Note: this post is not about how to use Shadowsocks or how it works. It's about a possibility that we can automate the process. This post assume you have some basic knowledge about Shadowsocks.
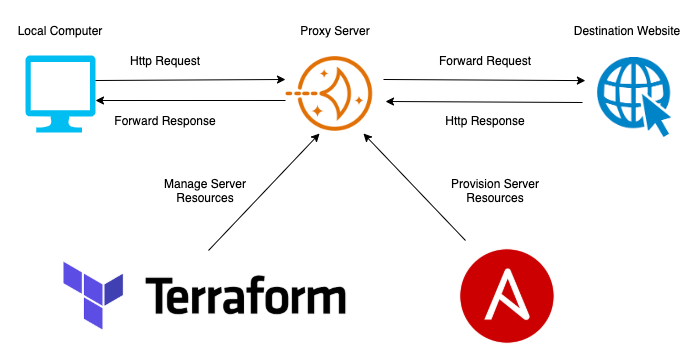
Shadowsocks is a proxy server which can be used as a bridge to redirect your internet traffic. It's secure, fast and cross platform. I will be configuring Shadowsocks server application on an AWS Lightsail instance and using ShadowsocksX-NG as client to communicate with Shadowsocks server.
The idea to automate building VPN has been in my mind for a long time. I was struggled to get free Internet access when living in China. I used to manually setup VPN, but from time to time, the server's IP was banned for reasons I don't know. The thing I know is someone is "watching" us. Anytime my server was banned, I need to redo the work again and again.
Before I know the tool Terraform, I don't know how to spin up a server automatically. As an Infrastructure as Code tool, Terraform can work with all mainstream cloud providers to automate build cloud infrastructure. In my use case, it is very simple: define my resources and ask Terraform to spin up and configure my resources, like instance configuration, static ip creation and attachment. Here is a good guidance of how to user Terraform to spin up an AWS Lightsail instance.
The instance configuration can be found under terraform/main.tf file. It defines a few resources: lightsail instance, static ip and attaching static ip to instance. The reason why we need to static ip(AKA public ip) is we need to use this IP later when configuring the ShadowsocksX-NG client.
I have put variables in terraform/terraform.tfvars file. If you want to use this framework, please fill in your own information:
access_key_aws: this is your AWS access keysecret_key_aws: this is your AWS secret keyprivate_key_path: this is your lightsail default private key path, I downloaded it from lightsail page under my account. Note: if you haven't create any lightsail instance before, you may need to manually create an instance and find the default private key. This key will be used for ssh connection.
Once we spin up the instance with Terraform, next Ansible comes into play. You may ask why do I use Ansible? Ansible is a provision tool developed by RedHat. As a good practice of Infrastructure as Code, we can programmatically automate the provision phase. The code structure is more human readable than pure scripting language like shell/bash. Also, we can define roles, which can be reused in other places.
The provision configuration can be found in ansible-playbook/main.yml, it includes 4 main roles:
install-ss-libev-- this role is to download and install Shadowsocks-libev. This is a lightweight server application.enable-simple-obfs-- this role is to download and enable simple obfs, which is a tool to obfuscate internet traffic, so that your traffic looks normal as others.copy-file-- this role is to upload your local config file to your remote instance. In theansible-playbook/config.json, you can find all basic configuration required for Shadowsocks proxy server. Note: you need to change the password in theconfig.json, so that you don't use my default passwordjeffinbao.start-ss-libev-- this role is to start Shadowsocks-libev service.
- I set
server_port:443inconfig.json. Since this port is not open by default when instance is spun up, we need to open this port. Terraform doesn't support opening Lightsail port for now, so using AWS CLI is a workaround. We can have alocal-execprovisioner after lightsail instance is up and running. Note: After you runterraform apply, if you see error likeinstance not exist, check your default region information in local AWS CLI config file. It should point to the region where your Lightsail instance is created. For me, the region isap-northeast-1. - At first, I am not able to integrate Ansible with Terraform, because I can't find public ip of my instance, and Ansible is not able to reach my instance. After some research, I find
${self.public_ip_address}is the correct way to get public ip address for Ansible to use. Here is a good answer for this problem. - Before running ansible playbook against remote instance, we need to make sure the ssh connection is available. That's why I add
connectionblock before otherlocal-execcommands. If we directly run ansible playbook without making sure the ssh connection is on, we will haveConnection Refusederror.
Overall, Terraform's support for AWS Lightsail is not comprehensive. For example, we still need to use AWS CLI to open a port. However, the workaround is acceptable, I can still achieve my goal to automate the building of a dedicated VPN. Therefore, I am fine with what it has currently.
- I use Mac to run Terraform and Ansible script. If you are Windows user, things are little tricky. You need to make some minor changes to
main.tf. Then, run Ansible scripts in WSL(Windows Subsystem in Linux), because Ansible doesn't support native Windows. - Install
Terraform,AnsibleandAWS CLI V2 - Configure
AWS CLIas per documentation
-
Download your ssh default private key from Lightsail page under you
Account/SSH keys. If you don't find your ssh key, maybe you need to manually create an instance for the first time. After you download your private key, it's better to put into~/.sshfolder. -
git clonemy repository -
Change the
passwordinansible-playbook/config.jsonto your own password. -
cdintolightsail-ss/terraformfolder -
Modify
terraform.tfvarsfile according to your own AWS account information. -
Run
terraform initto initialize terraform -
Run
terraform applyand wait for the command promt, then typeyes. Then, wait for the automation process finishes. In the end, a public ip will be printed in the terminal. You can use that ip to configure ShadowsocksX-NG client. -
If later you want to destroy the instance, run
terraform destroy. Terraform will take care of the state and destroy the resources for you.