| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
1307 |
Biweekly Contest 62 Q1 |
|
You are given a 0-indexed 1-dimensional (1D) integer array original, and two integers, m and n. You are tasked with creating a 2-dimensional (2D) array with m rows and n columns using all the elements from original.
The elements from indices 0 to n - 1 (inclusive) of original should form the first row of the constructed 2D array, the elements from indices n to 2 * n - 1 (inclusive) should form the second row of the constructed 2D array, and so on.
Return an m x n 2D array constructed according to the above procedure, or an empty 2D array if it is impossible.
Example 1:
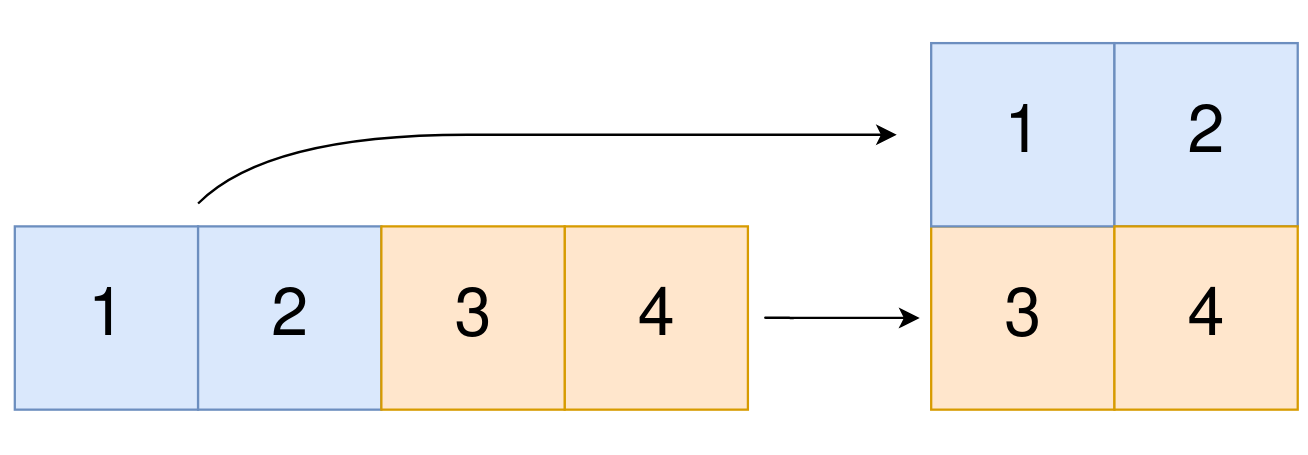
Input: original = [1,2,3,4], m = 2, n = 2 Output: [[1,2],[3,4]] Explanation: The constructed 2D array should contain 2 rows and 2 columns. The first group of n=2 elements in original, [1,2], becomes the first row in the constructed 2D array. The second group of n=2 elements in original, [3,4], becomes the second row in the constructed 2D array.
Example 2:
Input: original = [1,2,3], m = 1, n = 3 Output: [[1,2,3]] Explanation: The constructed 2D array should contain 1 row and 3 columns. Put all three elements in original into the first row of the constructed 2D array.
Example 3:
Input: original = [1,2], m = 1, n = 1 Output: [] Explanation: There are 2 elements in original. It is impossible to fit 2 elements in a 1x1 2D array, so return an empty 2D array.
Constraints:
1 <= original.length <= 5 * 1041 <= original[i] <= 1051 <= m, n <= 4 * 104
According to the problem description, we know that to construct an
If it does satisfy, we can follow the process described in the problem, and put the elements from the original array into the two-dimensional array in order.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def construct2DArray(self, original: List[int], m: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if m * n != len(original):
return []
return [original[i : i + n] for i in range(0, m * n, n)]class Solution {
public int[][] construct2DArray(int[] original, int m, int n) {
if (m * n != original.length) {
return new int[0][0];
}
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
ans[i][j] = original[i * n + j];
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> construct2DArray(vector<int>& original, int m, int n) {
if (m * n != original.size()) {
return {};
}
vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
ans[i][j] = original[i * n + j];
}
}
return ans;
}
};func construct2DArray(original []int, m int, n int) (ans [][]int) {
if m*n != len(original) {
return [][]int{}
}
for i := 0; i < m*n; i += n {
ans = append(ans, original[i:i+n])
}
return
}function construct2DArray(original: number[], m: number, n: number): number[][] {
if (m * n != original.length) {
return [];
}
const ans: number[][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m * n; i += n) {
ans.push(original.slice(i, i + n));
}
return ans;
}/**
* @param {number[]} original
* @param {number} m
* @param {number} n
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var construct2DArray = function (original, m, n) {
if (m * n != original.length) {
return [];
}
const ans = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m * n; i += n) {
ans.push(original.slice(i, i + n));
}
return ans;
};