- Oracle VM Virtualbox
- Vagrant
- Vagrant plugins Execute below command in your computer to install hostmanager plugin
$ vagrant plugin install vagrant-hostmanager
- Git bash or equivalent editor
- Clone source code.
- Cd into the repository.
- Switch to the main branch.
- cd into vagrant/Manual_Provisioning
Bring up vm’s
$ vagrant up
NOTE: Bringing up all the vm’s may take a long time based on various factors. If vm setup stops in the middle run “vagrant up” command again.
INFO: All the vm’s hostname and /etc/hosts file entries will be automatically updated.
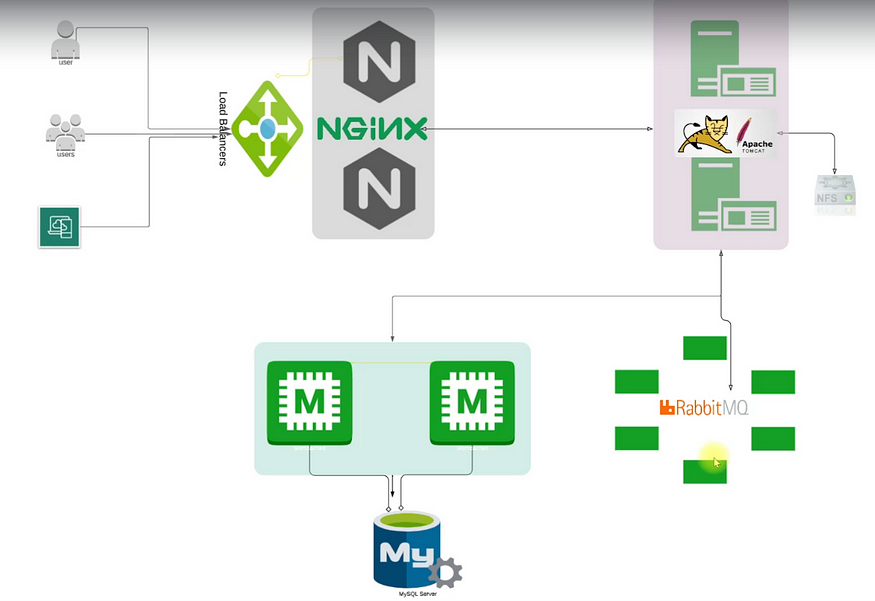
Services
1. Nginx => Web Service
2. Tomcat => Application Server
3. RabbitMQ => Broker/Queuing Agent
4. Memcache => DB Caching
5. ElasticSearch => Indexing/Search service
6. MySQL => SQL Database
1. MySQL (Database SVC)
2. Memcache (DB Caching SVC)
3. RabbitMQ (Broker/Queue SVC)
4. Tomcat (Application SVC)
5. Nginx (Web SVC)
Login to the db vm
$ vagrant ssh db01
$ sudo -i
Verify Hosts entry, if entries missing update the it with IP and hostnames
# cat /etc/hosts
Update OS with latest patches
# yum update -y
Set Repository
# yum install epel-release -y
Install Maria DB Package
# yum install git mariadb-server -y
Starting & enabling mariadb-server
# systemctl start mariadb
# systemctl enable mariadb
RUN mysql secure installation script.
# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: Set db root password, I will be using admin123 as password
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into aproduction environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Set DB name and users.
# mysql -u root -padmin123
mysql> create database accounts;```
mysql> grant all privileges on accounts.* TO 'admin'@'%' identified by 'admin123';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> exit;
Download Source code & Initialize Database.
