K510 nncase developer Guide
文档版本:V1.0.0
发布日期:2022-03-07
免责声明 您购买的产品、服务或特性等应受北京嘉楠捷思信息技术有限公司(“本公司”,下同)商业合同和条款的约束,本文档中描述的全部或部分产品、服务或特性可能不在您的购买或使用范围之内。除非合同另有约定,本公司不对本文档的任何陈述、信息、内容的准确性、可靠性、完整性、营销型、特定目的性和非侵略性提供任何明示或默示的声明或保证。除非另有约定,本文档仅作为使用指导的推理。 由于产品版本升级或其他原因,本文档内容将可能在未经任何通知的情况下,不定期进行更新或修改。
商标声明
“ ”、“Canaan”图标、嘉楠和嘉楠其他商标均为北京嘉楠捷思信息技术有限公司的商标。本文档可能提及的其他所有商标或注册商标,由各自的所有人拥有。
”、“Canaan”图标、嘉楠和嘉楠其他商标均为北京嘉楠捷思信息技术有限公司的商标。本文档可能提及的其他所有商标或注册商标,由各自的所有人拥有。
版权所有©2022北京嘉楠捷思信息技术有限公司 本文档仅适用K510平台开发设计,非经本公司书面许可,任何单位和个人不得以任何形式对本文档的部分或全部内容传播。
北京嘉楠捷思信息技术有限公司 网址:canaan-creative.com 商务垂询:[email protected]
免责声明 您购买的产品、服务或特性等应受嘉楠公司商业合同和条款的约束,本文档中描述的全部或部分产品、服务或特性可能不在您的购买或使用范围之内。除非合同另有约定,嘉楠公司对本文档内容不做任何明示或默示的声明或保证。由于产品版本升级或其他原因,本文档内容会不定期进行更新。除非另有约定,本文档仅作为使用指导,本文档中的所有陈述、信息和建议不构成任何明示或暗示的担保。
商标声明 Canaan图标、嘉楠和嘉楠其他商标均为嘉楠捷思信息技术有限公司的商标,并归嘉楠股份有限公司所有。本文档提及的其他所有商标或注册商标,由各自的所有人拥有。
版权所有©嘉楠股份有限公司 本文档仅适用K510平台开发设计,非经本公司书面许可,任何单位和个人不得擅自摘抄、复制本文档内容的部分或全部应用于非K510平台开发应用。
[toc]
本文档为nncase/K510 compiler的使用说明文档,提供给用户如何安装nncase, 如何调用compiler APIs编译神经网络模型和runtime APIs编写AI推理程序.
本文档面向的人员:
- 软件开发人员
- 技术支持人员
| 术语 | 解释/全称 |
|---|---|
| PTQ | Post-training quantization, 训练后量化 |
| MSE | mean-square error, 均方误差 |
| 版本号 | 修改说明 | 修改者 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.8.0 | nncase_v1.4.0 | 张扬/张济昭 | 2022-3-3 |
| V0.7.0 | nncase_v1.3.0 | 张扬 | 2022-1-28 |
| V0.6.0 | nncase_v1.2.0 | 张扬 | 2021-12-31 |
| V0.5.0 | nncase_v1.1.0 | 张扬 | 2021-12-3 |
| V0.4.0 | nncase_v1.0.0 | 张扬/杨浩琪/郑启航 | 2021-10-29 |
| V0.3.0 | nncase_v1.0.0_rc1 | 张扬/杨浩琪 | 2021-9-28 |
| V0.2.0 | nncase_v1.0.0_beta2 | 张扬/杨浩琪 | 2021-9-2 |
| V0.1.0 | nncase_v1.0.0_beta1 | 张扬/杨浩琪 | 2021-8-31 |
说明:初始版本为V0.1.0,Release前的编辑过程中可调整次/修订版本号。Release至产品的初版为V1.0.0。
nncase是一个为 AI 加速器设计的神经网络编译器, 目前支持的 target有cpu/K210/K510等
nncase提供的功能
- 支持多输入多输出网络,支持多分支结构
- 静态内存分配,不需要堆内存
- 算子合并和优化
- 支持 float 和uint8/int8量化推理
- 支持训练后量化,使用浮点模型和量化校准集
- 平坦模型,支持零拷贝加载
nncase支持的神经网络框架
- tflite
- onnx
- caffe
- paddle
-
简单的端到端部署
减少与用户交互的次数。用户使用和部署 CPU、GPU 模型相同的工具和流程就可完成在 KPU 上的部署。无需设置复杂的参数,降低使用门槛,加速 AI 算法的迭代周期。
-
充分利用现有AI生态
依附于业内广泛使用的框架。一方面可以提高知名度,享受到成熟生态的红利。另一方面可以降低中小开发商的开发成本,业界成熟的模型和算法可以直接部署。
-
充分发挥硬件性能
NPU的优势就在于效能比CPU、GPU高,DL Compiler必须能够充分发挥硬件的性能。Compiler还需要对新模型结构自适应地优化性能,因此需要在手工优化之外探索一条新的自动优化技术。
-
可扩展性和可维护性
能够支持 K210、K510 以及将来芯片的 AI 模型部署。需要在架构层面提供一定的可扩展性。增加新 Target 的代价要小,能够尽可能复用更多的模块。加快新产品的研发速度实现 DL Compiler 的技术积累。
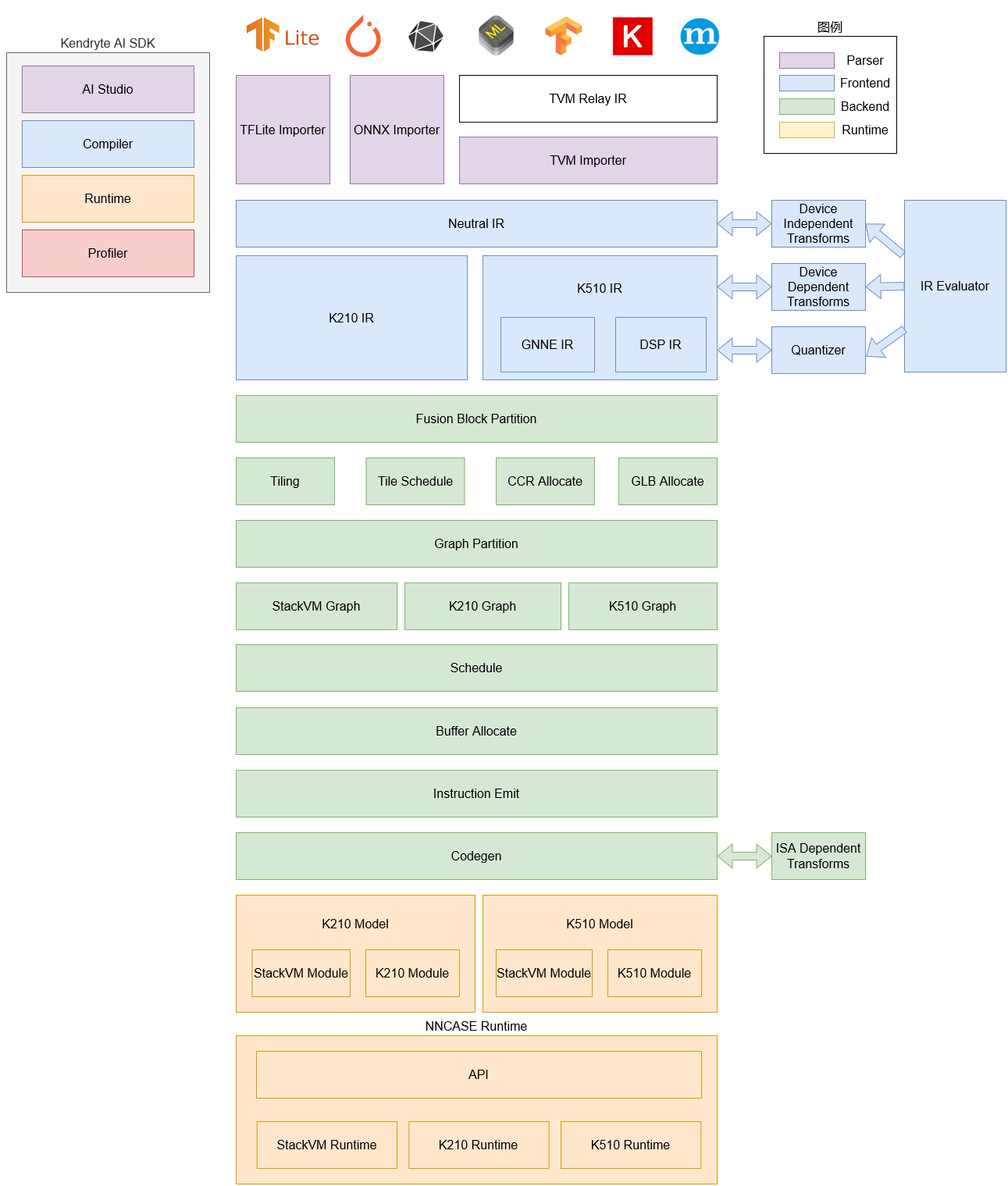
nnncase软件栈目前包括compiler和runtime两部分。
Compiler: 用于在PC上编译神经网络模型,最终生成kmodel文件。主要包括importer, IR, Evaluator, Quantize, Transform优化, Tiling, Partition, Schedule, Codegen等模块。
- Importer: 将其它神经网络框架的模型导入到nncase中
- IR: 中间表示, 分为importer导入的Neutral IR(设备无关)和Neutral IR经lowering转换生成的Target IR(设备相关)
- Evaluator: Evaluator提供IR的解释执行能力,常被用于Constant Folding/PTQ Calibration等场景
- Transform: 用于IR转换和图的遍历优化等
- Quantize: 训练后量化, 对要量化的tensor加入量化标记, 根据输入的校正集, 调用 Evaluator进行解释执行, 收集tensor的数据范围, 插入量化/反量化结点, 最后优化消除不必要的量化/反量化结点等
- Tiling: 受限于NPU较低的存储器容量,需要将大块计算进行拆分. 另外, 计算存在大量数据复用时选择Tiling参数会对时延和带宽产生影响
- Partition: 将图按ModuleType进行切分, 切分后的每个子图会对应RuntimeModule, 不同类型的RuntimeModule对应不同的Device(cpu/K510)
- Schedule: 根据优化后图中的数据依赖关系生成计算顺序并分配Buffer
- Codegen: 对每个子图分别调用ModuleType对应的codegen,生成RuntimeModule
Runtime: 集成于用户App, 提供加载kmodel/设置输入数据/KPU执行/获取输出数据等功能.
- Ubuntu 18.04/20.04
软件环境要求如下表所示:
| 序号 | 软件资源 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Python | Python 3.6/3.7/3.8/3.9/3.10 |
| 2 | pip3 | pip3版本 >= 20.3 |
| 3 | onnx | onnx版本为1.9.0 |
| 4 | onnx-simplifier | onnx-simplifier版本为0.3.6 |
| 5 | onnxoptimizer | onnxoptimizer版本为0.2.6 |
硬件环境要求如下表所示:
| 序号 | 硬件资源 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | K510 EVB | EVB板 |
nncase工具链compiler部分包括nncase和K510 compiler, 均需安装相应wheel包.
- nncase wheel包在nncase github发布, 支持Python 3.6/3.7/3.8/3.9/3.10, 用户可根据操作系统和Python选择相应版本下载 .
- K510 compiler wheel包在nncase sdk的x86_64目录下, 不依赖Python版本, 可直接安装
用户若没有Ubuntu环境, 可使用nncase docker(Ubuntu 20.04 + Python 3.8)
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk
$ docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/kendryte/nncase:latest
$ docker run -it --rm -v `pwd`:/mnt -w /mnt registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/kendryte/nncase:latest /bin/bash -c "/bin/bash"下面以Ubuntu 20.04 + Python 3.8安装nncase为例
root@2b11cc15c7f8:/mnt# wget -P x86_64 https://github.com/kendryte/nncase/releases/download/v1.4.0/nncase-1.4.0.20220303-cp38-cp38-manylinux_2_24_x86_64.whl
root@2b11cc15c7f8:/mnt# pip3 install x86_64/*.whlnncase提供了Python APIs, 用于在PC上编译/推理深度学习模型.
目前编译模型API支持tflite/onnx/caffe等深度学习框架.
CompileOptions类, 用于配置nncase编译选项
py::class_<compile_options>(m, "CompileOptions")
.def(py::init())
.def_readwrite("target", &compile_options::target)
.def_readwrite("quant_type", &compile_options::quant_type)
.def_readwrite("w_quant_type", &compile_options::w_quant_type)
.def_readwrite("use_mse_quant_w", &compile_options::use_mse_quant_w)
.def_readwrite("preprocess", &compile_options::preprocess)
.def_readwrite("swapRB", &compile_options::swapRB)
.def_readwrite("mean", &compile_options::mean)
.def_readwrite("std", &compile_options::std)
.def_readwrite("input_range", &compile_options::input_range)
.def_readwrite("input_shape", &compile_options::input_shape)
.def_readwrite("letterbox_value", &compile_options::letterbox_value)
.def_readwrite("input_type", &compile_options::input_type)
.def_readwrite("output_type", &compile_options::output_type)
.def_readwrite("input_layout", &compile_options::input_layout)
.def_readwrite("output_layout", &compile_options::output_layout)
.def_readwrite("is_fpga", &compile_options::is_fpga)
.def_readwrite("dump_ir", &compile_options::dump_ir)
.def_readwrite("dump_asm", &compile_options::dump_asm)
.def_readwrite("dump_quant_error", &compile_options::dump_quant_error)
.def_readwrite("dump_dir", &compile_options::dump_dir)
.def_readwrite("benchmark_only", &compile_options::benchmark_only);各属性说明如下
| 属性名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| target | string | 是 | 指定编译目标, 如'k210', 'k510' |
| quant_type | string | 否 | 指定数据量化类型, 如'uint8', 'int8' |
| w_quant_type | string | 否 | 指定权重量化类型, 如'uint8', 'int8', 默认为'uint8' |
| use_mse_quant_w | bool | 否 | 指定权重量化时是否使用最小化均方误差(mean-square error, MSE)算法优化量化参数 |
| preprocess | bool | 否 | 是否开启前处理,默认为False |
| swapRB | bool | 否 | 是否交换RGB输入数据的红和蓝两个通道(RGB-->BGR或者BGR-->RGB),默认为False |
| mean | list | 否 | 前处理标准化参数均值,默认为[0, 0, 0] |
| std | list | 否 | 前处理标准化参数方差,默认为[1, 1, 1] |
| input_range | list | 否 | 输入数据反量化后对应浮点数的范围,默认为[0,1] |
| input_shape | list | 否 | 指定输入数据的shape,input_shape的layout需要与input layout保持一致,输入数据的input_shape与模型的input shape不一致时会进行letterbox操作(resize/pad等) |
| letterbox_value | float | 否 | 指定前处理letterbox的填充值 |
| input_type | string | 否 | 指定输入数据的类型, 默认为'float32' |
| output_type | string | 否 | 指定输出数据的类型, 如'float32', 'uint8'(仅用于指定量化情况下), 默认为'float32' |
| input_layout | string | 否 | 指定输入数据的layout, 如'NCHW', 'NHWC'. 若输入数据layout与模型本身layout不同, nncase会插入transpose进行转换 |
| output_layout | string | 否 | 指定输出数据的layout, 如'NCHW', 'NHWC'. 若输出数据layout与模型本身layout不同, nncase会插入transpose进行转换 |
| is_fpga | bool | 否 | 指定kmodel是否用于fpga, 默认为False |
| dump_ir | bool | 否 | 指定是否dump IR, 默认为False |
| dump_asm | bool | 否 | 指定是否dump asm汇编文件, 默认为False |
| dump_quant_error | bool | 否 | 指定是否dump量化前后的模型误差 |
| dump_dir | string | 否 | 前面指定dump_ir等开关后, 这里指定dump的目录, 默认为空字符串 |
| benchmark_only | bool | 否 | 指定kmodel是否只用于benchmark, 默认为False |
- input range为浮点数的范围,即如果输入数据类型为uint8,则input range为反量化到浮点之后的范围(可以不为0~1),可以自由指定.
- input_shape需要按照input_layout进行指定,以[1,224,224,3]为例,如果input_layout为NCHW,则input_shape需指定为[1,3,224,224];input_layout为NHWC,则input_shape需指定为[1,224,224,3];
- mean和std为浮点数进行normalize的参数,用户可以自由指定;
- 使用letterbox功能时,需要限制输入size在1.5MB内,单channel的size在0.75MB内;
例如:
- 输入数据类型设定为uint8,input_range设定为[0,255],则反量化的作用只是进行类型转化,将uint8的数据转化为float32,mean和std参数仍然可以按照0~255的数据进行指定.
- 输入数据类型设定为uint8,input_range设定为[0,1],则会将定点数反量化为范围为[0,1]的浮点数, mean 和std需要按照新的浮点数范围进行指定。
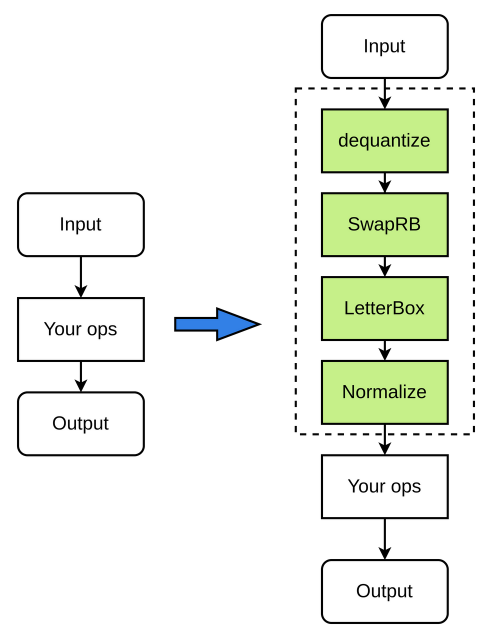
前处理流程如下(图中绿色节点皆为可选):
实例化CompileOptions, 配置各属性的值
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = target
compile_options.input_type = 'float32' # or 'uint8' 'int8'
compile_options.preprocess = True # if False, the args below will unworked
compile_options.swapRB = True
compile_options.input_shape = [1,224,224,3] # keep layout same as input layout
compile_options.input_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.mean = [0,0,0]
compile_options.std = [1,1,1]
compile_options.input_range = [0,1]
compile_options.letterbox_value = 114. # pad what you want
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = 'tmp'ImportOptions类, 用于配置nncase导入选项
py::class_<import_options>(m, "ImportOptions")
.def(py::init())
.def_readwrite("output_arrays", &import_options::output_arrays);各属性说明如下
| 属性名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| output_arrays | string | 否 | 输出名称 |
实例化ImportOptions, 配置各属性的值
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
import_options.output_arrays = 'output' # Your output node namePTQTensorOptions类, 用于配置nncase PTQ选项
py::class_<ptq_tensor_options>(m, "PTQTensorOptions")
.def(py::init())
.def_readwrite("calibrate_method", &ptq_tensor_options::calibrate_method)
.def_readwrite("samples_count", &ptq_tensor_options::samples_count)
.def("set_tensor_data", [](ptq_tensor_options &o, py::bytes bytes) {
uint8_t *buffer;
py::ssize_t length;
if (PyBytes_AsStringAndSize(bytes.ptr(), reinterpret_cast<char **>(&buffer), &length))
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid bytes");
o.tensor_data.assign(buffer, buffer + length);
});各属性说明如下
| 字段名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| calibrate_method | string | 否 | 校准方法 , 支持'no_clip', 'l2', 'kld_m0', 'kld_m1', 'kld_m2', 'cdf', 默认是'no_clip' |
| samples_count | int | 否 | 样本个数 |
设置校正数据
set_tensor_data(calib_data)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| calib_data | byte[] | 是 | 校正数据 |
N/A
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = cfg.generate_calibs.batch_size
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(np.asarray([sample['data'] for sample in self.calibs]).tobytes())Compiler类, 用于编译神经网络模型
py::class_<compiler>(m, "Compiler")
.def(py::init(&compiler::create))
.def("import_tflite", &compiler::import_tflite)
.def("import_onnx", &compiler::import_onnx)
.def("import_caffe", &compiler::import_caffe)
.def("compile", &compiler::compile)
.def("use_ptq", py::overload_cast<ptq_tensor_options>(&compiler::use_ptq))
.def("gencode", [](compiler &c, std::ostream &stream) { c.gencode(stream); })
.def("gencode_tobytes", [](compiler &c) {
std::stringstream ss;
c.gencode(ss);
return py::bytes(ss.str());
})
.def("create_evaluator", [](compiler &c, uint32_t stage) {
auto &graph = c.graph(stage);
return std::make_unique<graph_evaluator>(c.target(), graph);
});compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)导入tflite模型
import_tflite(model_content, import_options)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| model_content | byte[] | 是 | 读取的模型内容 |
| import_options | ImportOptions | 是 | 导入选项 |
N/A
model_content = read_model_file(model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)导入onnx模型
import_onnx(model_content, import_options)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| model_content | byte[] | 是 | 读取的模型内容 |
| import_options | ImportOptions | 是 | 导入选项 |
N/A
model_content = read_model_file(model)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)导入caffe模型
用户需在本地机器自行编译/安装caffe.
