| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
2078 |
Weekly Contest 231 Q3 |
|
There is an undirected weighted connected graph. You are given a positive integer n which denotes that the graph has n nodes labeled from 1 to n, and an array edges where each edges[i] = [ui, vi, weighti] denotes that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi with weight equal to weighti.
A path from node start to node end is a sequence of nodes [z0, z1, z2, ..., zk] such that z0 = start and zk = end and there is an edge between zi and zi+1 where 0 <= i <= k-1.
The distance of a path is the sum of the weights on the edges of the path. Let distanceToLastNode(x) denote the shortest distance of a path between node n and node x. A restricted path is a path that also satisfies that distanceToLastNode(zi) > distanceToLastNode(zi+1) where 0 <= i <= k-1.
Return the number of restricted paths from node 1 to node n. Since that number may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
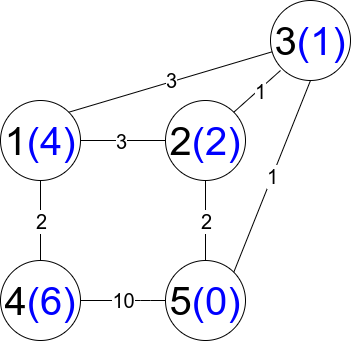
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[2,3,1],[1,4,2],[5,2,2],[3,5,1],[5,4,10]]
Output: 3
Explanation: Each circle contains the node number in black and its distanceToLastNode value in blue. The three restricted paths are:
1) 1 --> 2 --> 5
2) 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 5
3) 1 --> 3 --> 5
Example 2:
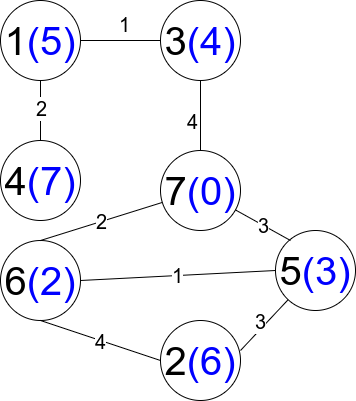
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,3,1],[4,1,2],[7,3,4],[2,5,3],[5,6,1],[6,7,2],[7,5,3],[2,6,4]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Each circle contains the node number in black and its distanceToLastNode value in blue. The only restricted path is 1 --> 3 --> 7.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 104n - 1 <= edges.length <= 4 * 104edges[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi1 <= weighti <= 105- There is at most one edge between any two nodes.
- There is at least one path between any two nodes.
class Solution:
def countRestrictedPaths(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
@cache
def dfs(i):
if i == n:
return 1
ans = 0
for j, _ in g[i]:
if dist[i] > dist[j]:
ans = (ans + dfs(j)) % mod
return ans
g = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, w in edges:
g[u].append((v, w))
g[v].append((u, w))
q = [(0, n)]
dist = [inf] * (n + 1)
dist[n] = 0
mod = 10**9 + 7
while q:
_, u = heappop(q)
for v, w in g[u]:
if dist[v] > dist[u] + w:
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
heappush(q, (dist[v], v))
return dfs(1)class Solution {
private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static final int MOD = (int) 1e9 + 7;
private List<int[]>[] g;
private int[] dist;
private int[] f;
private int n;
public int countRestrictedPaths(int n, int[][] edges) {
this.n = n;
g = new List[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; ++i) {
g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2];
g[u].add(new int[] {v, w});
g[v].add(new int[] {u, w});
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
q.offer(new int[] {0, n});
dist = new int[n + 1];
f = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
Arrays.fill(f, -1);
dist[n] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int u = p[1];
for (int[] ne : g[u]) {
int v = ne[0], w = ne[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
q.offer(new int[] {dist[v], v});
}
}
}
return dfs(1);
}
private int dfs(int i) {
if (f[i] != -1) {
return f[i];
}
if (i == n) {
return 1;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int[] ne : g[i]) {
int j = ne[0];
if (dist[i] > dist[j]) {
ans = (ans + dfs(j)) % MOD;
}
}
f[i] = ans;
return ans;
}
}using pii = pair<int, int>;
class Solution {
public:
const int inf = INT_MAX;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
