| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
Given the root of a binary search tree, a target value, and an integer k, return the k values in the BST that are closest to the target. You may return the answer in any order.
You are guaranteed to have only one unique set of k values in the BST that are closest to the target.
Example 1:
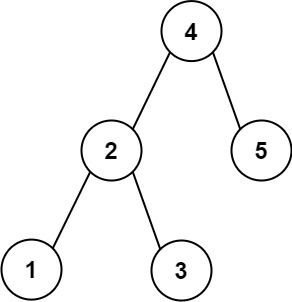
Input: root = [4,2,5,1,3], target = 3.714286, k = 2 Output: [4,3]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 0.000000, k = 1 Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 104.0 <= Node.val <= 109-109 <= target <= 109
Follow up: Assume that the BST is balanced. Could you solve it in less than O(n) runtime (where n = total nodes)?
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestKValues(self, root: TreeNode, target: float, k: int) -> List[int]:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
dfs(root.left)
if len(q) < k:
q.append(root.val)
else:
if abs(root.val - target) >= abs(q[0] - target):
return
q.popleft()
q.append(root.val)
dfs(root.right)
q = deque()
dfs(root)
return list(q)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans;
private double target;
private int k;
public List<Integer> closestKValues(TreeNode root, double target, int k) {
ans = new LinkedList<>();
this.target = target;
this.k = k;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
if (ans.size() < k) {
ans.add(root.val);
} else {
if (Math.abs(root.val - target) >= Math.abs(ans.get(0) - target)) {
return;
}
ans.remove(0);
ans.add(root.val);
}
dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
queue<int> q;
double target;
int k;
vector<int> closestKValues(TreeNode* root, double target, int k) {
this->target = target;
this->k = k;
dfs(root);
vector<int> ans;
while (!q.empty()) {
ans.push_back(q.front());
q.pop();
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
dfs(root->left);
if (q.size() < k)
q.push(root->val);
else {
if (abs(root->val - target) >= abs(q.front() - target)) return;
q.pop();
q.push(root->val);
}
dfs(root->right);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func closestKValues(root *TreeNode, target float64, k int) []int {
var ans []int
var dfs func(root *TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Left)
if len(ans) < k {
ans = append(ans, root.Val)
} else {
if math.Abs(float64(root.Val)-target) >= math.Abs(float64(ans[0])-target) {
return
}
ans = ans[1:]
ans = append(ans, root.Val)
}
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}