You are given a m x n matrix grid consisting of non-negative integers where grid[row][col] represents the minimum time required to be able to visit the cell (row, col), which means you can visit the cell (row, col) only when the time you visit it is greater than or equal to grid[row][col].
You are standing in the top-left cell of the matrix in the 0th second, and you must move to any adjacent cell in the four directions: up, down, left, and right. Each move you make takes 1 second.
Return the minimum time required in which you can visit the bottom-right cell of the matrix. If you cannot visit the bottom-right cell, then return -1.
Example 1:
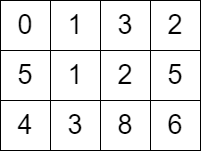
Input: grid = [[0,1,3,2],[5,1,2,5],[4,3,8,6]] Output: 7 Explanation: One of the paths that we can take is the following: - at t = 0, we are on the cell (0,0). - at t = 1, we move to the cell (0,1). It is possible because grid[0][1] <= 1. - at t = 2, we move to the cell (1,1). It is possible because grid[1][1] <= 2. - at t = 3, we move to the cell (1,2). It is possible because grid[1][2] <= 3. - at t = 4, we move to the cell (1,1). It is possible because grid[1][1] <= 4. - at t = 5, we move to the cell (1,2). It is possible because grid[1][2] <= 5. - at t = 6, we move to the cell (1,3). It is possible because grid[1][3] <= 6. - at t = 7, we move to the cell (2,3). It is possible because grid[2][3] <= 7. The final time is 7. It can be shown that it is the minimum time possible.
Example 2:
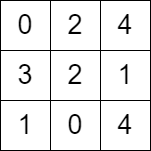
Input: grid = [[0,2,4],[3,2,1],[1,0,4]] Output: -1 Explanation: There is no path from the top left to the bottom-right cell.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 1050 <= grid[i][j] <= 105grid[0][0] == 0
<style type="text/css">.spoilerbutton {display:block; border:dashed; padding: 0px 0px; margin:10px 0px; font-size:150%; font-weight: bold; color:#000000; background-color:cyan; outline:0; } .spoiler {overflow:hidden;} .spoiler > div {-webkit-transition: all 0s ease;-moz-transition: margin 0s ease;-o-transition: all 0s ease;transition: margin 0s ease;} .spoilerbutton[value="Show Message"] + .spoiler > div {margin-top:-500%;} .spoilerbutton[value="Hide Message"] + .spoiler {padding:5px;} </style>
We observe that if we cannot move at the cell
Next, we define
We use a priority queue (min heap) to maintain the cells that can currently move. The elements in the priority queue are
Each time we take out the cell
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def minimumTime(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if grid[0][1] > 1 and grid[1][0] > 1:
return -1
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dist = [[inf] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[0][0] = 0
q = [(0, 0, 0)]
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
while 1:
t, i, j = heappop(q)
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return t
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n:
nt = t + 1
if nt < grid[x][y]:
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - nt) % 2
if nt < dist[x][y]:
dist[x][y] = nt
heappush(q, (nt, x, y))class Solution {
public int minimumTime(int[][] grid) {
if (grid[0][1] > 1 && grid[1][0] > 1) {
return -1;
}
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (var e : dist) {
Arrays.fill(e, 1 << 30);
}
dist[0][0] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
pq.offer(new int[] {0, 0, 0});
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (true) {
var p = pq.poll();
int i = p[1], j = p[2];
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return p[0];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
int nt = p[0] + 1;
if (nt < grid[x][y]) {
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - nt) % 2;
}
if (nt < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = nt;
pq.offer(new int[] {nt, x, y});
}
}
}
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumTime(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
if (grid[0][1] > 1 && grid[1][0] > 1) {
return -1;
}
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int dist[m][n];
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[0][0] = 0;
using tii = tuple<int, int, int>;
priority_queue<tii, vector<tii>, greater<tii>> pq;
pq.emplace(0, 0, 0);
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (1) {
auto [t, i, j] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return t;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
int nt = t + 1;
if (nt < grid[x][y]) {
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y] - nt) % 2;
}
if (nt < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = nt;
pq.emplace(nt, x, y);
}
}
}
}
}
};func minimumTime(grid [][]int) int {
if grid[0][1] > 1 && grid[1][0] > 1 {
return -1
}
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dist := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = 1 << 30
}
}
dist[0][0] = 0
pq := hp{}
heap.Push(&pq, tuple{0, 0, 0})
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for {
p := heap.Pop(&pq).(tuple)
i, j := p.i, p.j
if i == m-1 && j == n-1 {
return p.t
}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
nt := p.t + 1
if nt < grid[x][y] {
nt = grid[x][y] + (grid[x][y]-nt)%2
}
if nt < dist[x][y] {
dist[x][y] = nt
heap.Push(&pq, tuple{nt, x, y})
}
}
}
}
}
type tuple struct{ t, i, j int }
type hp []tuple
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].t < h[j].t }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(tuple)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }