| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给定一个二叉树,找到其中最大的二叉搜索树(BST)子树,并返回该子树的大小。其中,最大指的是子树节点数最多的。
二叉搜索树(BST)中的所有节点都具备以下属性:
-
左子树的值小于其父(根)节点的值。
-
右子树的值大于其父(根)节点的值。
注意:子树必须包含其所有后代。
示例 1:
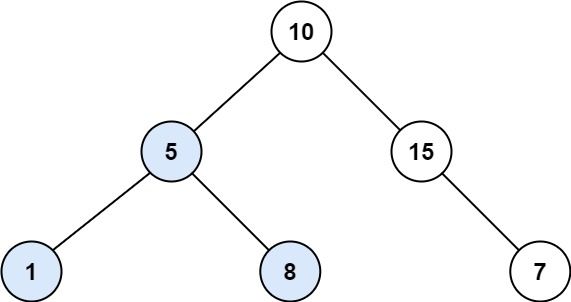
输入:root = [10,5,15,1,8,null,7] 输出:3 解释:本例中最大的 BST 子树是高亮显示的子树。返回值是子树的大小,即 3 。
示例 2:
输入:root = [4,2,7,2,3,5,null,2,null,null,null,null,null,1] 输出:2
提示:
- 树上节点数目的范围是
[0, 104] -104 <= Node.val <= 104
进阶: 你能想出 O(n) 时间复杂度的解法吗?
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def largestBSTSubtree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return inf, -inf, 0
lmi, lmx, ln = dfs(root.left)
rmi, rmx, rn = dfs(root.right)
nonlocal ans
if lmx < root.val < rmi:
ans = max(ans, ln + rn + 1)
return min(lmi, root.val), max(rmx, root.val), ln + rn + 1
return -inf, inf, 0
ans = 0
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans;
public int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new int[] {Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0};
}
int[] left = dfs(root.left);
int[] right = dfs(root.right);
if (left[1] < root.val && root.val < right[0]) {
ans = Math.max(ans, left[2] + right[2] + 1);
return new int[] {
Math.min(root.val, left[0]), Math.max(root.val, right[1]), left[2] + right[2] + 1};
}
return new int[] {Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0};
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans;
int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode* root) {
ans = 0;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
vector<int> dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {INT_MAX, INT_MIN, 0};
auto left = dfs(root->left);
auto right = dfs(root->right);
if (left[1] < root->val && root->val < right[0]) {
ans = max(ans, left[2] + right[2] + 1);
return {min(root->val, left[0]), max(root->val, right[1]), left[2] + right[2] + 1};
}
return {INT_MIN, INT_MAX, 0};
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func largestBSTSubtree(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
var dfs func(root *TreeNode) []int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{math.MaxInt32, math.MinInt32, 0}
}
left := dfs(root.Left)
right := dfs(root.Right)
if left[1] < root.Val && root.Val < right[0] {
ans = max(ans, left[2]+right[2]+1)
return []int{min(root.Val, left[0]), max(root.Val, right[1]), left[2] + right[2] + 1}
}
return []int{math.MinInt32, math.MaxInt32, 0}
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}