| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2178 |
Weekly Contest 266 Q4 |
|
There is an undirected graph with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). You are given a 0-indexed integer array values where values[i] is the value of the ith node. You are also given a 0-indexed 2D integer array edges, where each edges[j] = [uj, vj, timej] indicates that there is an undirected edge between the nodes uj and vj, and it takes timej seconds to travel between the two nodes. Finally, you are given an integer maxTime.
A valid path in the graph is any path that starts at node 0, ends at node 0, and takes at most maxTime seconds to complete. You may visit the same node multiple times. The quality of a valid path is the sum of the values of the unique nodes visited in the path (each node's value is added at most once to the sum).
Return the maximum quality of a valid path.
Note: There are at most four edges connected to each node.
Example 1:
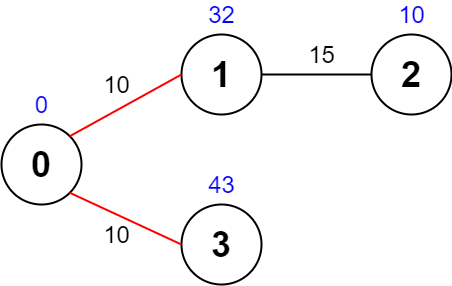
Input: values = [0,32,10,43], edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,15],[0,3,10]], maxTime = 49 Output: 75 Explanation: One possible path is 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 3 -> 0. The total time taken is 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 = 40 <= 49. The nodes visited are 0, 1, and 3, giving a maximal path quality of 0 + 32 + 43 = 75.
Example 2:
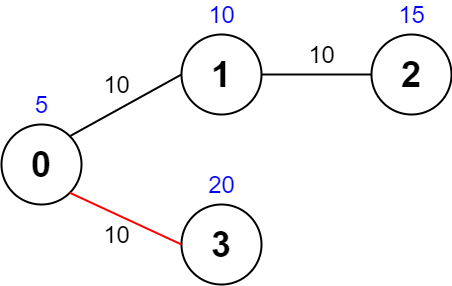
Input: values = [5,10,15,20], edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,10],[0,3,10]], maxTime = 30 Output: 25 Explanation: One possible path is 0 -> 3 -> 0. The total time taken is 10 + 10 = 20 <= 30. The nodes visited are 0 and 3, giving a maximal path quality of 5 + 20 = 25.
Example 3:
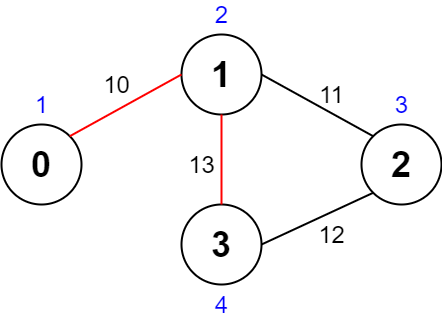
Input: values = [1,2,3,4], edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,11],[2,3,12],[1,3,13]], maxTime = 50 Output: 7 Explanation: One possible path is 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 1 -> 0. The total time taken is 10 + 13 + 13 + 10 = 46 <= 50. The nodes visited are 0, 1, and 3, giving a maximal path quality of 1 + 2 + 4 = 7.
Constraints:
n == values.length1 <= n <= 10000 <= values[i] <= 1080 <= edges.length <= 2000edges[j].length == 30 <= uj < vj <= n - 110 <= timej, maxTime <= 100- All the pairs
[uj, vj]are unique. - There are at most four edges connected to each node.
- The graph may not be connected.
We observe the data range of the problem and find that the number of edges in each valid path starting from
First, we store the edges of the graph in the adjacency list
The logic of the function
- If the current node number
$u$ equals$0$ , it means we have returned to the starting point, so we update the answer to$\max(\text{ans}, \text{value})$ ; - For each neighbor node
$v$ of the current node$u$ , if the current path's cost time plus the time$t$ of the edge$(u, v)$ does not exceed$\text{maxTime}$ , then we can choose to continue visiting node$v$ ;- If node
$v$ has already been visited, we directly recursively call$\text{dfs}(v, \text{cost} + t, \text{value})$ ; - If node
$v$ has not been visited, we mark node$v$ as visited, then recursively call$\text{dfs}(v, \text{cost} + t, \text{value} + \text{values}[v])$ , and finally restore the visit status of node$v$ .