import_caffe(caffemodel, prototxt)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| caffemodel | byte[] | 是 | 读取的caffemodel内容 |
| prototxt | byte[] | 是 | 读取的prototxt内容 |
N/A
# import
caffemodel = read_model_file('test.caffemodel')
prototxt = read_model_file('test.prototxt')
compiler.import_caffe(caffemodel, prototxt)设置PTQ配置选项
use_ptq(ptq_options)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ptq_options | PTQTensorOptions | 是 | PTQ配置选项 |
N/A
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)编译神经网络模型
compile()N/A
N/A
compiler.compile()生成代码字节流
gencode_tobytes()N/A
bytes[]
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(infer_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)| Operator | Is Supported |
|---|---|
| ABS | ✅ |
| ADD | ✅ |
| ARG_MAX | ✅ |
| ARG_MIN | ✅ |
| AVERAGE_POOL_2D | ✅ |
| CAST | ✅ |
| CEIL | ✅ |
| CONCATENATION | ✅ |
| CONV_2D | ✅ |
| COS | ✅ |
| DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D | ✅ |
| DIV | ✅ |
| EXP | ✅ |
| EXPAND_DIMS | ✅ |
| FLOOR | ✅ |
| FLOOR_DIV | ✅ |
| FLOOR_MOD | ✅ |
| FULLY_CONNECTED | ✅ |
| L2_NORMALIZATION | ✅ |
| LEAKY_RELU | ✅ |
| LOG | ✅ |
| LOGISTIC | ✅ |
| MAX_POOL_2D | ✅ |
| MAXIMUM | ✅ |
| MEAN | ✅ |
| MINIMUM | ✅ |
| MUL | ✅ |
| NEG | ✅ |
| PAD | ✅ |
| PADV2 | ✅ |
| MIRROR_PAD | ✅ |
| PACK | ✅ |
| POW | ✅ |
| REDUCE_MAX | ✅ |
| REDUCE_MIN | ✅ |
| RELU | ✅ |
| PRELU | ✅ |
| RELU6 | ✅ |
| RESHAPE | ✅ |
| RESIZE_BILINEAR | ✅ |
| RESIZE_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR | ✅ |
| ROUND | ✅ |
| RSQRT | ✅ |
| SHAPE | ✅ |
| SIN | ✅ |
| SLICE | ✅ |
| SOFTMAX | ✅ |
| SPACE_TO_BATCH_ND | ✅ |
| SQUEEZE | ✅ |
| BATCH_TO_SPACE_ND | ✅ |
| STRIDED_SLICE | ✅ |
| SQRT | ✅ |
| SQUARE | ✅ |
| SUB | ✅ |
| SUM | ✅ |
| TANH | ✅ |
| TRANSPOSE | ✅ |
| TRANSPOSE_CONV | ✅ |
| QUANTIZE | ✅ |
| FAKE_QUANT | ✅ |
| DEQUANTIZE | ✅ |
| GATHER | ✅ |
| GATHER_ND | ✅ |
| ONE_HOT | ✅ |
| SQUARED_DIFFERENCE | ✅ |
| LOG_SOFTMAX | ✅ |
| SPLIT | ✅ |
| Operator | Is Supported |
|---|---|
| Abs | ✅ |
| Acos | ✅ |
| Acosh | ✅ |
| And | ✅ |
| ArgMax | ✅ |
| ArgMin | ✅ |
| Asin | ✅ |
| Asinh | ✅ |
| Add | ✅ |
| AveragePool | ✅ |
| BatchNormalization | ✅ |
| Cast | ✅ |
| Ceil | ✅ |
| Celu | ✅ |
| Clip | ✅ |
| Concat | ✅ |
| Constant | ✅ |
| ConstantOfShape | ✅ |
| Conv | ✅ |
| ConvTranspose | ✅ |
| Cos | ✅ |
| Cosh | ✅ |
| CumSum | ✅ |
| DepthToSpace | ✅ |
| DequantizeLinear | ✅ |
| Div | ✅ |
| Dropout | ✅ |
| Elu | ✅ |
| Exp | ✅ |
| Expand | ✅ |
| Equal | ✅ |
| Flatten | ✅ |
| Floor | ✅ |
| Gather | ✅ |
| GatherND | ✅ |
| Gemm | ✅ |
| GlobalAveragePool | ✅ |
| GlobalMaxPool | ✅ |
| Hardmax | ✅ |
| HardSigmoid | ✅ |
| HardSwish | ✅ |
| Identity | ✅ |
| InstanceNormalization | ✅ |
| LpNormalization | ✅ |
| LeakyRelu | ✅ |
| Log | ✅ |
| LogSoftmax | ✅ |
| LRN | ✅ |
| LSTM | ✅ |
| MatMul | ✅ |
| MaxPool | ✅ |
| Max | ✅ |
| Min | ✅ |
| Mul | ✅ |
| Neg | ✅ |
| Not | ✅ |
| OneHot | ✅ |
| Pad | ✅ |
| Pow | ✅ |
| PRelu | ✅ |
| QuantizeLinear | ✅ |
| RandomNormal | ✅ |
| RandomNormalLike | ✅ |
| RandomUniform | ✅ |
| RandomUniformLike | ✅ |
| ReduceL1 | ✅ |
| ReduceL2 | ✅ |
| ReduceLogSum | ✅ |
| ReduceLogSumExp | ✅ |
| ReduceMax | ✅ |
| ReduceMean | ✅ |
| ReduceMin | ✅ |
| ReduceProd | ✅ |
| ReduceSum | ✅ |
| ReduceSumSquare | ✅ |
| Relu | ✅ |
| Reshape | ✅ |
| Resize | ✅ |
| ReverseSequence | ✅ |
| RoiAlign | ✅ |
| Round | ✅ |
| Selu | ✅ |
| Shape | ✅ |
| Sign | ✅ |
| Sin | ✅ |
| Sinh | ✅ |
| Sigmoid | ✅ |
| Size | ✅ |
| Slice | ✅ |
| Softmax | ✅ |
| Softplus | ✅ |
| Softsign | ✅ |
| SpaceToDepth | ✅ |
| Split | ✅ |
| Sqrt | ✅ |
| Squeeze | ✅ |
| Sub | ✅ |
| Sum | ✅ |
| Tanh | ✅ |
| Tile | ✅ |
| TopK | ✅ |
| Transpose | ✅ |
| Trilu | ✅ |
| Upsample | ✅ |
| Unsqueeze | ✅ |
| Where | ✅ |
| Operator | Is Supported |
|---|---|
| Input | ✅ |
| Concat | ✅ |
| Convolution | ✅ |
| Eltwise | ✅ |
| Permute | ✅ |
| ReLU | ✅ |
| Reshape | ✅ |
| Slice | ✅ |
| Softmax | ✅ |
| Split | ✅ |
| ContinuationIndicator | ✅ |
| Pooling | ✅ |
| BatchNorm | ✅ |
| Scale | ✅ |
| Reverse | ✅ |
| LSTM | ✅ |
| InnerProduct | ✅ |
下面示例中使用到的模型和python编译脚本
- 模型位于/path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/models/子目录
- python编译脚本位于/path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/scripts子目录
- mobilenetv2_tflite_fp32_image.py脚本如下
import nncase
import os
import argparse
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
# compile_options
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_tflite_fp32_image'
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
model_content = read_model_file(args.model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- 执行如下命令即可编译mobilenetv2的tflite模型, target为k510
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_tflite_fp32_image.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenet_v2_1.0_224.tflite- 针对onnx模型, 建议先使用ONNX Simplifier进行简化, 然后再使用nncase编译.
- mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py 脚本如下
import os
import onnxsim
import onnx
import nncase
import argparse
def parse_model_input_output(model_file):
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_file)
input_all = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.input]
input_initializer = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.initializer]
input_names = list(set(input_all) - set(input_initializer))
input_tensors = [node for node in onnx_model.graph.input if node.name in input_names]
# input
inputs= []
for _, e in enumerate(input_tensors):
onnx_type = e.type.tensor_type
input_dict = {}
input_dict['name'] = e.name
input_dict['dtype'] = onnx.mapping.TENSOR_TYPE_TO_NP_TYPE[onnx_type.elem_type]
input_dict['shape'] = [(i.dim_value if i.dim_value != 0 else d) for i, d in zip(
onnx_type.shape.dim, [1, 3, 224, 224])]
inputs.append(input_dict)
return onnx_model, inputs
def onnx_simplify(model_file, dump_dir):
onnx_model, inputs = parse_model_input_output(model_file)
onnx_model = onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx_model)
input_shapes = {}
for input in inputs:
input_shapes[input['name']] = input['shape']
onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model, input_shapes=input_shapes)
assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated"
model_file = os.path.join(dump_dir, 'simplified.onnx')
onnx.save_model(onnx_model, model_file)
return model_file
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image'
if not os.path.exists(dump_dir):
os.makedirs(dump_dir)
# onnx simplify
model_file = onnx_simplify(args.model, dump_dir)
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
model_content = read_model_file(model_file)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- 执行如下命令即可编译mobilenetv2的onnx模型, target为k510
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenetv2-7.onnx- caffe wheel包从kendryte caffe获取
- conv2d_caffe_fp32.py 脚本如下
import nncase
import os
import argparse
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--caffemodel", type=str, help='caffemodel file')
parser.add_argument("--prototxt", type=str, help='prototxt file')
args = parser.parse_args()
# compile_options
dump_dir = 'tmp/conv2d_caffe_fp32'
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
caffemodel = read_model_file(args.caffemodel)
prototxt = read_model_file(args.prototxt)
compiler.import_caffe(caffemodel, prototxt)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- 执行如下命令即可编译conv2d的caffe模型, target为k510
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ python3 scripts/conv2d_caffe_fp32.py --target k510 --caffemodel models/test.caffemodel --prototxt models/test.prototxt- 针对onnx模型, 建议先使用ONNX Simplifier进行简化, 然后再使用nncase编译.
- mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_preprocess.py脚本如下
import os
import onnxsim
import onnx
import nncase
import argparse
def parse_model_input_output(model_file):
onnx_model = onnx.load(model_file)
input_all = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.input]
input_initializer = [node.name for node in onnx_model.graph.initializer]
input_names = list(set(input_all) - set(input_initializer))
input_tensors = [node for node in onnx_model.graph.input if node.name in input_names]
# input
inputs= []
for _, e in enumerate(input_tensors):
onnx_type = e.type.tensor_type
input_dict = {}
input_dict['name'] = e.name
input_dict['dtype'] = onnx.mapping.TENSOR_TYPE_TO_NP_TYPE[onnx_type.elem_type]
input_dict['shape'] = [(i.dim_value if i.dim_value != 0 else d) for i, d in zip(
onnx_type.shape.dim, [1, 3, 224, 224])]
inputs.append(input_dict)
return onnx_model, inputs
def onnx_simplify(model_file, dump_dir):
onnx_model, inputs = parse_model_input_output(model_file)
onnx_model = onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx_model)
input_shapes = {}
for input in inputs:
input_shapes[input['name']] = input['shape']
onnx_model, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx_model, input_shapes=input_shapes)
assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated"
model_file = os.path.join(dump_dir, 'simplified.onnx')
onnx.save_model(onnx_model, model_file)
return model_file
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_preprocess'
if not os.path.exists(dump_dir):
os.makedirs(dump_dir)
# onnx simplify
model_file = onnx_simplify(args.model, dump_dir)
# compile_options
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.input_type = 'uint8'
compile_options.preprocess = True
compile_options.swapRB = True
compile_options.input_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NCHW'
compile_options.input_shape = [1, 256, 256, 3]
compile_options.mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
compile_options.std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
compile_options.input_range = [0, 1]
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# import
model_content = read_model_file(model_file)
compiler.import_onnx(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- 执行如下命令即可编译添加前处理的mobilenetv2的onnx模型, target为k510
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_preprocess.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenetv2-7.onnx- mobilenetv2_tflite_uint8_image.py脚本如下
import nncase
import os
import argparse
import numpy as np
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def generate_data(shape, batch):
shape[0] *= batch
data = np.random.rand(*shape).astype(np.float32)
return data
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--target", type=str, help='target to run')
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, help='model file')
args = parser.parse_args()
input_shape = [1, 224, 224, 3]
# compile_options
dump_dir = 'tmp/mobilenetv2_tflite_uint8_image'
compile_options = nncase.CompileOptions()
compile_options.target = args.target
compile_options.input_type = 'float32'
compile_options.input_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.output_layout = 'NHWC'
compile_options.dump_ir = True
compile_options.dump_asm = True
compile_options.dump_dir = dump_dir
# compiler
compiler = nncase.Compiler(compile_options)
# import_options
import_options = nncase.ImportOptions()
# quantize model
compile_options.quant_type = 'uint8'
# ptq_options
ptq_options = nncase.PTQTensorOptions()
ptq_options.samples_count = 10
ptq_options.set_tensor_data(generate_data(input_shape, ptq_options.samples_count).tobytes())
# import
model_content = read_model_file(args.model)
compiler.import_tflite(model_content, import_options)
# compile
compiler.use_ptq(ptq_options)
compiler.compile()
# kmodel
kmodel = compiler.gencode_tobytes()
with open(os.path.join(dump_dir, 'test.kmodel'), 'wb') as f:
f.write(kmodel)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- 执行如下命令即可编译uint8量化的mobilenetv2的tflite模型, target为k510
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_tflite_uint8_image.py --target k510 --model models/mobilenet_v2_1.0_224.tflite除了编译模型APIs, nncase还提供了推理模型的APIs, 在PC上可推理前面编译生成的kmodel, 用来验证nncase推理结果和相应深度学习框架的runtime的结果是否一致等.