vector<vector<pii>> g;
vector<int> dist;
vector<int> f;
int n;
int countRestrictedPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
this->n = n;
g.resize(n + 1);
dist.assign(n + 1, inf);
f.assign(n + 1, -1);
dist[n] = 0;
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2];
g[u].emplace_back(v, w);
g[v].emplace_back(u, w);
}
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii>> q;
q.emplace(0, n);
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [_, u] = q.top();
q.pop();
for (auto [v, w] : g[u]) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
q.emplace(dist[v], v);
}
}
}
return dfs(1);
}
int dfs(int i) {
if (f[i] != -1) return f[i];
if (i == n) return 1;
int ans = 0;
for (auto [j, _] : g[i]) {
if (dist[i] > dist[j]) {
ans = (ans + dfs(j)) % mod;
}
}
f[i] = ans;
return ans;
}
};const inf = math.MaxInt32
const mod = 1e9 + 7
type pair struct {
first int
second int
}
var _ heap.Interface = (*pairs)(nil)
type pairs []pair
func (a pairs) Len() int { return len(a) }
func (a pairs) Less(i int, j int) bool {
return a[i].first < a[j].first || a[i].first == a[j].first && a[i].second < a[j].second
}
func (a pairs) Swap(i int, j int) { a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] }
func (a *pairs) Push(x any) { *a = append(*a, x.(pair)) }
func (a *pairs) Pop() any { l := len(*a); t := (*a)[l-1]; *a = (*a)[:l-1]; return t }
func countRestrictedPaths(n int, edges [][]int) int {
g := make([]pairs, n+1)
for _, e := range edges {
u, v, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
g[u] = append(g[u], pair{v, w})
g[v] = append(g[v], pair{u, w})
}
dist := make([]int, n+1)
f := make([]int, n+1)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = inf
f[i] = -1
}
dist[n] = 0
h := make(pairs, 0)
heap.Push(&h, pair{0, n})
for len(h) > 0 {
u := heap.Pop(&h).(pair).second
for _, ne := range g[u] {
v, w := ne.first, ne.second
if dist[v] > dist[u]+w {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
heap.Push(&h, pair{dist[v], v})
}
}
}
var dfs func(int) int
dfs = func(i int) int {
if f[i] != -1 {
return f[i]
}
if i == n {
return 1
}
ans := 0
for _, ne := range g[i] {
j := ne.first
if dist[i] > dist[j] {
ans = (ans + dfs(j)) % mod
}
}
f[i] = ans
return ans
}
return dfs(1)
}class Solution:
def countRestrictedPaths(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, w in edges:
g[u].append((v, w))
g[v].append((u, w))
dist = [inf] * (n + 1)
dist[n] = 0
q = [(0, n)]
mod = 10**9 + 7
while q:
_, u = heappop(q)
for v, w in g[u]:
if dist[v] > dist[u] + w:
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
heappush(q, (dist[v], v))
arr = list(range(1, n + 1))
arr.sort(key=lambda i: dist[i])
f = [0] * (n + 1)
f[n] = 1
for i in arr:
for j, _ in g[i]:
if dist[i] > dist[j]:
f[i] = (f[i] + f[j]) % mod
return f[1]class Solution {
private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static final int MOD = (int) 1e9 + 7;
public int countRestrictedPaths(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<int[]>[] g = new List[n + 1];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2];
g[u].add(new int[] {v, w});
g[v].add(new int[] {u, w});
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
q.offer(new int[] {0, n});
int[] dist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[n] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int u = p[1];
for (int[] ne : g[u]) {
int v = ne[0], w = ne[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
q.offer(new int[] {dist[v], v});
}
}
}
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
f[n] = 1;
Integer[] arr = new Integer[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
Arrays.sort(arr, (i, j) -> dist[i] - dist[j]);
for (int i : arr) {
for (int[] ne : g[i]) {
int j = ne[0];
if (dist[i] > dist[j]) {
f[i] = (f[i] + f[j]) % MOD;
}
}
}
return f[1];
}
}