ℹ️ Created in 2014 by Pierre Raybaut and maintained by the PlotPyStack organization.
The PythonQwt project was initiated to solve -at least temporarily- the obsolescence issue of PyQwt (the Python-Qwt C++ bindings library) which is no longer maintained. The idea was to translate the original Qwt C++ code to Python and then to optimize some parts of the code by writing new modules based on NumPy and other libraries.
The PythonQwt package consists of a single Python package named qwt and of a few other files (examples, doc, ...).
See documentation online or PDF for more details on the library and changelog for recent history of changes.
import numpy as np
from qtpy import QtWidgets as QW
import qwt
app = QW.QApplication([])
# Create plot widget
plot = qwt.QwtPlot("Trigonometric functions")
plot.insertLegend(qwt.QwtLegend(), qwt.QwtPlot.BottomLegend)
# Create two curves and attach them to plot
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)
qwt.QwtPlotCurve.make(x, np.cos(x), "Cosinus", plot, linecolor="red", antialiased=True)
qwt.QwtPlotCurve.make(x, np.sin(x), "Sinus", plot, linecolor="blue", antialiased=True)
# Resize and show plot
plot.resize(600, 300)
plot.show()
app.exec_()The GUI-based test launcher may be executed from Python:
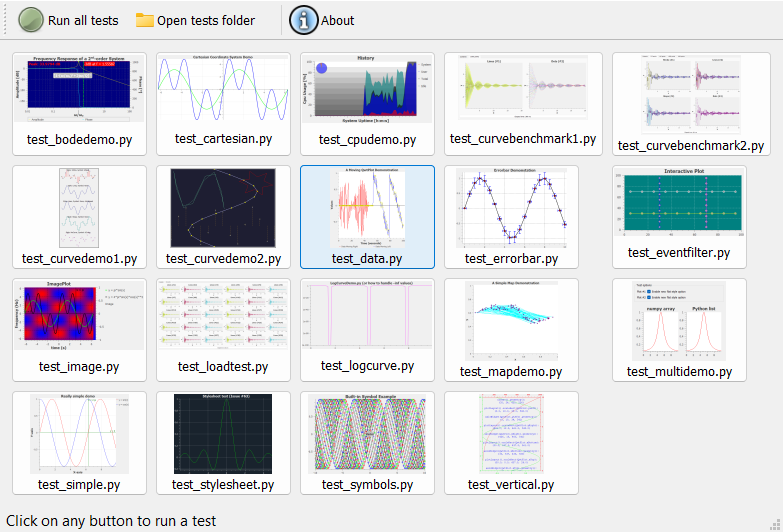
from qwt import tests
tests.run()or from the command line:
PythonQwtTests may also be executed in unattended mode:
PythonQwt-tests --mode unattendedThe qwt package is a pure Python implementation of Qwt C++ library with the following limitations.
The following Qwt classes won't be reimplemented in qwt because more powerful features already exist in guiqwt: QwtPlotZoomer, QwtCounter, QwtEventPattern, QwtPicker, QwtPlotPicker.
Only the following plot items are currently implemented in qwt (the only plot items needed by guiqwt): QwtPlotItem (base class), QwtPlotItem, QwtPlotMarker, QwtPlotSeriesItem and QwtPlotCurve.
See "Overview" section in documentation for more details on API limitations when comparing to Qwt.
The qwt package short-term roadmap is the following:
- Drop support for PyQt4 and PySide2
- Drop support for Python <= 3.8
- Replace
setup.pybypyproject.toml, usingsetuptools(e.g. seeguidata) - Add more unit tests: the ultimate goal is to reach 90% code coverage
The whole PlotPyStack set of libraries relies on the Qt GUI toolkit, thanks to QtPy, an abstraction layer which allows to use the same API to interact with different Python-to-Qt bindings (PyQt5, PyQt6, PySide2, PySide6).
Compatibility table:
| PythonQwt version | PyQt5 | PyQt6 | PySide2 | PySide6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.16 and earlier | ✅ | ❌ | ||
| Latest | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
- Python >=3.9
- QtPy >= 1.3 (and a Python-to-Qt binding library, see above)
- NumPy >= 1.5
- coverage, pytest (for unit tests)
- sphinx (for documentation generation)
From the source package:
python -m build- Copyright © 2002 Uwe Rathmann, for the original Qwt C++ code
- Copyright © 2015 Pierre Raybaut, for the Qwt C++ to Python translation and optimization
- Copyright © 2015 Pierre Raybaut, for the PythonQwt specific and exclusive Python material
- Copyright © 2003-2009 Gerard Vermeulen, for the original PyQwt code
- Copyright © 2015 Pierre Raybaut, for the PyQt5/PySide port and further developments (e.g. ported to PythonQwt API)
The qwt Python package was partly (>95%) translated from Qwt C++ library: the associated code is distributed under the terms of the LGPL license. The rest of the code was either wrote from scratch or strongly inspired from MIT licensed third-party software.
See included LICENSE file for more details about licensing terms.