MemoryRange类, 用于表示内存范围
py::class_<memory_range>(m, "MemoryRange")
.def_readwrite("location", &memory_range::memory_location)
.def_property(
"dtype", [](const memory_range &range) { return to_dtype(range.datatype); },
[](memory_range &range, py::object dtype) { range.datatype = from_dtype(py::dtype::from_args(dtype)); })
.def_readwrite("start", &memory_range::start)
.def_readwrite("size", &memory_range::size);各属性说明如下
| 属性名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| location | int | 否 | 内存位置, 0表示input, 1表示output, 2表示rdata, 3表示data, 4表示shared_data |
| dtype | python数据类型 | 否 | 数据类型 |
| start | int | 否 | 内存起始地址 |
| size | int | 否 | 内存大小 |
实例化MemoryRange
mr = nncase.MemoryRange()RuntimeTensor类, 用于表示运行时tensor
py::class_<runtime_tensor>(m, "RuntimeTensor")
.def_static("from_numpy", [](py::array arr) {
auto src_buffer = arr.request();
auto datatype = from_dtype(arr.dtype());
auto tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(
datatype,
to_rt_shape(src_buffer.shape),
to_rt_strides(src_buffer.itemsize, src_buffer.strides),
gsl::make_span(reinterpret_cast<gsl::byte *>(src_buffer.ptr), src_buffer.size * src_buffer.itemsize),
[=](gsl::byte *) { arr.dec_ref(); })
.unwrap_or_throw();
arr.inc_ref();
return tensor;
})
.def("copy_to", [](runtime_tensor &from, runtime_tensor &to) {
from.copy_to(to).unwrap_or_throw();
})
.def("to_numpy", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
auto host = tensor.as_host().unwrap_or_throw();
auto src_map = std::move(hrt::map(host, hrt::map_read).unwrap_or_throw());
auto src_buffer = src_map.buffer();
return py::array(
to_dtype(tensor.datatype()),
tensor.shape(),
to_py_strides(runtime::get_bytes(tensor.datatype()), tensor.strides()),
src_buffer.data());
})
.def_property_readonly("dtype", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
return to_dtype(tensor.datatype());
})
.def_property_readonly("shape", [](runtime_tensor &tensor) {
return to_py_shape(tensor.shape());
});各属性说明如下
| 属性名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| dtype | int | 否 | tensor的数据类型 |
| shape | list | 否 | tensor的形状 |
从numpy.ndarray构造RuntimeTensor对象
from_numpy(py::array arr)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| arr | numpy.ndarray | 是 | numpy.ndarray对象 |
RuntimeTensor
tensor = nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(self.inputs[i]['data'])拷贝RuntimeTensor
copy_to(RuntimeTensor to)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| to | RuntimeTensor | 是 | RuntimeTensor对象 |
N/A
sim.get_output_tensor(i).copy_to(to)将RuntimeTensor转换为numpy.ndarray对象
to_numpy()N/A
numpy.ndarray对象
arr = sim.get_output_tensor(i).to_numpy()Simulator类, 用于在PC上推理kmodel
py::class_<interpreter>(m, "Simulator")
.def(py::init())
.def("load_model", [](interpreter &interp, gsl::span<const gsl::byte> buffer) { interp.load_model(buffer).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def_property_readonly("inputs_size", &interpreter::inputs_size)
.def_property_readonly("outputs_size", &interpreter::outputs_size)
.def("get_input_desc", &interpreter::input_desc)
.def("get_output_desc", &interpreter::output_desc)
.def("get_input_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index) { return interp.input_tensor(index).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("set_input_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) { return interp.input_tensor(index, tensor).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("get_output_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index) { return interp.output_tensor(index).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("set_output_tensor", [](interpreter &interp, size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) { return interp.output_tensor(index, tensor).unwrap_or_throw(); })
.def("run", [](interpreter &interp) { interp.run().unwrap_or_throw(); });各属性说明如下
| 属性名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputs_size | int | 否 | 输入个数 |
| outputs_size | int | 否 | 输出个数 |
实例化Simulator
sim = nncase.Simulator()加载kmodel
load_model(model_content)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| model_content | byte[] | 是 | kmodel字节流 |
N/A
sim.load_model(kmodel)获取指定索引的输入的描述信息
get_input_desc(index)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | 是 | 输入的索引 |
MemoryRange
input_desc_0 = sim.get_input_desc(0)获取指定索引的输出的描述信息
get_output_desc(index)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | 是 | 输出的索引 |
MemoryRange
output_desc_0 = sim.get_output_desc(0)获取指定索引的输入的RuntimeTensor
get_input_tensor(index)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | 是 | 输入tensor的索引 |
RuntimeTensor
input_tensor_0 = sim.get_input_tensor(0)设置指定索引的输入的RuntimeTensor
set_input_tensor(index, tensor)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | 是 | 输入RuntimeTensor的索引 |
| tensor | RuntimeTensor | 是 | 输入RuntimeTensor |
N/A
sim.set_input_tensor(0, nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(self.inputs[0]['data']))获取指定索引的输出的RuntimeTensor
get_output_tensor(index)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | 是 | 输出RuntimeTensor的索引 |
RuntimeTensor
output_arr_0 = sim.get_output_tensor(0).to_numpy()设置指定索引的输出的RuntimeTensor
set_output_tensor(index, tensor)| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | int | 是 | 输出RuntimeTensor的索引 |
| tensor | RuntimeTensor | 是 | 输出RuntimeTensor |
N/A
sim.set_output_tensor(0, tensor)运行kmodel推理
run()N/A
N/A
sim.run()前置条件: mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py脚本已编译过mobilenetv2-7.onnx模型
mobilenetv2_onnx_simu.py位于/path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/scripts子目录, 内容如下
import os
import copy
import argparse
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime as ort
import nncase
def read_model_file(model_file):
with open(model_file, 'rb') as f:
model_content = f.read()
return model_content
def cosine(gt, pred):
return (gt @ pred) / (np.linalg.norm(gt, 2) * np.linalg.norm(pred, 2))
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog="nncase")
parser.add_argument("--model_file", type=str, help='original model file')
parser.add_argument("--kmodel_file", type=str, help='kmodel file')
parser.add_argument("--input_file", type=str, help='input bin file for kmodel')
args = parser.parse_args()
# create simulator
sim = nncase.Simulator()
# read kmodel
kmodel = read_model_file(args.kmodel_file)
# load kmodel
sim.load_model(kmodel)
# read input.bin
input_tensor=sim.get_input_tensor(0).to_numpy()
input = np.fromfile(args.input_file, input_tensor.dtype).reshape(input_tensor.shape)
# set input for simulator
sim.set_input_tensor(0, nncase.RuntimeTensor.from_numpy(input))
# simulator inference
nncase_results = []
sim.run()
for i in range(sim.outputs_size):
nncase_result = sim.get_output_tensor(i).to_numpy()
nncase_results.append(copy.deepcopy(nncase_result))
# cpu inference
cpu_results = []
ort_session = ort.InferenceSession(args.model_file)
input_name = ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name
output_name = ort_session.get_outputs()[0].name
cpu_results = ort_session.run([output_name], { input_name : input })
# compare
for i in range(sim.outputs_size):
cos = cosine(np.reshape(nncase_results[i], (-1)), np.reshape(cpu_results[i], (-1)))
print('output {0} cosine similarity : {1}'.format(i, cos))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()执行推理脚本
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ python3 scripts/mobilenetv2_onnx_simu.py --model_file models/mobilenetv2-7.onnx --kmodel_file tmp/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image/test.kmodel --input_file mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image/data/input_0_0.binnncase simulator和cpu推理结果对比如下
... ...
output 0 cosine similarity : 0.9992437958717346nncase runtime用于在AI设备加载kmodel/设置输入数据/执行KPU计算/获取输出数据等.
目前只提供C++版本的APIs, 相关的头文件和静态库在nncase sdk/riscv64目录下.
$ tree -L 3 riscv64/
riscv64/
├── include
│ ├── gsl
│ │ └── gsl-lite.hpp
│ ├── gsl-lite
│ │ └── gsl-lite.hpp
│ ├── mpark
│ │ ├── config.hpp
│ │ ├── in_place.hpp
│ │ ├── lib.hpp
│ │ └── variant.hpp
│ └── nncase
│ ├── functional
│ ├── kernels
│ ├── runtime
│ └── version.h
└── lib
├── cmake
│ ├── nncasefunctional
│ ├── nncase_rt_modules_k510
│ └── nncaseruntime
├── libnncase.functional.a
├── libnncase.rt_modules.k510.a
└── libnncase.runtime.a
13 directories, 10 files用于存储模型输入/输出数据的tensor
创建runtime_tensor
(1) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(datatype_t datatype, runtime_shape_t shape, memory_pool_t pool = pool_cpu_only, uintptr_t physical_address = 0) noexcept;
(2) NNCASE_API result<runtime_tensor> create(datatype_t datatype, runtime_shape_t shape, gsl::span<gsl::byte> data, bool copy, memory_pool_t pool = pool_cpu_only, uintptr_t physical_address = 0) noexcept;| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| datatype | datatype_t | 是 | 数据类型, 如dt_float32 |
| shape | runtime_shape_t | 是 | tensor的形状 |
| data | gsl::span<gsl::byte> | 是 | 用户态数据buffer |
| copy | bool | 是 | 是否拷贝 |
| pool | memory_pool_t | 否 | 内存池类型, 默认值为pool_cpu_only |
| physical_address | uintptr_t | 否 | 物理地址, 默认值为0 |
result<runtime_tensor>
// create input
auto in_shape = interp.input_shape(0);
auto input_tensor = host_runtime_tensor::create(dt_float32, in_shape,
{(gsl::byte *)mat.data, mat.cols * mat.rows * mat.elemSize()},
true, hrt::pool_shared).expect("cannot create input tensor");interpreter是nncase runtime的运行实例, 它提供了load_model()/run()/input_tensor()/output_tensor()等核心功能函数.
