| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1428 |
Biweekly Contest 40 Q2 |
|
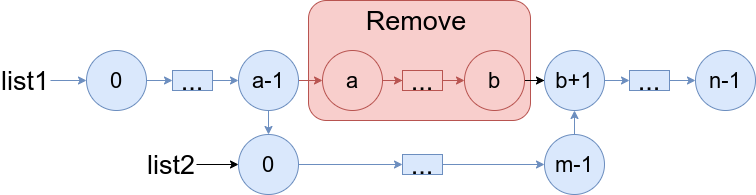
You are given two linked lists: list1 and list2 of sizes n and m respectively.
Remove list1's nodes from the ath node to the bth node, and put list2 in their place.
The blue edges and nodes in the following figure indicate the result:
Build the result list and return its head.
Example 1:
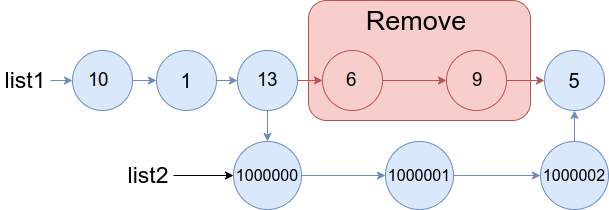
Input: list1 = [10,1,13,6,9,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002] Output: [10,1,13,1000000,1000001,1000002,5] Explanation: We remove the nodes 3 and 4 and put the entire list2 in their place. The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Example 2:
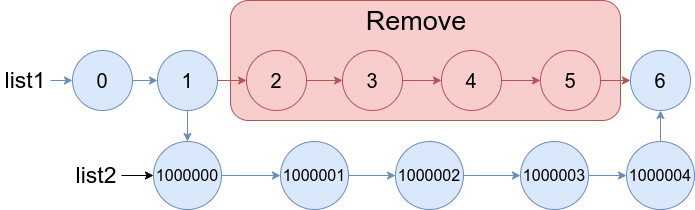
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6], a = 2, b = 5, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004] Output: [0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6] Explanation: The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Constraints:
3 <= list1.length <= 1041 <= a <= b < list1.length - 11 <= list2.length <= 104
We can directly simulate the operations described in the problem.
In the implementation, we use two pointers list1.
Then we move pointers list1, and pointer list1. At this point, we set the next pointer of list2, and set the next pointer of the tail node of list2 to the node pointed to by the next pointer of
The time complexity is list1 and list2 respectively.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeInBetween(
self, list1: ListNode, a: int, b: int, list2: ListNode
) -> ListNode:
p = q = list1
for _ in range(a - 1):
p = p.next
for _ in range(b):
q = q.next
p.next = list2
while p.next:
p = p.next
p.next = q.next
q.next = None
return list1/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p = list1, q = list1;
while (--a > 0) {
p = p.next;
}
while (b-- > 0) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = list2;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = q.next;
q.next = null;
return list1;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) {
auto p = list1, q = list1;
while (--a) {
p = p->next;
}
while (b--) {
q = q->next;
}
p->next = list2;
while (p->next) {
p = p->next;
}
p->next = q->next;
q->next = nullptr;
return list1;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func mergeInBetween(list1 *ListNode, a int, b int, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
p, q := list1, list1
for ; a > 1; a-- {
p = p.Next
}
for ; b > 0; b-- {
q = q.Next
}
p.Next = list2
for p.Next != nil {
p = p.Next
}
p.Next = q.Next
q.Next = nil
return list1
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function mergeInBetween(
list1: ListNode | null,
a: number,
b: number,
list2: ListNode | null,
): ListNode | null {
let p = list1;
let q = list1;
while (--a > 0) {
p = p.next;
}
while (b-- > 0) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = list2;
while (p.next) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = q.next;
q.next = null;
return list1;
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode MergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p = list1, q = list1;
while (--a > 0) {
p = p.next;
}
while (b-- > 0) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = list2;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = q.next;
q.next = null;
return list1;
}
}