelligence teams seeking to enhance marketing ROI by focusing on high-value customer segments. This can also be used as a highly effective tool for Post Campaign / Marketing Campaign Analysis.
Business teams often segment customers to identify conversion patterns and apply different marketing strategies to distinct groups.
Revenue Calculation
Total revenue for each segment is calculated as the sum of revenue from converted customers minus the total acquisition costs for targeting all customers in that segment. While the tool assumes a constant revenue per conversion (which can be customized), acquisition costs vary by segment, reflecting the real-world scenario where higher costs are incurred for more focused marketing.
Customer Propensities
Machine learning models (binary classifiers, for example) predict customer conversion probabilities (propensities) for products or services. Business teams often prioritize customers based on these predicted probabilities rather than binary outcomes, using propensities to target marketing efforts.
Segmentation Strategies
Customers are segmented based on their propensities, and different strategies are applied to various segments. For example:
- Low Propensity Groups: Generic, low-cost marketing strategies.
- High Propensity Groups: Targeted, higher-cost strategies designed to guarantee conversions.
Traditional segmentation strategies typically fall into one of two categories:
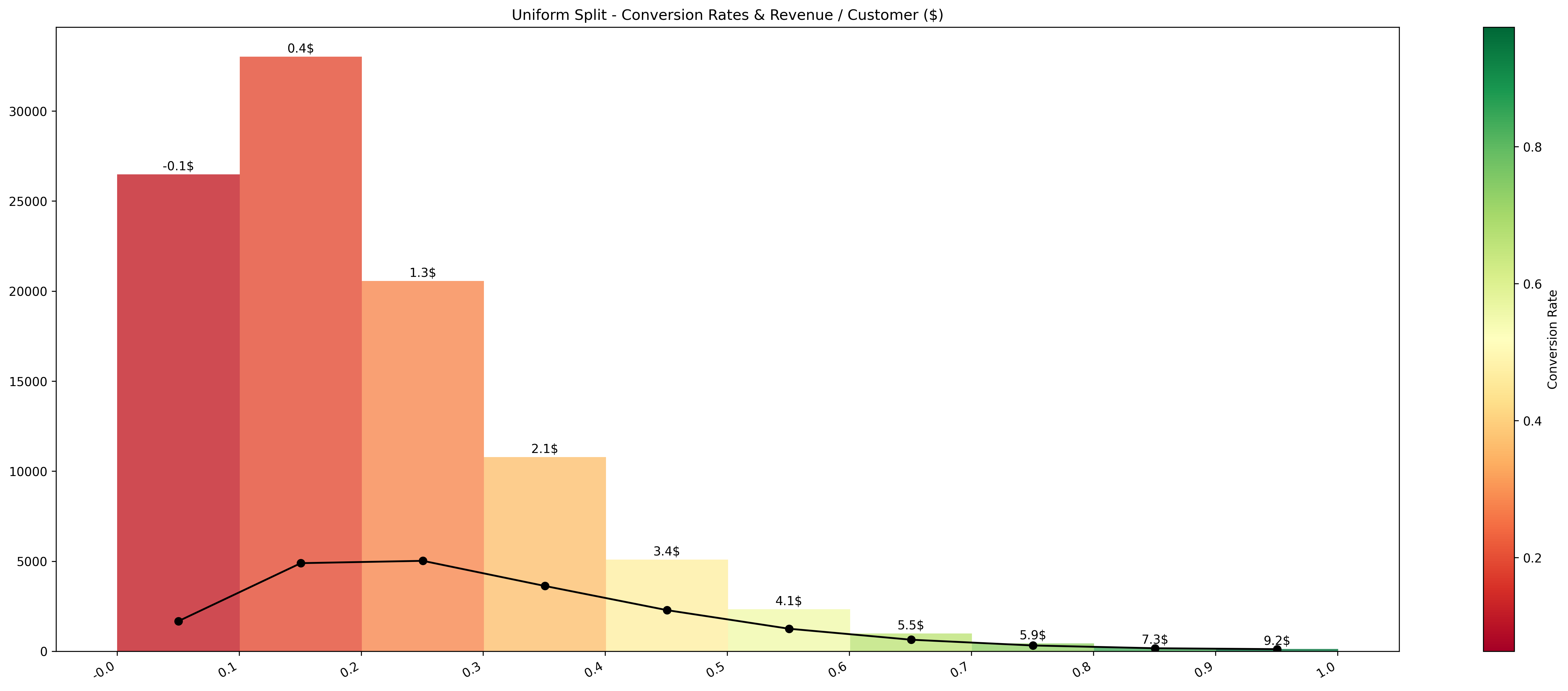
- Uniform: Propensities are split into equal intervals (e.g., 10 bands of 0.1).