加载kmodel模型
NNCASE_NODISCARD result<void> load_model(gsl::span<const gsl::byte> buffer) noexcept;| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| buffer | gsl::span <const gsl::byte> |
是 | kmodel buffer |
result <void>
template <class T>
std::vector<T>read_binary_file(const char *file_name)
{
std::ifstream ifs(file_name, std::ios::binary);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.end);
size_t len = ifs.tellg();
std::vector<T> vec(len / sizeof(T), 0);
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.beg);
ifs.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(vec.data()), len);
ifs.close();
return vec;
}
interpreter interp;
auto model = read_binary_file<unsigned char>(kmodel);
interp.load_model({(const gsl::byte *)model.data(), model.size()}).expect("cannot load model.");获取模型输入的个数
size_t inputs_size() const noexcept;N/A
size_t
auto inputs_size = interp.inputs_size();获取模型输出的个数
size_t outputs_size() const noexcept;N/A
size_t
auto outputs_size = interp.outputs_size();获取模型指定输入的shape
const runtime_shape_t &input_shape(size_t index) const noexcept;| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | 是 | 输入的索引 |
runtime_shape_t
auto in_shape = interp.input_shape(0);获取模型指定输出的shape
const runtime_shape_t &output_shape(size_t index) const noexcept;| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | 是 | 输出的索引 |
runtime_shape_t
auto out_shape = interp.output_shape(0);获取/设置指定索引的input tensor
(1) result<runtime_tensor> input_tensor(size_t index) noexcept;
(2) result<void> input_tensor(size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) noexcept;| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | 是 | kmodel buffer |
| tensor | runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入对应的runtime tensor |
(1) 返回result<runtime_tensor>
(2) 返回result <void>
// set input
interp.input_tensor(0, input_tensor).expect("cannot set input tensor");获取/设置指定索引的output tensor
(1) result<runtime_tensor> output_tensor(size_t index) noexcept;
(2) result<void> output_tensor(size_t index, runtime_tensor tensor) noexcept;| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| index | size_t | 是 | |
| tensor | runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入对应的runtime tensor |
(1) 返回result<runtime_tensor>
(2) 返回result <void>
// get output
auto output_tensor = interp.output_tensor(0).expect("cannot get output tensor");
auto mapped_buf = std::move(hrt::map(output_tensor, hrt::map_read).unwrap_or_throw());
float *output_data = reinterpret_cast<float *>(mapped_buf.buffer().data());
auto out_shape = interp.output_shape(0);
auto it = std::max_element(output_data, output_data + compute_size(out_shape));
size_t idx = it - output_data;
std::cout << "image classification result: " << labels[idx] << "(" << *it << ")" << std::endl;执行kpu计算
result<void> run() noexcept;N/A
result <void>
// run
interp.run().expect("error occurred in running model");示例代码位于/path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image
前置条件
- mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py脚本已编译过mobilenetv2-7.onnx模型
- 由于该示例依赖OpenCV库,需要在示例的CMakeLists.txt中指定OpenCV的路径。
交叉编译app
$ cd /path/to/nncase_sdk/examples
$ ./build.sh最后在out/bin目录下生成mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image
k510 EVB上板运行
将下面几个文件拷贝到k510 EVB板上
| 文件 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image | 交叉编译examples生成 |
| test.kmodel | 使用mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image.py编译mobilenetv2-7.onnx生成 |
| cat.png和labels_1000.txt | 位于/path/to/nncase_sdk/examples/mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image/data/子目录下 |
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/mnt/zhangyang/nncase_check/lib/gomp:/mnt/zhangyang/nncase_check/lib/opencv
$ ./mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image test.kmodel cat.png labels_1000.txt
case ./mobilenetv2_onnx_fp32_image build at Mar 1 2022 16:31:29
interp.run() duration: 12.6642 ms
image classification result: tiger cat(9.25)nncase Functional用于提升用户对模型进行前后处理时的易用性
目前只提供C++版本的APIs, 相关的头文件和库在nncase sdk的riscv64目录下.
计算平方,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > square(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto squared = F::square(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算根号值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > sqrt(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::sqrt(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算log值,输入的负数会被转换为Nan,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > log(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::log(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算exp值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > exp(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::exp(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算sin值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > sin(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::sin(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算cos值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > cos(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::cos(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算round值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > round(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::round(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算floor值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > floor(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::floor(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算ceil值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > ceil(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::ceil(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算abs值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > abs(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::abs(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();计算neg值,目前支持输入uint8/int8,输出也为uint8/int8,注意输入为定点且输出为浮点时需要设置量化参数.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > neg(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
if ((input_type == dt_uint8 or input_type == dt_int8) and (output_type == dt_float32 or output_type == dt_bfloat16))
{
input.quant_param(xxx);
}
auto output = F::neg(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();输入dt_bfloat16, dt_float32 数据,输出dt_int8或 dt_uint8输出
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > quantize(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入, 类型必须为float32 或 bfloat16 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
auto quantized = F::quantize(input, dt_int8).unwrap_or_throw();输入 uint8 or int8 输入,转换到 float or bfloat数据. 注意,用户必须提前为数据设置好正确的量化参数用于反量化.
public inline NNCASE_API result< runtime::runtime_tensor > dequantize(runtime::runtime_tensor & input,datatype_t dtype) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入 |
dtype |
datatype_t | 是 | 输出tensor datatype |
result<runtime_tensor>
input.quant_param({ 0, 1 });
auto dequantized = F::dequantize(input, output_type).unwrap_or_throw();给定bboxs,从原始tensor中裁剪并resize输出到新tensor中. 接受dt_bfloat16, dt_float32, dt_int8, dt_uint8类型输出,输出相同类型.
NNCASE_API inline result<runtime::runtime_tensor> crop(runtime::runtime_tensor &input, runtime::runtime_tensor &bbox, size_t out_h, size_t out_w, image_resize_mode_t resize_mode, bool align_corners, bool half_pixel_centers) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入数据,需要 [n,c,h,w] 格式排布 ,如果数据为uint8或int8 请保证数据量化参数的正确性 |
| bbox | runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入bbox数据, 需要 [1,1,m,4] 格式排布, 内部数据为[y0,x0,y1,x1], 类型为[float32,bfloat16] |
| out_h | size_t | 是 | 输出数据height |
| out_w | size_t | 是 | 输入数据width |
| resize_mode | image_resize_mode_t | 是 | resize方法模式 |
| align_corners | bool | 是 | resize 是否 align_corners |
| half_pixel_centers | bool | 是 | resize是否pixel中心对齐 |
result<runtime_tensor>
auto bbox = get_rand_bbox(input_shape, roi_amount);
auto &&[out_h, out_w] = get_rand_out_hw();
auto output_opt = F::crop(input, bbox, out_h, out_w, resize_mode).unwrap_or_throw();给定输出高度 宽度,把输入tensor resize到新尺寸. 接受dt_bfloat16, dt_float32, dt_int8, dt_uint8类型输出,输出相同类型.
