| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are given an m x n grid where each cell can have one of three values:
0representing an empty cell,1representing a fresh orange, or2representing a rotten orange.
Every minute, any fresh orange that is 4-directionally adjacent to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
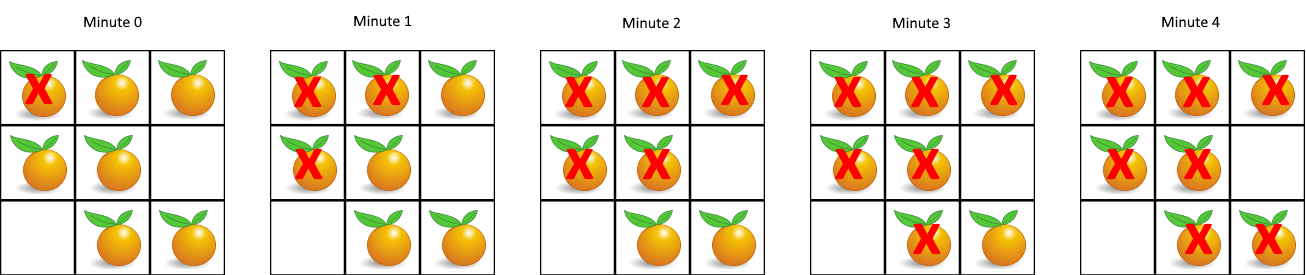
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]] Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]] Output: -1 Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[0,2]] Output: 0 Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10grid[i][j]is0,1, or2.
First, we traverse the entire grid once, count the number of fresh oranges, denoted as
Next, we perform a breadth-first search. In each round of the search, we let all the rotten oranges in the queue rot the fresh oranges in four directions, until the queue is empty or the number of fresh oranges is
Finally, if the number of fresh oranges is
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
q = deque()
cnt = 0
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, x in enumerate(row):
if x == 1:
cnt += 1
elif x == 2:
q.append((i, j))
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
ans = 0
while q and cnt:
ans += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] == 1:
grid[x][y] = 2
q.append((x, y))
cnt -= 1
return -1 if cnt > 0 else ansclass Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
++cnt;
} else if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
q.offer(new int[] {i, j});
}
}
}
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int ans = 0;
for (; !q.isEmpty() && cnt > 0; ++ans) {
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
var p = q.poll();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int x = p[0] + dirs[d], y = p[1] + dirs[d + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
grid[x][y] = 2;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
--cnt;
}
}
}
}
return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
++cnt;
} else if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
q.emplace(i, j);
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
const int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (; q.size() && cnt; ++ans) {
for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int x = i + dirs[d], y = j + dirs[d + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
grid[x][y] = 2;
q.emplace(x, y);
--cnt;
}
}
}
}
return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans;
}
};func orangesRotting(grid [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
q := [][2]int{}
cnt := 0
for i, row := range grid {
for j, x := range row {
if x == 1 {
cnt++
} else if x == 2 {
q = append(q, [2]int{i, j})
}
}
}
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for ; len(q) > 0 && cnt > 0; ans++ {
for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for d := 0; d < 4; d++ {
x, y := p[0]+dirs[d], p[1]+dirs[d+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 {
grid[x][y] = 2
q = append(q, [2]int{x, y})
cnt--
}
}
}
}
if cnt > 0 {
return -1
}
return
}function orangesRotting(grid: number[][]): number {
const m: number = grid.length;
const n: number = grid[0].length;
const q: number[][] = [];
let cnt: number = 0;
for (let i: number = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j: number = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
cnt++;
} else if (grid[i][j] === 2) {
q.push([i, j]);
}
}
}
let ans: number = 0;
const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (; q.length && cnt; ++ans) {
const t: number[][] = [];
for (const [i, j] of q) {
for (let d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
const [x, y] = [i + dirs[d], j + dirs[d + 1]];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] === 1) {
grid[x][y] = 2;
t.push([x, y]);
cnt--;
}
}
}
q.splice(0, q.length, ...t);
}
return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans;
}use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn oranges_rotting(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
let mut cnt = 0;
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
cnt += 1;
} else if grid[i][j] == 2 {
q.push_back(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
}
}
}
let dirs: [i32; 5] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
let mut ans = 0;
while !q.is_empty() && cnt > 0 {
let q_size = q.len();
for _ in 0..q_size {
let p = q.pop_front().unwrap();
for d in 0..4 {
let x = p[0] + dirs[d];
let y = p[1] + dirs[d + 1];
if x >= 0
&& x < (m as i32)
&& y >= 0
&& y < (n as i32)
&& grid[x as usize][y as usize] == 1
{
grid[x as usize][y as usize] = 2;
q.push_back(vec![x, y]);
cnt -= 1;
}
}
}
ans += 1;
}
if cnt > 0 {
return -1;
}
ans
}
}