- Percentile: Propensities are split based on percentiles (e.g. 10 quantiles).
Smart Segment improves upon these methods by leveraging historical conversion data to optimize segmentation, maximizing revenue while minimizing acquisition costs and balancing segment sizes.
- The optimization is run simulating model propensities with a Gamma distribution to reflect typically skewed data.
- A constant revenue function is used to represent the median customer revenue across segments.
- A increasing cost function (dependent on the split group) to indicate the varying acquisition costs from generic to specific marketing efforts.
This model calculates the optimal segments significantly outperforming conventional approaches across relevant criteria of conversion rates and revenue.
| Metric | Uniform | Percentile | Smart Segment (Optimized) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | (-0.00058, 0.1] | (-0.00058, 0.0535] | (0.0, 0.154] |
| Group 2 | (0.1, 0.2] | (0.0535, 0.0829] | (0.154, 0.264] |
| Group 3 | (0.2, 0.3] | (0.0829, 0.11] | (0.264, 0.406] |
| Group 4 | (0.3, 0.4] | (0.11, 0.138] | (0.406, 0.612] |
| Group 5 | (0.4, 0.5] | (0.138, 0.168] | (0.612, 0.898] |
| Group 6 | (0.5, 0.6] | (0.168, 0.202] | (0.898, 0.915] |
| Group 7 | (0.6, 0.7] | (0.202, 0.244] | (0.915, 0.965] |
| Group 8 | (0.7, 0.8] | (0.244, 0.3] | (0.965, 1.0] |
| Group 9 | (0.8, 0.9] | (0.3, 0.39] | |
| Group 10 | (0.9, 1.0] | (0.39, 1.0] | |
| Best Conversion Rate | 97.48% (0.9-1.0) | 50.92% (0.39-1.0) | 100% (0.965-1.0) |
| Total Revenue ($) | $70,280 | -$542,580 | $216,448 |
| Best Revenue / Customer | $9.24 (0.9-1.0) | -$4.72 (0.39-1.0) | $15.23 (0.915-0.965) |
More metrics (such as group sizes) can be found in the Performance section below with granular statistics in the examples directory.
-
Higher Conversion Rates: Identifies high-potential segments with significantly higher conversion rates compared to naive or percentile methods.
-
Fine-Grained Segmentation: Enables more precise and dynamic customer segmentation based on behavior, supporting personalized marketing strategies.
-
Dynamic Response: Adjusts in real-time to customer behavior, providing more accurate segmentation than fixed-interval methods.
-
Mitigates Underperformance in Small Bins: Automatically merges bins with insufficient samples, preventing small bins from skewing insights.
-
Maximizes Net Revenue: Optimizes both conversion rates and acquisition costs, focusing on total revenue generation.
-
Strategic Focus on High-Value Segments: Prioritizes high-value customer segments for enhanced marketing ROI.
You can install the package from the PyPI repository
pip install smart-segmentThis example shows how to use the find_optimal_bins function to find the optimal segmentation for a marketing campaign:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from smart_segment import find_optimal_bins
# Example data (Simulating imbalanced data with a Gamma distribution)
dists = np.random.gamma(2, 2, 100_000)
data = {'propensity': np.sort(np.clip(dists, 0, 20)/20.0),
'y': np.random.choice([0, 1], 100_000)}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Constant revenue, with varying cost (depending on propensity)
revenue_fn = lambda ix: 30
cost_fn = lambda ix: 2 * ix
# Find optimal bins with custom revenue and cost functions
result = find_optimal_bins(df['propensity'], df['y'], n_bins=10,
revenue_fn=revenue_fn,
cost_fn=cost_fn, penalty_factor=0,
min_samples=10, global_search=True)
best_n_bins, best_cutoffs, max_revenue = result
# Apply the segmentation to the DataFrame
df['optim_global'] = pd.cut(df['propensity'], best_cutoffs, include_lowest=False, duplicates='drop')
print(f"Best number of bins: {best_n_bins}")
print(f"Best cutoffs: {best_cutoffs}")
print(f"Maximum Revenue: {max_revenue}")The first two parameters are:
propensities: Machine Learning / AI model output probabilitiespredictions: Binary outcome on customer activity (or) purchase
The configurable parameters are as follows:
n_bins: Number of bins to split intorevenue_fn: Revenue per customer, function of bin id (starting from 0), usually constant.cost_fn: Cost per customer, function of bin id (starting from 0), usally incremental over segments.penalty_factor: Penalty factor for exploration,> 0value if your search is stuck in a local minimummin_samples: Minimum number of samples in a groupglobal_search: Whether to use the differential evolution or the quantile based algorithm
NOTE: All examples here use global_search=True as the quantile-based method (global_search=False) is identical to the Percentile split.