- If node
In the main function, we call
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def maximalPathQuality(
self, values: List[int], edges: List[List[int]], maxTime: int
) -> int:
def dfs(u: int, cost: int, value: int):
if u == 0:
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, value)
for v, t in g[u]:
if cost + t <= maxTime:
if vis[v]:
dfs(v, cost + t, value)
else:
vis[v] = True
dfs(v, cost + t, value + values[v])
vis[v] = False
n = len(values)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, t in edges:
g[u].append((v, t))
g[v].append((u, t))
vis = [False] * n
vis[0] = True
ans = 0
dfs(0, 0, values[0])
return ansclass Solution {
private List<int[]>[] g;
private boolean[] vis;
private int[] values;
private int maxTime;
private int ans;
public int maximalPathQuality(int[] values, int[][] edges, int maxTime) {
int n = values.length;
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], t = e[2];
g[u].add(new int[] {v, t});
g[v].add(new int[] {u, t});
}
vis = new boolean[n];
vis[0] = true;
this.values = values;
this.maxTime = maxTime;
dfs(0, 0, values[0]);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int u, int cost, int value) {
if (u == 0) {
ans = Math.max(ans, value);
}
for (var e : g[u]) {
int v = e[0], t = e[1];
if (cost + t <= maxTime) {
if (vis[v]) {
dfs(v, cost + t, value);
} else {
vis[v] = true;
dfs(v, cost + t, value + values[v]);
vis[v] = false;
}
}
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maximalPathQuality(vector<int>& values, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int maxTime) {
int n = values.size();
vector<pair<int, int>> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], t = e[2];
g[u].emplace_back(v, t);
g[v].emplace_back(u, t);
}
bool vis[n];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
vis[0] = true;
int ans = 0;
auto dfs = [&](auto&& dfs, int u, int cost, int value) -> void {
if (u == 0) {
ans = max(ans, value);
}
for (auto& [v, t] : g[u]) {
if (cost + t <= maxTime) {
if (vis[v]) {
dfs(dfs, v, cost + t, value);
} else {
vis[v] = true;
dfs(dfs, v, cost + t, value + values[v]);
vis[v] = false;
}
}
}
};
dfs(dfs, 0, 0, values[0]);
return ans;
}
};func maximalPathQuality(values []int, edges [][]int, maxTime int) (ans int) {
n := len(values)
g := make([][][2]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
u, v, t := e[0], e[1], e[2]
g[u] = append(g[u], [2]int{v, t})
g[v] = append(g[v], [2]int{u, t})
}
vis := make([]bool, n)
vis[0] = true
var dfs func(u, cost, value int)
dfs = func(u, cost, value int) {
if u == 0 {
ans = max(ans, value)
}
for _, e := range g[u] {
v, t := e[0], e[1]
if cost+t <= maxTime {
if vis[v] {
dfs(v, cost+t, value)
} else {
vis[v] = true
dfs(v, cost+t, value+values[v])
vis[v] = false
}
}
}
}
dfs(0, 0, values[0])
return
}function maximalPathQuality(values: number[], edges: number[][], maxTime: number): number {
const n = values.length;
const g: [number, number][][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [u, v, t] of edges) {
g[u].push([v, t]);
g[v].push([u, t]);
}
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
vis[0] = true;
let ans = 0;
const dfs = (u: number, cost: number, value: number) => {
if (u === 0) {
ans = Math.max(ans, value);
}
for (const [v, t] of g[u]) {
if (cost + t <= maxTime) {
if (vis[v]) {
dfs(v, cost + t, value);
} else {
vis[v] = true;
dfs(v, cost + t, value + values[v]);
vis[v] = false;
}
}
}
};
dfs(0, 0, values[0]);
return ans;
}