| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
简单 |
|
给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 后序遍历 。
n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
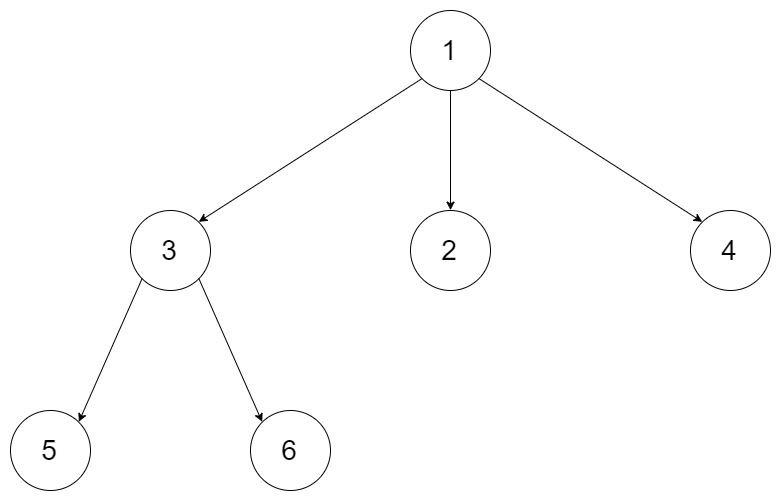
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 输出:[5,6,3,2,4,1]
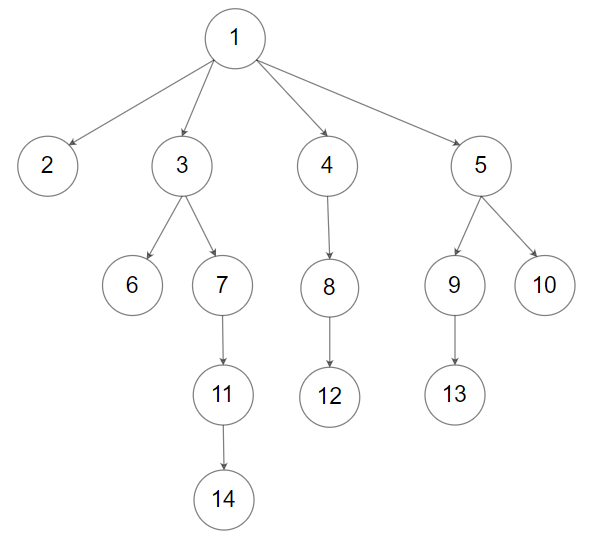
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 输出:[2,6,14,11,7,3,12,8,4,13,9,10,5,1]
提示:
- 节点总数在范围
[0, 104]内 0 <= Node.val <= 104- n 叉树的高度小于或等于
1000
进阶:递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
我们可以递归地遍历整棵树。对于每个节点,先对该节点的每个子节点递归地调用函数,然后将节点的值加入答案。
时间复杂度
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def postorder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[int]:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
for child in root.children:
dfs(child)
ans.append(root.val)
ans = []
dfs(root)
return ans/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
for (Node child : root.children) {
dfs(child);
}
ans.add(root.val);
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> ans;
function<void(Node*)> dfs = [&](Node* root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
for (auto& child : root->children) {
dfs(child);
}
ans.push_back(root->val);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func postorder(root *Node) (ans []int) {
var dfs func(*Node)
dfs = func(root *Node) {
if root == nil {
return
}
for _, child := range root.Children {
dfs(child)
}
ans = append(ans, root.Val)
}
dfs(root)
return
}/**
* Definition for node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* children: Node[]
* constructor(val?: number) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.children = []
* }
* }
*/
function postorder(root: Node | null): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [];
const dfs = (root: Node | null) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
for (const child of root.children) {
dfs(child);
}
ans.push(root.val);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}我们也可以用迭代的方法来解决这个问题。
我们使用一个栈来帮助我们得到后序遍历,我们首先把根节点入栈,因为后序遍历是左子树、右子树、根节点,栈的特点是先进后出,所以我们先把节点的值加入答案,然后对该节点的每个子节点按照从左到右的顺序依次入栈,这样可以得到根节点、右子树、左子树的遍历结果。最后把答案反转即可得到后序遍历的结果。
时间复杂度
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def postorder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[int]:
ans = []
if root is None:
return ans
stk = [root]
while stk:
node = stk.pop()
ans.append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
stk.append(child)
return ans[::-1]/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
LinkedList<Integer> ans = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<Node> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
stk.offer(root);
while (!stk.isEmpty()) {
root = stk.pollLast();
ans.addFirst(root.val);
for (Node child : root.children) {
stk.offer(child);
}
}
return ans;
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> ans;
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
stack<Node*> stk{{root}};
while (!stk.empty()) {
root = stk.top();
ans.push_back(root->val);
stk.pop();
for (Node* child : root->children) {
stk.push(child);
}
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func postorder(root *Node) []int {
var ans []int
if root == nil {
return ans
}
stk := []*Node{root}
for len(stk) > 0 {
root = stk[len(stk)-1]
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
ans = append([]int{root.Val}, ans...)
for _, child := range root.Children {
stk = append(stk, child)
}
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* children: Node[]
* constructor(val?: number) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.children = []
* }
* }
*/
function postorder(root: Node | null): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
const stk: Node[] = [root];
while (stk.length) {
const { val, children } = stk.pop()!;
ans.push(val);
stk.push(...children);
}
return ans.reverse();
}