| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
A room is represented by a 0-indexed 2D binary matrix room where a 0 represents an empty space and a 1 represents a space with an object. The top left corner of the room will be empty in all test cases.
A cleaning robot starts at the top left corner of the room and is facing right. The robot will continue heading straight until it reaches the edge of the room or it hits an object, after which it will turn 90 degrees clockwise and repeat this process. The starting space and all spaces that the robot visits are cleaned by it.
Return the number of clean spaces in the room if the robot runs indefinitely.
Example 1:
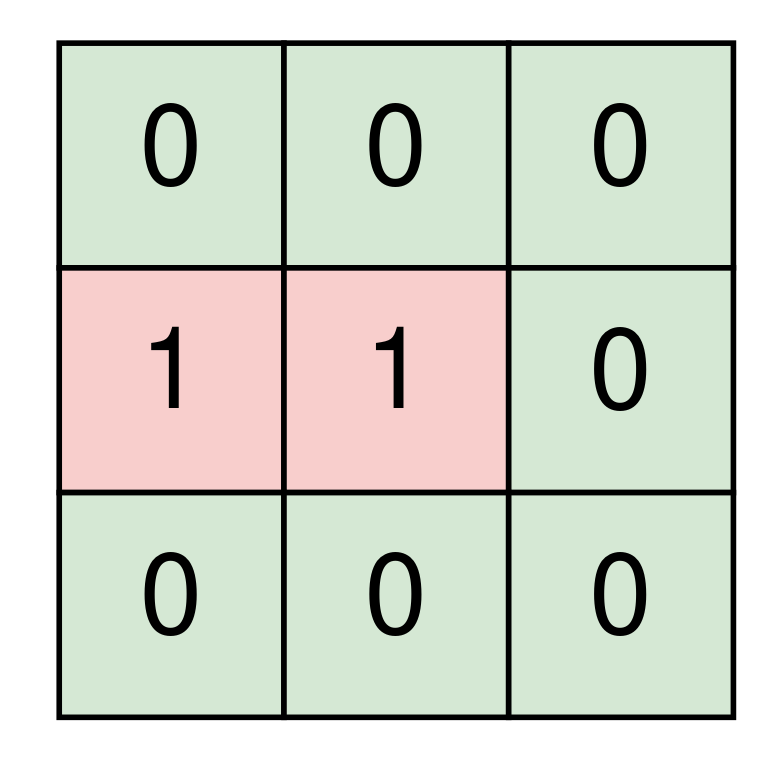
Input: room = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 7
Explanation:
- The robot cleans the spaces at (0, 0), (0, 1), and (0, 2).
- The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces down.
- The robot cleans the spaces at (1, 2), and (2, 2).
- The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces left.
- The robot cleans the spaces at (2, 1), and (2, 0).
- The robot has cleaned all 7 empty spaces, so return 7.
Example 2:
Input: room = [[0,1,0],[1,0,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 1
Explanation:
- The robot cleans the space at (0, 0).
- The robot hits an object, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces down.
- The robot hits an object, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces left.
- The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces up.
- The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces right.
- The robot is back at its starting position.
- The robot has cleaned 1 space, so return 1.
Example 3:
Input: room = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 8
Constraints:
m == room.lengthn == room[r].length1 <= m, n <= 300room[r][c]is either0or1.room[0][0] == 0
class Solution:
def numberOfCleanRooms(self, room: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i, j, k):
if (i, j, k) in vis:
return
nonlocal ans
ans += room[i][j] == 0
room[i][j] = -1
vis.add((i, j, k))
x, y = i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]
if 0 <= x < len(room) and 0 <= y < len(room[0]) and room[x][y] != 1:
dfs(x, y, k)
else:
dfs(i, j, (k + 1) % 4)
vis = set()
dirs = (0, 1, 0, -1, 0)
ans = 0
dfs(0, 0, 0)
return ansclass Solution {
private boolean[][][] vis;
private int[][] room;
private int ans;
public int numberOfCleanRooms(int[][] room) {
vis = new boolean[room.length][room[0].length][4];
this.room = room;
dfs(0, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i, int j, int k) {
if (vis[i][j][k]) {
return;
}
int[] dirs = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
ans += room[i][j] == 0 ? 1 : 0;
room[i][j] = -1;
vis[i][j][k] = true;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < room.length && y >= 0 && y < room[0].length && room[x][y] != 1) {
dfs(x, y, k);
} else {
dfs(i, j, (k + 1) % 4);
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numberOfCleanRooms(vector<vector<int>>& room) {
int m = room.size(), n = room[0].size();
bool vis[m][n][4];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int ans = 0;
function<void(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int j, int k) {
if (vis[i][j][k]) {
return;
}
ans += room[i][j] == 0;
room[i][j] = -1;
vis[i][j][k] = true;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && room[x][y] != 1) {
dfs(x, y, k);
} else {
dfs(i, j, (k + 1) % 4);
}
};
dfs(0, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
};func numberOfCleanRooms(room [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(room), len(room[0])
vis := make([][][4]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([][4]bool, n)
}
dirs := [5]int{0, 1, 0, -1, 0}
var dfs func(i, j, k int)
dfs = func(i, j, k int) {
if vis[i][j][k] {
return
}
if room[i][j] == 0 {
ans++
room[i][j] = -1
}
vis[i][j][k] = true
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && room[x][y] != 1 {
dfs(x, y, k)
} else {
dfs(i, j, (k+1)%4)
}
}
dfs(0, 0, 0)
return
}class Solution:
def numberOfCleanRooms(self, room: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dirs = (0, 1, 0, -1, 0)
i = j = k = 0
ans = 0
vis = set()
while (i, j, k) not in vis:
vis.add((i, j, k))
ans += room[i][j] == 0
room[i][j] = -1
x, y = i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]
if 0 <= x < len(room) and 0 <= y < len(room[0]) and room[x][y] != 1:
i, j = x, y
else:
k = (k + 1) % 4
return ansclass Solution {
public int numberOfCleanRooms(int[][] room) {
int[] dirs = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
int m = room.length, n = room[0].length;
boolean[][][] vis = new boolean[m][n][4];
int ans = 0;
while (!vis[i][j][k]) {
vis[i][j][k] = true;
ans += room[i][j] == 0 ? 1 : 0;
room[i][j] = -1;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && room[x][y] != 1) {
i = x;
j = y;
} else {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numberOfCleanRooms(vector<vector<int>>& room) {
int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
int m = room.size(), n = room[0].size();
bool vis[m][n][4];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
int ans = 0;
while (!vis[i][j][k]) {
vis[i][j][k] = true;
ans += room[i][j] == 0 ? 1 : 0;
room[i][j] = -1;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && room[x][y] != 1) {
i = x;
j = y;
} else {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func numberOfCleanRooms(room [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(room), len(room[0])
vis := make([][][4]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([][4]bool, n)
}
dirs := [5]int{0, 1, 0, -1, 0}
var i, j, k int
for !vis[i][j][k] {
vis[i][j][k] = true
if room[i][j] == 0 {
ans++
room[i][j] = -1
}
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && room[x][y] != 1 {
i, j = x, y
} else {
k = (k + 1) % 4
}
}
return
}