NNCASE_API inline result<runtime::runtime_tensor> resize(runtime::runtime_tensor &input, size_t out_h, size_t out_w, image_resize_mode_t resize_mode, bool align_corners, bool half_pixel_centers) noexcept
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入数据,需要 [n,c,h,w] 格式排布, 如果数据为uint8或int8 请保证数据量化参数的正确性 |
| out_h | size_t | 是 | 输出数据height |
| out_w | size_t | 是 | 输入数据width |
| resize_mode | image_resize_mode_t | 是 | resize方法模式 |
| align_corners | bool | 是 | resize 是否 align_corners |
| half_pixel_centers | bool | 是 | resize是否pixel中心对齐 |
result<runtime_tensor>
auto &&[out_h, out_w] = get_rand_out_hw();
auto output_opt = F::resize(input, out_h, out_w, resize_mode, false, false).unwrap_or_throw();在每个维度上padding数据,接受dt_bfloat16, dt_float32, dt_int8, dt_uint8类型输出,输出相同类型.
NNCASE_API inline result<runtime::runtime_tensor> pad(runtime::runtime_tensor &input, runtime_paddings_t &paddings, pad_mode_t pad_mode, float fill_v)
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | runtime_tensor | 是 | 输入数据,如果数据为uint8或int8 请保证数据量化参数的正确性 |
| padding | runtime_paddings_t | 是 | 每个维度的padding值, 注意顺序为逆向. 比如padding值为 [ {2,3}, {1,3} ]表示在最后一维前面pad 2,后面pad 3. 倒数第二维前面pad 1, 后面pad 2 |
| pad_mode | pad_mode_t | 是 | 目前暂时只支持const 模式 |
| fill_v | float | 是 | 填充值 |
result<runtime_tensor>
runtime_paddings_t paddings{ { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, 2 } };
auto output = F::pad(input, paddings, pad_constant, pad_value).unwrap_or_throw();| 分类模型 | cpu精度(Top-1) | 浮点精度(Top-1) | uint8精度(Top-1) | int8精度(Top-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alexnet | 0.531 | 0.53 | N/A | 0.52 |
| densenet 121 | 0.732 | 0.732 | 0.723 | N/A |
| inception v3 | 0.766 | 0.765 | 0.773 | 0.77 |
| inception v4 | 0.789 | 0.789 | 0.793 | 0.792 |
| mobilenet v1 | 0.731 | 0.73 | 0.723 | 0.718 |
| mobilenet v2 | 0.713 | 0.715 | 0.713 | 0.719 |
| resnet50 v2 | 0.747 | 0.74 | 0.748 | 0.749 |
| vgg 16 | 0.689 | 0.687 | 0.690 | 0.689 |
本表格主要为了对比量化的性能,cpu精度为完整ImageNet验证集数据,浮点和量化精度为验证集中1000类按照序号首先出现的图片作为数据子集测试的结果。
Alexnet和DenseNet的测试结果为旧数据,均为验证集前1000张图像作为数据子集的测试结果,N/A为当时的测试数据子集与CPU不同,因此不作为比较。
因为所选网络不一定来源于官方或者预处理等存在差异,可能与官方性能有所不同。
- YOLOV3
| COCOAPI | 官方结果 | CPU浮点精度 | gnne浮点精度 | uint8精度 | int8精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.314 | 0.307 | 0.306 | 0.295 | 0.288 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.559 | 0.555 | 0.554 | 0.555 | 0.554 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.75| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.318 | 0.308 | 0.307 | 0.287 | 0.275 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] | 0.142 | 0.150 | 0.149 | 0.147 | 0.144 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] | 0.341 | 0.332 | 0.332 | 0.322 | 0.316 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] | 0.464 | 0.437 | 0.437 | 0.414 | 0.404 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 1] | 0.278 | 0.270 | 0.271 | 0.262 | 0.256 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 10] | 0.419 | 0.412 | 0.412 | 0.399 | 0.392 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.442 | 0.433 | 0.433 | 0.421 | 0.414 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] | 0.239 | 0.251 | 0.251 | 0.248 | 0.246 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] | 0.482 | 0.462 | 0.463 | 0.451 | 0.443 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] | 0.611 | 0.586 | 0.585 | 0.559 | 0.550 |
- ssd-mobilenetv1
| COCOAPI | 官方结果 | CPU浮点精度 | gnne浮点精度 | uint8精度 | int8精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.184 | 0.184 | 0.184 | 0.183 | 0.183 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.306 | 0.307 | 0.306 | 0.305 | 0.306 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.75| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.191 | 0.192 | 0.190 | 0.189 | 0.190 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] | 0.157 | 0.157 | 0.157 | 0.156 | 0.155 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] | 0.371 | 0.372 | 0.371 | 0.370 | 0.369 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 1] | 0.180 | 0.180 | 0.180 | 0.181 | 0.181 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 10] | 0.242 | 0.242 | 0.242 | 0.243 | 0.243 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.242 | 0.242 | 0.242 | 0.243 | 0.243 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.026 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] | 0.206 | 0.206 | 0.206 | 0.206 | 0.205 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] | 0.489 | 0.491 | 0.490 | 0.490 | 0.491 |
- YOLOV5S
| COCOAPI | 官方结果 | CPU浮点精度 | gnne浮点精度 | uint8精度 | int8精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.367 | 0.365 | 0.335 | 0.334 | 0.335 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.555 | 0.552 | 0.518 | 0.518 | 0.518 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.75| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.398 | 0.395 | 0.364 | 0.363 | 0.362 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] | 0.223 | 0.220 | 0.199 | 0.199 | 0.197 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] | 0.419 | 0.418 | 0.387 | 0.386 | 0.386 |
| Average Precision (AP) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] | 0.463 | 0.459 | 0.423 | 0.422 | 0.423 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 1] | 0.306 | 0.306 | 0.288 | 0.287 | 0.287 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 10] | 0.518 | 0.518 | 0.487 | 0.486 | 0.487 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = all | maxDets = 100] | 0.576 | 0.576 | 0.540 | 0.539 | 0.540 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = small | maxDets = 100] | 0.391 | 0.399 | 0.350 | 0.350 | 0.347 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU= 0.50:0.95| area = medium | maxDets = 100] | 0.641 | 0.640 | 0.606 | 0.605 | 0.607 |
| Average Recall (AR) @ [IoU = 0.50:0.95| area = large | maxDets = 100] | 0.716 | 0.710 | 0.680 | 0.683 | 0.685 |
Q: 安装nncase wheel包, 出现ERROR: nncase-1.0.0.20210830-cp37-cp37m-manylinux_2_24_x86_64.whl is not a supported wheel on this platform.
A: 升级 pip >= 20.3
$ sudo pip3 install --upgrade pipQ: EVB上运行App推理程序, 抛出"std::bad_alloc"异常
$ ./cpp.sh
case ./yolov3_bfloat16 build at Sep 16 2021 18:12:03
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::bad_alloc'
what(): std::bad_allocA: std::bad_alloc异常通常是因为内存分配失败导致的, 可做如下排查.
- 检查生成的kmodel是否超过当前系统可用内存(如yolov3 bfloat16 kmodel大小为121MB, 当前linux可用内存只有70MB, 则会抛出该异常). 若超过, 可尝试使用训练后量化来减小kmodel大小.
- 检查App是否存在内存泄露
Q: simulator运行App推理程序, 抛出"[..t_runtime_tensor.cpp:310 (create)] data.size_bytes() == size = false (bool)"异常
A: 检查设置的输入tensor信息, 重点是输入shape和每个元素占用的字节数(fp32/uint8)