| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1418 |
Weekly Contest 306 Q2 |
|
You are given a directed graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, where each node has exactly one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented by a given 0-indexed integer array edges of length n, where edges[i] indicates that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i].
The edge score of a node i is defined as the sum of the labels of all the nodes that have an edge pointing to i.
Return the node with the highest edge score. If multiple nodes have the same edge score, return the node with the smallest index.
Example 1:
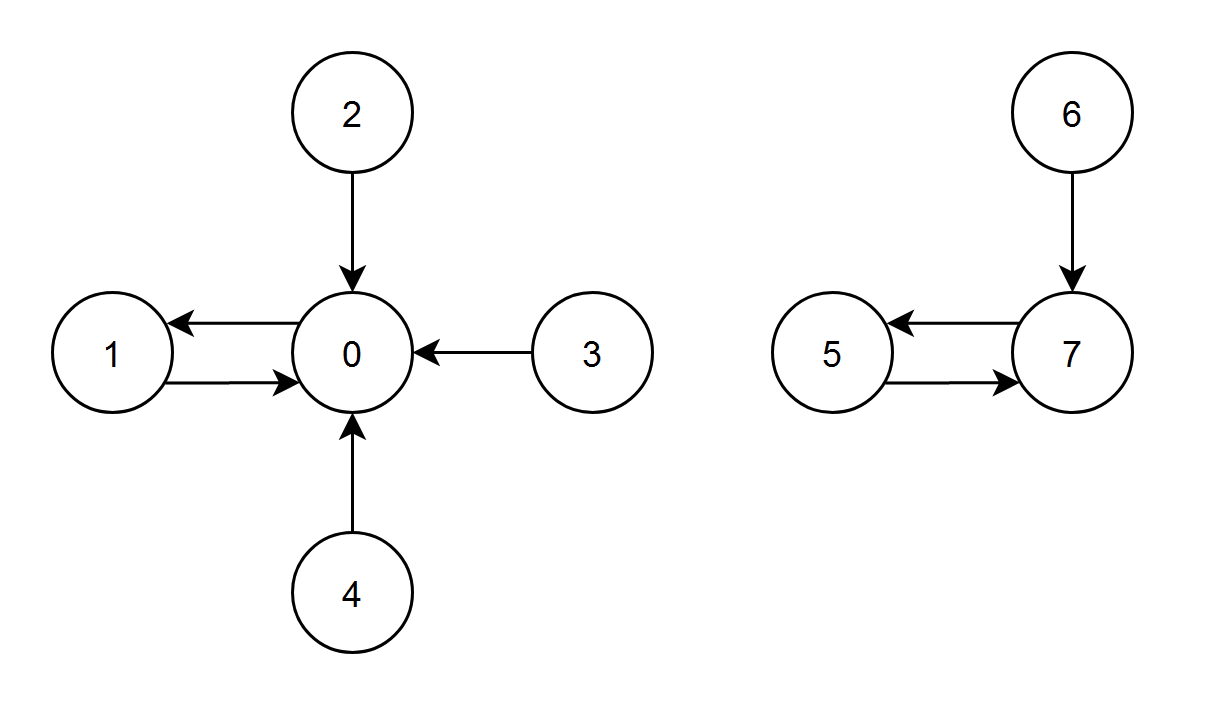
Input: edges = [1,0,0,0,0,7,7,5] Output: 7 Explanation: - The nodes 1, 2, 3 and 4 have an edge pointing to node 0. The edge score of node 0 is 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10. - The node 0 has an edge pointing to node 1. The edge score of node 1 is 0. - The node 7 has an edge pointing to node 5. The edge score of node 5 is 7. - The nodes 5 and 6 have an edge pointing to node 7. The edge score of node 7 is 5 + 6 = 11. Node 7 has the highest edge score so return 7.
Example 2:
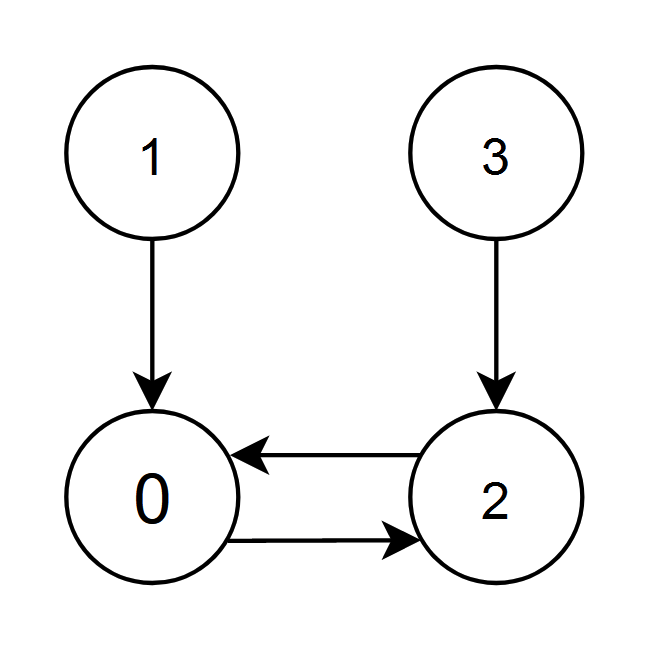
Input: edges = [2,0,0,2] Output: 0 Explanation: - The nodes 1 and 2 have an edge pointing to node 0. The edge score of node 0 is 1 + 2 = 3. - The nodes 0 and 3 have an edge pointing to node 2. The edge score of node 2 is 0 + 3 = 3. Nodes 0 and 2 both have an edge score of 3. Since node 0 has a smaller index, we return 0.
Constraints:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= edges[i] < nedges[i] != i
class Solution:
def edgeScore(self, edges: List[int]) -> int:
cnt = Counter()
for i, v in enumerate(edges):
cnt[v] += i
ans = 0
for i in range(len(edges)):
if cnt[ans] < cnt[i]:
ans = i
return ansclass Solution {
public int edgeScore(int[] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
long[] cnt = new long[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cnt[edges[i]] += i;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (cnt[ans] < cnt[i]) {
ans = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int edgeScore(vector<int>& edges) {
int n = edges.size();
vector<long long> cnt(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cnt[edges[i]] += i;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (cnt[ans] < cnt[i]) {
ans = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func edgeScore(edges []int) int {
n := len(edges)
cnt := make([]int, n)
for i, v := range edges {
cnt[v] += i
}
ans := 0
for i, v := range cnt {
if cnt[ans] < v {
ans = i
}
}
return ans
}function edgeScore(edges: number[]): number {
const n = edges.length;
const sum = new Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum[edges[i]] += i;
}
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (sum[res] < sum[i]) {
res = i;
}
}
return res;
}