| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1407 |
第 172 场周赛 Q3 |
|
给你一棵以 root 为根的二叉树和一个整数 target ,请你删除所有值为 target 的 叶子节点 。
注意,一旦删除值为 target 的叶子节点,它的父节点就可能变成叶子节点;如果新叶子节点的值恰好也是 target ,那么这个节点也应该被删除。
也就是说,你需要重复此过程直到不能继续删除。
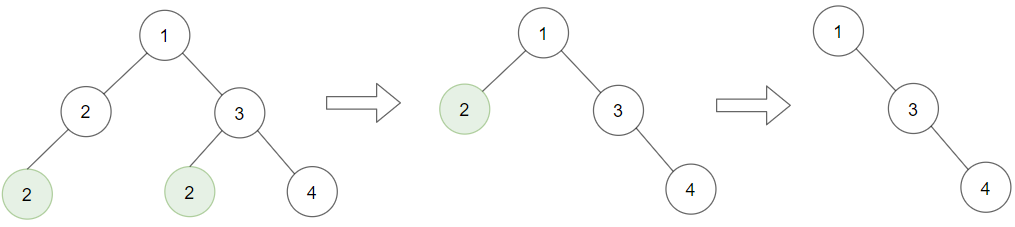
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2 输出:[1,null,3,null,4] 解释: 上面左边的图中,绿色节点为叶子节点,且它们的值与 target 相同(同为 2 ),它们会被删除,得到中间的图。 有一个新的节点变成了叶子节点且它的值与 target 相同,所以将再次进行删除,从而得到最右边的图。
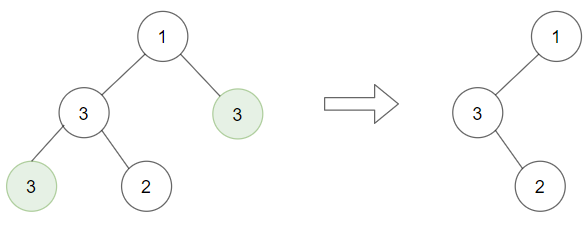
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3 输出:[1,3,null,null,2]
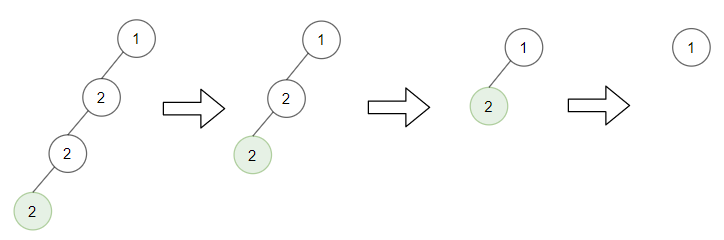
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2 输出:[1] 解释:每一步都删除一个绿色的叶子节点(值为 2)。
提示:
- 树中节点数量的范围是
[1, 3000]。 1 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
我们先判断
否则,递归地处理 root.left = removeLeafNodes(root.left, target) 和 root.right = removeLeafNodes(root.right, target)。
然后判断
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def removeLeafNodes(
self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: int
) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
root.left = self.removeLeafNodes(root.left, target)
root.right = self.removeLeafNodes(root.right, target)
if root.left is None and root.right is None and root.val == target:
return None
return root/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode removeLeafNodes(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
root.left = removeLeafNodes(root.left, target);
root.right = removeLeafNodes(root.right, target);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == target) {
return null;
}
return root;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* removeLeafNodes(TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (!root) {
return nullptr;
}
root->left = removeLeafNodes(root->left, target);
root->right = removeLeafNodes(root->right, target);
if (!root->left && !root->right && root->val == target) {
return nullptr;
}
return root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func removeLeafNodes(root *TreeNode, target int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
root.Left = removeLeafNodes(root.Left, target)
root.Right = removeLeafNodes(root.Right, target)
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && root.Val == target {
return nil
}
return root
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function removeLeafNodes(root: TreeNode | null, target: number): TreeNode | null {
if (!root) {
return null;
}
root.left = removeLeafNodes(root.left, target);
root.right = removeLeafNodes(root.right, target);
if (!root.left && !root.right && root.val == target) {
return null;
}
return root;
}