SyntaxNet is a neural-network Natural Language Processing framework for TensorFlow released by Google. It is one of the most powerful and accurate parsers in the world today.
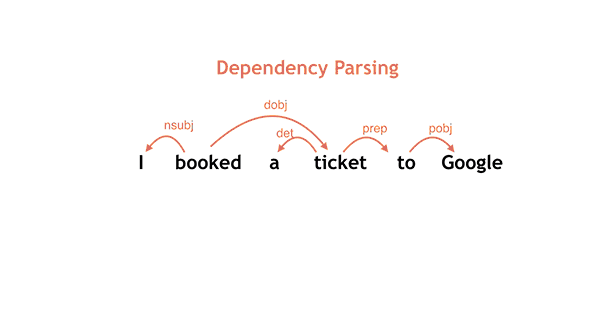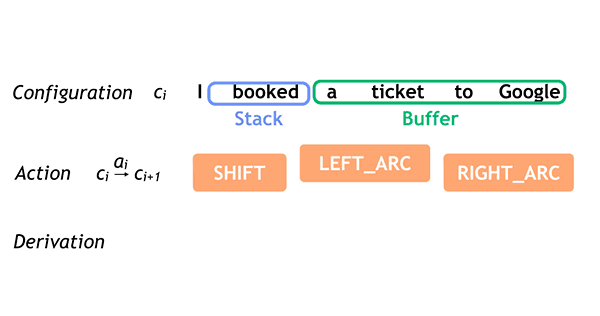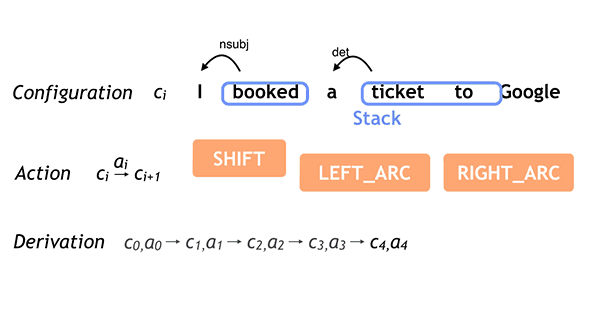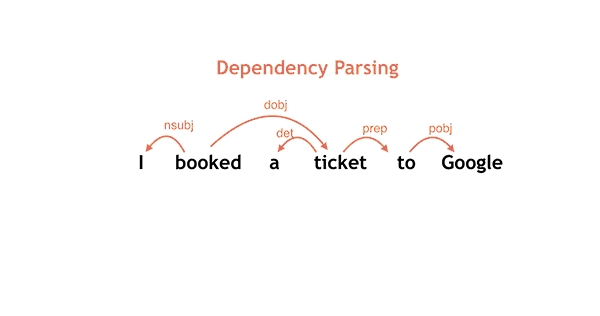
Given a sentence as input, SyntaxNet tags each word with a part-of-speech (POS) tag that describes the word's syntactic function, and it determines the syntactic relationships between words in the sentence, represented in the dependency parse tree. These syntactic relationships are directly related to the underlying meaning of the sentence in question.
There are two ways to actually build and run SyntaxNet:
- Building from source.
- Using Docker.
You can build SyntaxNet by following the nice guide provided in the main SyntaxNet github branch.
Building from source is doable but its computationally expensive and can result in few bugs while building if we mess up with the steps provided. Hence a clean way to build SyntaxNet is by using Docker. Here's what we are going to require :
- A 64-bit computer with at least 2 GB of RAM
- The latest version of Docker
- Ubuntu (I have only tested it on Ubuntu as of yet.)
- Pulling the Docker Image
There could be other SyntaxNet images, but for demonstration, we'll be pulling an image created by brianlow.
docker pull brianlow/syntaxnet-docker
Depending on the speed of your network connection, you might have to wait for a while because the image is about 1GB.
- Once the SyntaxNet image is installed, you can now test it. You need to create a new container using it and run a Bash shell on it.
docker run --name mcparseface --rm -i -t brianlow/syntaxnet-docker bash
- Parsey McParseface, the pre-trained model that comes with SyntaxNet is powerful but slightly complicated. Thankfully, we can use the shell script
demo.shprovided with SyntaxNet itself. All you need to do is pass an English sentence to it.
echo "I found a website to post AI tutorials ." | syntaxnet/demo.sh
It generates the folling dependency parse tree as output:
Input: I found a website to post AI tutorials .
Parse:
found VBD ROOT
+-- I PRP nsubj
+-- website NN dobj
| +-- a DT det
| +-- post VB infmod
| +-- to TO aux
| +-- tutorials NNS dobj
| +-- AI NNP nn
+-- . . punct
Instead of running the shell script, the code in this repo shows you how to use SyntaxNet. I have built a Python wrapper which calls the shell script and runs SyntaxNet.
- Usage
python main.py '<some-english-text>.'
- Output :
Dependency tree:
Input: I found a website to post AI tutorials .
Parse:
found VBD ROOT
+-- I PRP nsubj
+-- website NN dobj
| +-- a DT det
| +-- post VB infmod
| +-- to TO aux
| +-- tutorials NNS dobj
| +-- AI NNP nn
+-- . . punct
Paraphrased sentence :
I established a website to post AI tutorials.
Basically what this script does is:
- it parses the input sentence
- finds the root verb from the sentence using the dependency tree created by SyntaxNet
- finds a synonym of the root verb using the nltk library
- replaces the original verb with the synonym
You'll have to run pip install nltk to install nltk. The Verb folder contains the code to find out the tense of the root verb so that its synonym can be coded to be the same tense, in order to keep the meaning of the sentence intact.
Thus, this code is a pretty simple approach to use SyntaxNet for basic paraphrasing. It's just a demo and it doesn't always find the paraphrase and hence in such cases returns the same sentence. But our main goal is to run SyntaxNet and leverage its capabilities to find the proper context in a given text and use it to find important pieces of text like the Root Word, Dependent Object etc.
-
To learn more about all the Part of Speech Tags that appear in the SyntaxNet output, please visit here.
-
And to understand the dependencies that SyntaxNet tries to find within a sentence, please visit here.
These links would definitely help you to understand the output of SyntaxNet better. Feel free to improvise!