Tests were conducted to compare the performance of various customer segmentation strategies using the generated propensity groups.
The peformances of this optimized method are compared with the conventional methods used:
- Uniform: Implemented with
pd.cutwith10bins. - Percentile: Implemented with
pd.qcutwith10quantiles.
Here are some key statistics comparing the methods with the graphical and aggregate analysis:
| Metric | Uniform | Percentile | Optimized |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Conversion Rate (%) | 19.98% | 19.98% | 19.98% |
| Lowest Conversion Rate (%) | 6.32% (0.0-0.1) [1,673/26,485] |
3.83% (0.0-0.0535) [383/10,000] |
9.12% (0.0-0.154) [4,154/45,550] |
| Highest Conversion Rate (%) | 97.48% (0.9-1.0) [116/119] |
50.92% (0.39-1.0) [5,092/10,000] |
100% (0.965-1.0) [63/63] |
| Overall Total Revenue ($) | $70,280 | -$542,580 | $216,448 |
| Lowest Total Revenue ($) | -$2,780 (0.0-0.1) [1,673/26,485] |
-$85,100 (0.0-0.0535) [383/10,000] |
$33,520 (0.0-0.154) [4,154/45,550] |
| Highest Total Revenue ($) | $1,100 (0.9-1.0) [116/119] |
-$47,240 (0.39-1.0) [5,092/10,000] |
$62,340 (0.264-0.406) [5,540/17,310] |
| Overall Revenue per Customer ($) | $0.53 | -$2.71 | $0.94 |
| Lowest Revenue per Customer ($) | -$0.105 (0.0-0.1) [1,673/26,485] |
-$8.028 (0.3-0.39) [3,324/10,000] |
$0.736 (0.0-0.154) [4,154/45,550] |
| Highest Revenue per Customer ($) | $9.244 (0.9-1.0) [116/119] |
-$4.724 (0.39-1.0) [5,092/10,000] |
$15.23 (0.915-0.965) [38/39] |
The table below presents key metrics for each segmentation strategy. Each cell contains the following information:
- Metric: Value of the metric
- Band: Range of propensity scores associated with that group formatted as (lower - upper)
- Customer Conversion: Number of customers that converted out of the total customers in the group, formatted as [converted/total]
The optimized model significantly outperforms both the uniform and percentile segmentation strategies across all metrics.
- It exhibits the highest lowest conversion rate, showing that even the least effective groups are yielding a better performance than their counterparts in the other strategies.
- The optimized model leads to a substantial increase in total revenue and revenue per customer, demonstrating its effectiveness in identifying high-value customer segments.
This results in a more efficient targeting strategy, ultimately enhancing overall business revenue.
Granular statistics across bands for each of the strategies can be found in the examples directory.
Here are plots showing the distribution of conversion rates and the revenue / customer across the various methods.
The conversion rates are represented through the following visualizations:
- Bar Chart: Displays the number of customers in each segment.
- Line Chart: Shows the corresponding number of conversions for each segment.
- Color Scale: Illustrates the conversion rate across the different bands.
Additionally, the Revenue per Customer is indicated above each bar in the bar chart, providing a clear view of the economic impact of each segment.
