| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
On an 8 x 8 chessboard, there is exactly one white rook 'R' and some number of white bishops 'B', black pawns 'p', and empty squares '.'.
When the rook moves, it chooses one of four cardinal directions (north, east, south, or west), then moves in that direction until it chooses to stop, reaches the edge of the board, captures a black pawn, or is blocked by a white bishop. A rook is considered attacking a pawn if the rook can capture the pawn on the rook's turn. The number of available captures for the white rook is the number of pawns that the rook is attacking.
Return the number of available captures for the white rook.
Example 1:
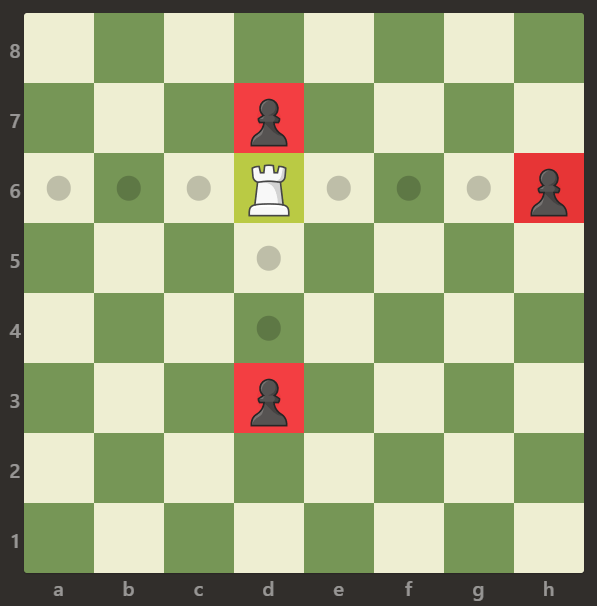
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","R",".",".",".","p"],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]] Output: 3 Explanation: In this example, the rook is attacking all the pawns.
Example 2:
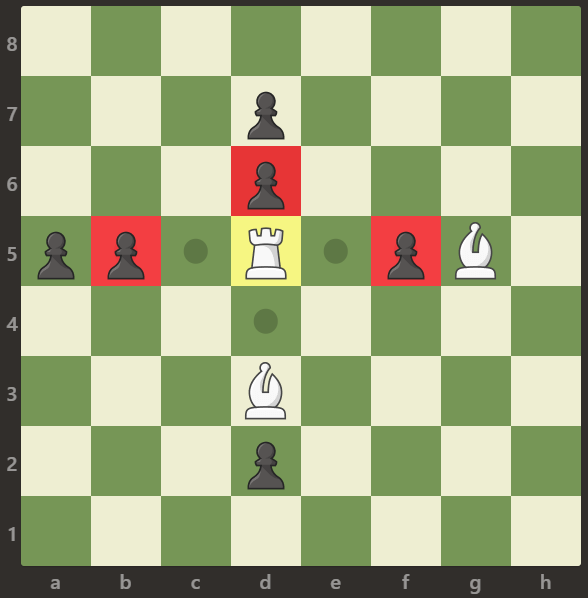
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","B","R","B","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]] Output: 0 Explanation: The bishops are blocking the rook from attacking any of the pawns.
Example 3:
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],["p","p",".","R",".","p","B","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","B",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]] Output: 3 Explanation: The rook is attacking the pawns at positions b5, d6, and f5.
Constraints:
board.length == 8board[i].length == 8board[i][j]is either'R','.','B', or'p'- There is exactly one cell with
board[i][j] == 'R'
First, we traverse the chessboard to find the position of the rook
- If we encounter a bishop or a boundary, we stop traversing in that direction.
- If we encounter a pawn, we increment the answer by one, and then stop traversing in that direction.
- Otherwise, we continue traversing.
After traversing in all four directions, we can get the answer.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def numRookCaptures(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> int:
ans = 0
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
if board[i][j] == "R":
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i, j
while 0 <= x + a < 8 and 0 <= y + b < 8:
x, y = x + a, y + b
if board[x][y] == "p":
ans += 1
break
if board[x][y] == "B":
break
return ansclass Solution {
public int numRookCaptures(char[][] board) {
int ans = 0;
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 'R') {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i, y = j;
int a = dirs[k], b = dirs[k + 1];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < 8 && y + b >= 0 && y + b < 8
&& board[x + a][y + b] != 'B') {
x += a;
y += b;
if (board[x][y] == 'p') {
++ans;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numRookCaptures(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int ans = 0;
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 'R') {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i, y = j;
int a = dirs[k], b = dirs[k + 1];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < 8 && y + b >= 0 && y + b < 8 && board[x + a][y + b] != 'B') {
x += a;
y += b;
if (board[x][y] == 'p') {
++ans;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func numRookCaptures(board [][]byte) (ans int) {
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for i := 0; i < 8; i++ {
for j := 0; j < 8; j++ {
if board[i][j] == 'R' {
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i, j
a, b := dirs[k], dirs[k+1]
for x+a >= 0 && x+a < 8 && y+b >= 0 && y+b < 8 && board[x+a][y+b] != 'B' {
x, y = x+a, y+b
if board[x][y] == 'p' {
ans++
break
}
}
}
}
}
}
return
}