| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1389 |
Biweekly Contest 10 Q2 |
|
Given the roots of two binary search trees, root1 and root2, return true if and only if there is a node in the first tree and a node in the second tree whose values sum up to a given integer target.
Example 1:
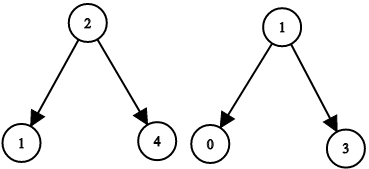
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3], target = 5 Output: true Explanation: 2 and 3 sum up to 5.
Example 2:
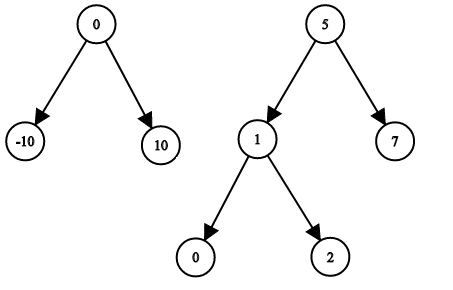
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2], target = 18 Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. -109 <= Node.val, target <= 109
We perform in-order traversals on the two trees separately, obtaining two sorted arrays
Initialize two pointers
Each time, compare the sum true; otherwise, if
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def twoSumBSTs(
self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode], target: int
) -> bool:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode], i: int):
if root is None:
return
dfs(root.left, i)
nums[i].append(root.val)
dfs(root.right, i)
nums = [[], []]
dfs(root1, 0)
dfs(root2, 1)
i, j = 0, len(nums[1]) - 1
while i < len(nums[0]) and ~j:
x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j]
if x == target:
return True
if x < target:
i += 1
else:
j -= 1
return False/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] nums = new List[2];
public boolean twoSumBSTs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2, int target) {
Arrays.setAll(nums, k -> new ArrayList<>());
dfs(root1, 0);
dfs(root2, 1);
int i = 0, j = nums[1].size() - 1;
while (i < nums[0].size() && j >= 0) {
int x = nums[0].get(i) + nums[1].get(j);
if (x == target) {
return true;
}
if (x < target) {
++i;
} else {
--j;
}
}
return false;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int i) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left, i);
nums[i].add(root.val);
dfs(root.right, i);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool twoSumBSTs(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2, int target) {
vector<int> nums[2];
function<void(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int i) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root->left, i);
nums[i].push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right, i);
};
dfs(root1, 0);
dfs(root2, 1);
int i = 0, j = nums[1].size() - 1;
while (i < nums[0].size() && j >= 0) {
int x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j];
if (x == target) {
return true;
}
if (x < target) {
++i;
} else {
--j;
}
}
return false;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func twoSumBSTs(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode, target int) bool {
nums := [2][]int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, i int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Left, i)
nums[i] = append(nums[i], root.Val)
dfs(root.Right, i)
}
dfs(root1, 0)
dfs(root2, 1)
i, j := 0, len(nums[1])-1
for i < len(nums[0]) && j >= 0 {
x := nums[0][i] + nums[1][j]
if x == target {
return true
}
if x < target {
i++
} else {
j--
}
}
return false
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function twoSumBSTs(root1: TreeNode | null, root2: TreeNode | null, target: number): boolean {
const nums: number[][] = Array(2)
.fill(0)
.map(() => []);
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, i: number) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left, i);
nums[i].push(root.val);
dfs(root.right, i);
};
dfs(root1, 0);
dfs(root2, 1);
let i = 0;
let j = nums[1].length - 1;
while (i < nums[0].length && j >= 0) {
const x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j];
if (x === target) {
return true;
}
if (x < target) {
++i;
} else {
--j;
}
}
return false;
}