Optimization Algorithm
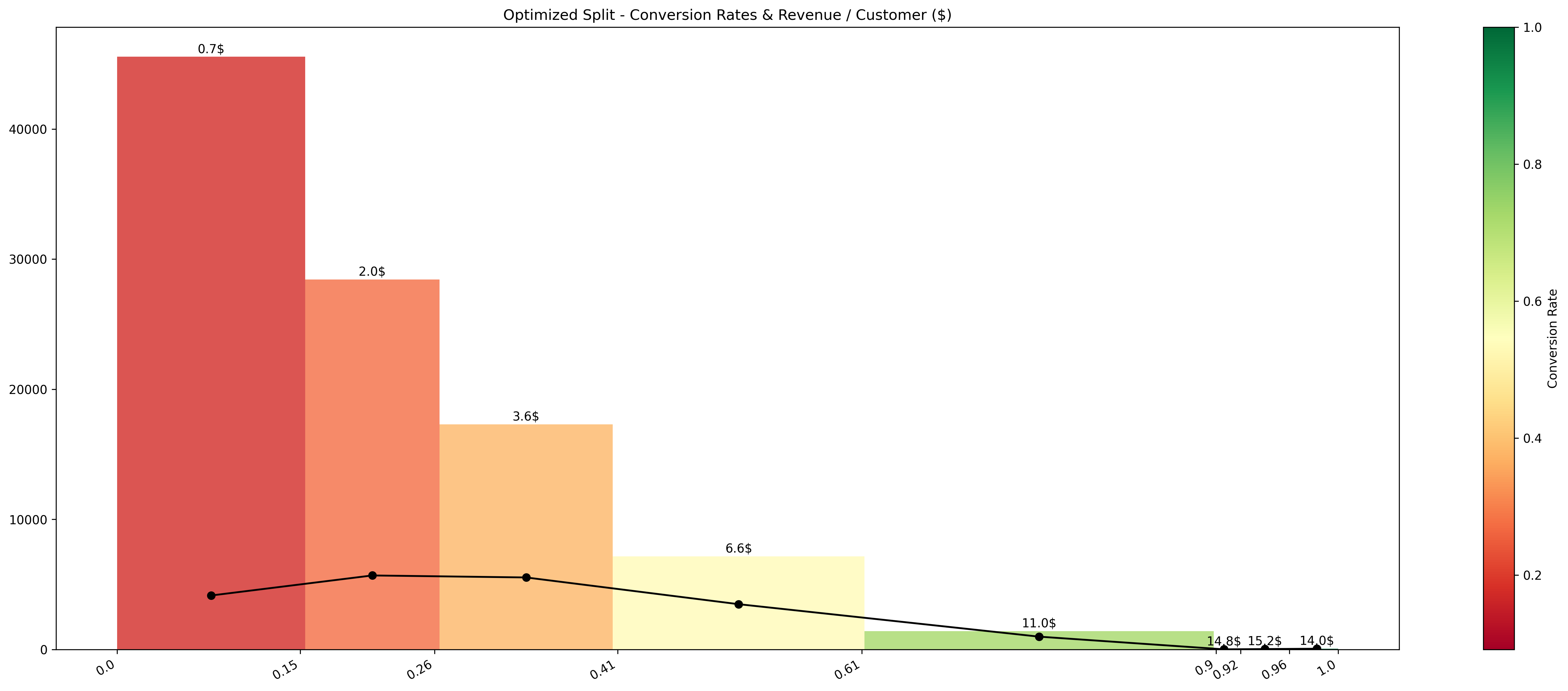 Optimized Segmentation Results
Optimized Segmentation Results
Uniform and Percentile Based old methods
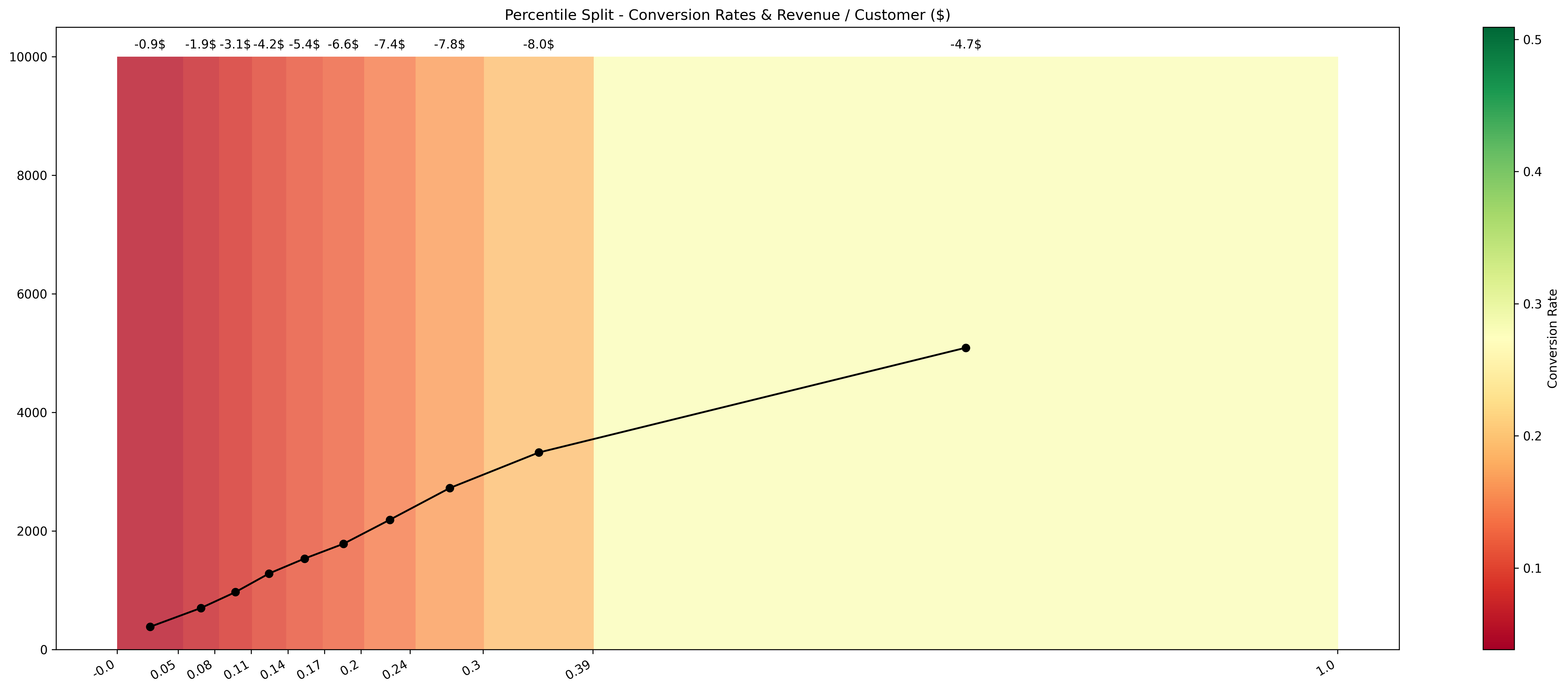 Percentile Segmentation Results
Percentile Segmentation Results
This novel optimization method results in a more effective targeting strategy, enabling businesses to maximize their revenue potential while ensuring that high-value customers are efficiently identified. By balancing customer volume with targeted conversion rates, the optimized approach surpasses traditional methods, yielding superior results in both overall conversions and revenue generation.
The repository is available on Github if you would like to install the latest version of the code.
The repository is organized as follows:
smart_segment/
segmentation.py # Main logic for customer segmentation
optimization.py # Optimization methods for determining cutoffs
utils.py # Utility functions for revenue calculation and bin merging
tests/
test_segmentation.py # Unit tests for the segmentation logic
test_optimization.py # Unit tests for the optimization methods
test_utils.py # Unit tests for utility functions
examples/
Example.html # HTML representation of a Jupyter notebook example
segments.csv # Sample results across various segmentation methods
analyses/
uniform_plot.png # Conversion plot for Uniform splits
uniform_stats.csv # Conversion statistics for Uniform splits
percentile_plot.png # Conversion plot for Percentile splits
percentile_stats.csv # Conversion statistics for Percentile splits
optimized_plot.png # Conversion plot for Optimized splits
optimized_stats.csv # Conversion statistics for Optimized splits
requirements.txt # List of required Python packages
setup.py # Installation script for the package
README.md # Documentation file for the packageNOTE: The plots here are for the Global optimization function. The Quantile based optimization is not included as it is identifical to the Percentile split with the same number of bins.
- Clone this repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/astronights/smart-segment.git
cd smart-segment- Install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt- To install the package in your Python environment:
pip install .To ensure that everything works as expected, you can run the test suite using pytest:
- Install pytest if you don't have it already:
pip install pytest- Run the tests:
pytestThis will execute the test files located in the tests directory and validate that the segmentation tool is functioning correctly.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. You are free to use, modify, and distribute this software as long as the terms of the license are met. For more information, see the LICENSE file.
Contributions are welcome! If you have ideas for improvements or find any issues, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request. Community contributions are encouraged to help make this tool even better.