# git clone -b main https://github.com/Amit-unchartered/VProfile_Project.git
# cd VProfile_Project
# mysql -u root -padmin123 accounts < src/main/resources/db_backup.sql
# mysql -u root -padmin123 accounts
mysql> show tables;
mysql> exit;
Restart mariadb-server
# systemctl restart mariadb
Starting the firewall and allowing the mariadb to access from port no. 3306
# systemctl start firewalld
# systemctl enable firewalld
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --reload
# systemctl restart mariadb
Login to the Memcache vm
$ vagrant ssh mc01
Verify Hosts entry, if entries missing update the it with IP and hostnames
# cat /etc/hosts
Update OS with latest patches
# yum update -y
Install, start & enable memcache on port 11211
# sudo dnf install epel-release -y
# sudo dnf install memcached -y
# sudo systemctl start memcached
# sudo systemctl enable memcached
# sudo systemctl status memcached
# sed -i 's/127.0.0.1/0.0.0.0/g' /etc/sysconfig/memcached
# sudo systemctl restart memcached
Starting the firewall and allowing the port 11211 to access memcache
# firewall-cmd --add-port=11211/tcp
# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
# firewall-cmd --add-port=11111/udp
# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
# sudo memcached -p 11211 -U 11111 -u memcached -d
Login to the RabbitMQ vm
$ vagrant ssh rmq01
Verify Hosts entry, if entries missing update the it with IP and hostnames
# cat /etc/hosts
Update OS with latest patches
# yum update -y
Set EPEL Repository
# yum install epel-release -y
Install Dependencies
# sudo yum install wget -y
# cd /tmp/
# dnf -y install centos-release-rabbitmq-38
# dnf --enablerepo=centos-rabbitmq-38 -y install rabbitmq-server
# systemctl enable --now rabbitmq-server
Setup access to user test and make it admin
# sudo sh -c 'echo "[{rabbit, [{loopback_users, []}]}]." > /etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.config'
# sudo rabbitmqctl add_user test test
# sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags test administrator
# sudo systemctl restart rabbitmq-server
Starting the firewall and allowing the port 5672 to access rabbitmq
# firewall-cmd --add-port=5672/tcp
# firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
# sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-server
# sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
# sudo systemctl status rabbitmq-server
Login to the tomcat vm
$ vagrant ssh app01
Verify Hosts entry, if entries missing update the it with IP and hostnames
# cat /etc/hosts
Update OS with latest patches
# yum update -y
Set Repository
# yum install epel-release -y
Install Dependencies
# dnf -y install java-11-openjdk java-11-openjdk-devel
# dnf install git maven wget -y
Change dir to /tmp
# cd /tmp/
Download & Tomcat Package
# wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.75/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.75.tar.gz
# tar xzvf apache-tomcat-9.0.75.tar.gz
Add tomcat user
# useradd --home-dir /usr/local/tomcat --shell /sbin/nologin tomcat
Copy data to tomcat home dir
# cp -r /tmp/apache-tomcat-9.0.75/* /usr/local/tomcat/
Make tomcat user owner of tomcat home dir
# chown -R tomcat.tomcat /usr/local/tomcat
Setup systemctl command for tomcat Create tomcat service file
# vi /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Update the file with below content
[Unit]
Description=Tomcat
After=network.target
[Service]
User=tomcat
WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/tomcat
Environment=JRE_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jre
Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jre
Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat
Environment=CATALINE_BASE=/usr/local/tomcat
ExecStart=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/catalina.sh run
ExecStop=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
SyslogIdentifier=tomcat-%i
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload systemd files
# systemctl daemon-reload
Start & Enable service
# systemctl start tomcat
# systemctl enable tomcat
Enabling the firewall and allowing port 8080 to access the tomcat
# systemctl start firewalld
# systemctl enable firewalld
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --reload
Download Source code
# git clone -b main https://github.com/Amit-unchartered/VProfile_Project.git
Update configuration
# cd VProfile_Project
# vim src/main/resources/application.properties
# Update file with backend server details
Build code Run below command inside the repository (VProfile_Project)
# mvn install
Deploy artifact
# systemctl stop tomcat
# rm -rf /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT*
# cp target/vprofile-v2.war /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT.war
# systemctl start tomcat
# chown tomcat.tomcat /usr/local/tomcat/webapps -R
# systemctl restart tomcat
Login to the Nginx vm
$ vagrant ssh web01
$ sudo -i
Verify Hosts entry, if entries missing update the it with IP and hostnames
# cat /etc/hosts
Update OS with latest patches
# apt update
# apt upgrade
Install nginx
# apt install nginx -y
Create Nginx conf file
# vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/vproapp
Update with below content
upstream vproapp {
server app01:8080;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://vproapp;
}
}
Remove default nginx conf
# rm -rf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Create link to activate website
# ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/vproapp /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/vproapp
Restart Nginx
# systemctl restart nginx