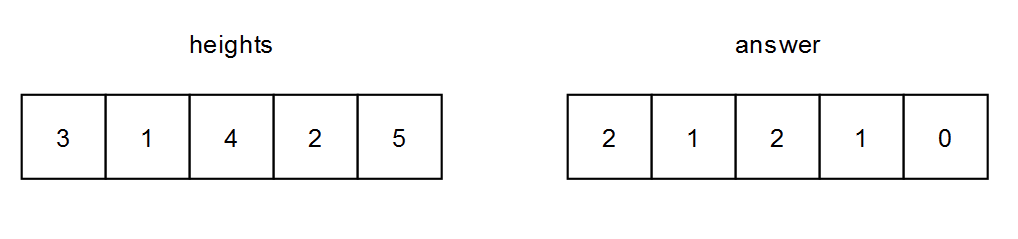| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给定一个 m x n 下标从 0 开始的二维正整数数组 heights,其中 heights[i][j] 是站在位置 (i, j) 上的人的高度。
站在 (row1, col1) 位置的人可以看到站在 (row2, col2) 位置的人,前提是:
(row2, col2)的人在(row1, col1)的人的右边 或 下面。更正式地说,要么row1 == row2时col1 < col2,要么row1 < row2时col1 == col2。- 他们中间的人 都 比他们两个矮。
返回一个 m x n 的二维整数数组answer,其中 answer[i][j] 是位于 (i, j) 位置的人可以看到的人数。
示例 1:
输入: heights = [[3,1,4,2,5]] 输出: [[2,1,2,1,0]] 解释: - (0,0) 上的人可以看到 (0,1) 和 (0,2) 的人。 注意,他看不到 (0,4) 上的人,因为 (0,2) 上的人比他高。 - (0,1) 上的人可以看到 (0,2) 上的人。 - (0,2) 上的人可以看到 (0,3) 和 (0,4) 的人。 - (0,3) 上的人可以看到 (0,4) 上的人。 - (0,4) 上的人看不到任何人。
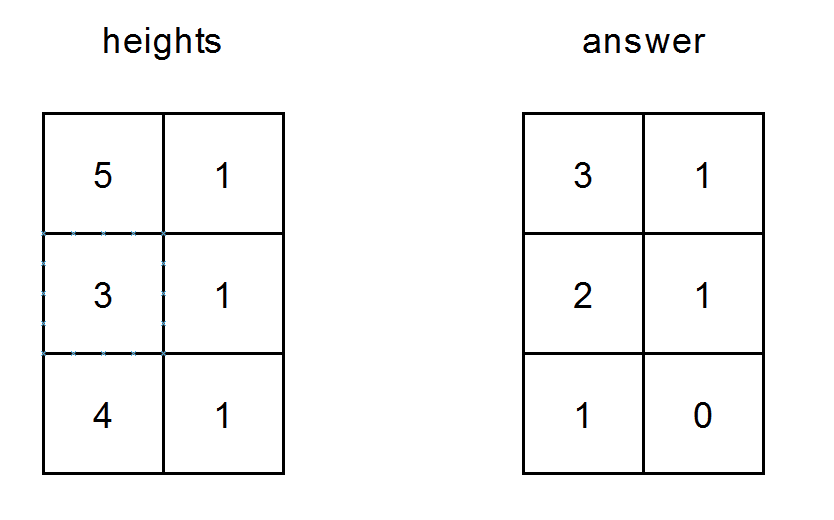
示例 2:
输入: heights = [[5,1],[3,1],[4,1]] 输出: [[3,1],[2,1],[1,0]] 解释: - (0,0) 上的人可以看到 (0,1)、(1,0) 和 (2,0) 的人。 - (0,1) 上的人可以看到 (1,1) 上的人。 - (1,0) 上的人可以看到 (1,1) 和 (2,0) 的人。 - (1,1) 上的人可以看到 (2,1) 上的人。 - (2,0) 上的人可以看到 (2,1) 上的人。 - (2,1) 上的人看不到任何人。
提示:
1 <= heights.length <= 4001 <= heights[i].length <= 4001 <= heights[i][j] <= 105
我们观察发现,对于第
因此,对于每一行,我们可以用单调栈来求出每个人能看到的人数。
具体地,我们可以倒序遍历数组,用一个从栈顶到栈底单调递增的栈
对于第
这样处理过后,我们就可以得到每一行每个人能看到的人数。
同理,我们可以对每一列进行处理,得到每一列每个人能看到的人数。最后,我们将每一行和每一列的答案相加,就可以得到最终的答案。
时间复杂度
相似题目:
class Solution:
def seePeople(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
def f(nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
stk = []
ans = [0] * n
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while stk and stk[-1] < nums[i]:
ans[i] += 1
stk.pop()
if stk:
ans[i] += 1
while stk and stk[-1] == nums[i]:
stk.pop()
stk.append(nums[i])
return ans
ans = [f(row) for row in heights]
m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])
for j in range(n):
add = f([heights[i][j] for i in range(m)])
for i in range(m):
ans[i][j] += add[i]
return ansclass Solution {
public int[][] seePeople(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[m][0];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans[i] = f(heights[i]);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int[] nums = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
nums[i] = heights[i][j];
}
int[] add = f(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans[i][j] += add[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
private int[] f(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
Deque<Integer> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() < nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
++ans[i];
}
if (!stk.isEmpty()) {
++ans[i];
}
while (!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() == nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(nums[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> seePeople(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
auto f = [](vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n);
stack<int> stk;
for (int i = n - 1; ~i; --i) {
while (stk.size() && stk.top() < nums[i]) {
++ans[i];
stk.pop();
}
if (stk.size()) {
++ans[i];
}
while (stk.size() && stk.top() == nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(nums[i]);
}
return ans;
};
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (auto& row : heights) {
ans.push_back(f(row));
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
vector<int> col;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
col.push_back(heights[i][j]);
}
vector<int> add = f(col);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans[i][j] += add[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
};func seePeople(heights [][]int) (ans [][]int) {
f := func(nums []int) []int {
n := len(nums)
ans := make([]int, n)
stk := []int{}
for i := n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for len(stk) > 0 && stk[len(stk)-1] < nums[i] {
ans[i]++
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
}
if len(stk) > 0 {
ans[i]++
}
for len(stk) > 0 && stk[len(stk)-1] == nums[i] {
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
}
stk = append(stk, nums[i])
}
return ans
}
for _, row := range heights {
ans = append(ans, f(row))
}
n := len(heights[0])
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
col := make([]int, len(heights))
for i := range heights {
col[i] = heights[i][j]
}
for i, v := range f(col) {
ans[i][j] += v
}
}
return
}function seePeople(heights: number[][]): number[][] {
const f = (nums: number[]): number[] => {
const n = nums.length;
const ans: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);
const stk: number[] = [];
for (let i = n - 1; ~i; --i) {
while (stk.length && stk.at(-1) < nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
++ans[i];
}
if (stk.length) {
++ans[i];
}
while (stk.length && stk.at(-1) === nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(nums[i]);
}
return ans;
};
const ans: number[][] = [];
for (const row of heights) {
ans.push(f(row));
}
const n = heights[0].length;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
const col: number[] = [];
for (const row of heights) {
col.push(row[j]);
}
const add = f(col);
for (let i = 0; i < ans.length; ++i) {
ans[i][j] += add[i];
}
}
return ans;
}