There is a grid with n + 2 horizontal bars and m + 2 vertical bars, and initially containing 1 x 1 unit cells.
The bars are 1-indexed.
You are given the two integers, n and m.
You are also given two integer arrays: hBars and vBars.
hBarscontains distinct horizontal bars in the range[2, n + 1].vBarscontains distinct vertical bars in the range[2, m + 1].
You are allowed to remove bars that satisfy any of the following conditions:
- If it is a horizontal bar, it must correspond to a value in
hBars. - If it is a vertical bar, it must correspond to a value in
vBars.
Return an integer denoting the maximum area of a square-shaped hole in the grid after removing some bars (possibly none).
Example 1:
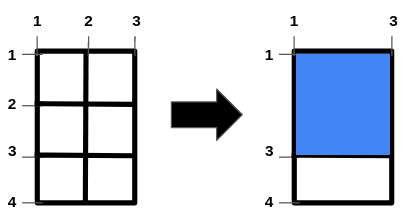
Input: n = 2, m = 1, hBars = [2,3], vBars = [2] Output: 4 Explanation: The left image shows the initial grid formed by the bars. The horizontal bars are in the range [1,4], and the vertical bars are in the range [1,3]. It is allowed to remove horizontal bars [2,3] and the vertical bar [2]. One way to get the maximum square-shaped hole is by removing horizontal bar 2 and vertical bar 2. The resulting grid is shown on the right. The hole has an area of 4. It can be shown that it is not possible to get a square hole with an area more than 4. Hence, the answer is 4.
Example 2:
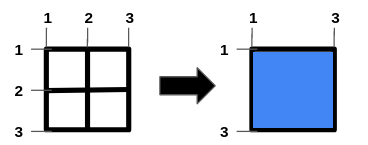
Input: n = 1, m = 1, hBars = [2], vBars = [2] Output: 4 Explanation: The left image shows the initial grid formed by the bars. The horizontal bars are in the range [1,3], and the vertical bars are in the range [1,3]. It is allowed to remove the horizontal bar [2] and the vertical bar [2]. To get the maximum square-shaped hole, we remove horizontal bar 2 and vertical bar 2. The resulting grid is shown on the right. The hole has an area of 4. Hence, the answer is 4, and it is the maximum possible.
Example 3:
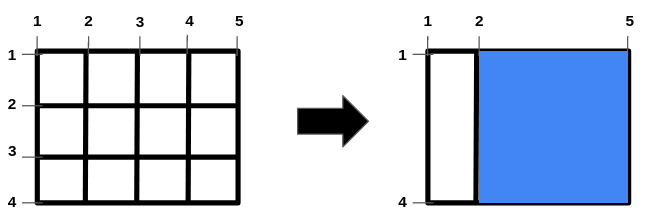
Input: n = 2, m = 3, hBars = [2,3], vBars = [2,3,4] Output: 9 Explanation: The left image shows the initial grid formed by the bars. The horizontal bars are in the range [1,4], and the vertical bars are in the range [1,5]. It is allowed to remove horizontal bars [2,3] and vertical bars [2,3,4]. One way to get the maximum square-shaped hole is by removing horizontal bars 2 and 3, and vertical bars 3 and 4. The resulting grid is shown on the right. The hole has an area of 9. It can be shown that it is not possible to get a square hole with an area more than 9. Hence, the answer is 9.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1091 <= m <= 1091 <= hBars.length <= 1002 <= hBars[i] <= n + 11 <= vBars.length <= 1002 <= vBars[i] <= m + 1- All values in
hBarsare distinct. - All values in
vBarsare distinct.
The problem essentially asks us to find the length of the longest consecutive increasing subsequence in the array, and then add 1 to it.
We define a function
For the array
After finding the length of the longest consecutive increasing subsequence in
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def maximizeSquareHoleArea(
self, n: int, m: int, hBars: List[int], vBars: List[int]
) -> int:
def f(nums: List[int]) -> int:
nums.sort()
ans = cnt = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1:
cnt += 1
ans = max(ans, cnt)
else:
cnt = 1
return ans + 1
return min(f(hBars), f(vBars)) ** 2class Solution {
public int maximizeSquareHoleArea(int n, int m, int[] hBars, int[] vBars) {
int x = Math.min(f(hBars), f(vBars));
return x * x;
}
private int f(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int ans = 1, cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1) {
ans = Math.max(ans, ++cnt);
} else {
cnt = 1;
}
}
return ans + 1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maximizeSquareHoleArea(int n, int m, vector<int>& hBars, vector<int>& vBars) {
auto f = [](vector<int>& nums) {
int ans = 1, cnt = 1;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1) {
ans = max(ans, ++cnt);
} else {
cnt = 1;
}
}
return ans + 1;
};
int x = min(f(hBars), f(vBars));
return x * x;
}
};func maximizeSquareHoleArea(n int, m int, hBars []int, vBars []int) int {
f := func(nums []int) int {
sort.Ints(nums)
ans, cnt := 1, 1
for i, x := range nums[1:] {
if x == nums[i]+1 {
cnt++
ans = max(ans, cnt)
} else {
cnt = 1
}
}
return ans + 1
}
x := min(f(hBars), f(vBars))
return x * x
}function maximizeSquareHoleArea(n: number, m: number, hBars: number[], vBars: number[]): number {
const f = (nums: number[]): number => {
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let [ans, cnt] = [1, 1];
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (nums[i] === nums[i - 1] + 1) {
ans = Math.max(ans, ++cnt);
} else {
cnt = 1;
}
}
return ans + 1;
};
return Math.min(f(hBars), f(vBars)) ** 2;
}impl Solution {
pub fn maximize_square_hole_area(n: i32, m: i32, h_bars: Vec<i32>, v_bars: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let f = |nums: &mut Vec<i32>| -> i32 {
let mut ans = 1;
let mut cnt = 1;
nums.sort();
for i in 1..nums.len() {
if nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1 {
cnt += 1;
ans = ans.max(cnt);
} else {
cnt = 1;
}
}
ans + 1
};
let mut h_bars = h_bars;
let mut v_bars = v_bars;
let x = f(&mut h_bars).min(f(&mut v_bars));
x * x
}
}