一系列高速公路连接从 0 到 n - 1 的 n 个城市。给定一个二维整数数组 highways,其中 highways[i] = [city1i, city2i, tolli] 表示有一条高速公路连接 city1i 和city2i,允许一辆汽车从 city1i 前往 city2i,反之亦然,费用为 tolli。
给你一个整数 k,你要正好经过 k 条公路。你可以从任何一个城市出发,但在旅途中每个城市最多只能访问一次。
返回您旅行的最大费用。如果没有符合要求的行程,则返回 -1。
示例 1:
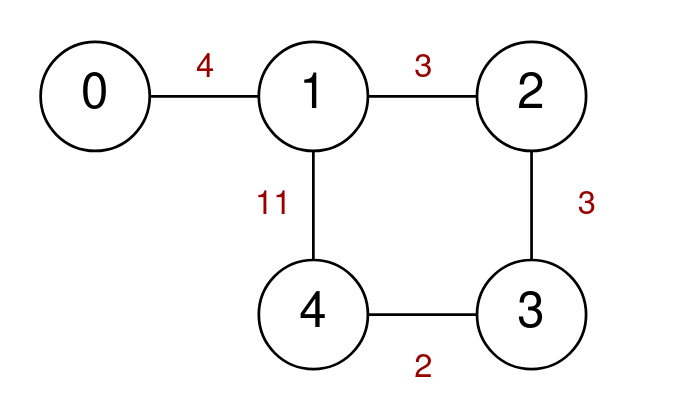
输入: n = 5, highways = [[0,1,4],[2,1,3],[1,4,11],[3,2,3],[3,4,2]], k = 3 输出: 17 解释: 一个可能的路径是从 0 -> 1 -> 4 -> 3。这次旅行的费用是 4 + 11 + 2 = 17。 另一种可能的路径是从 4 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3。这次旅行的费用是 11 + 3 + 3 = 17。 可以证明,17 是任何有效行程的最大可能费用。 注意,旅行 4 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 是不允许的,因为你访问了城市 1 两次。
示例 2:
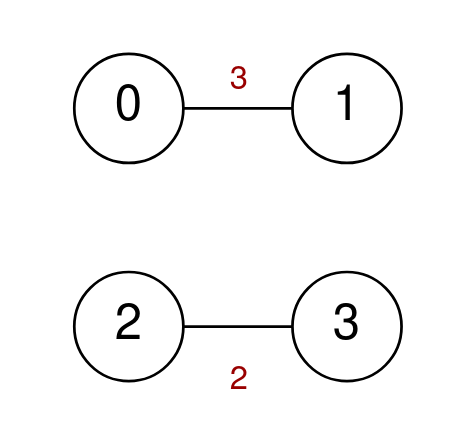
输入: n = 4, highways = [[0,1,3],[2,3,2]], k = 2 输出: -1 解释: 没有长度为 2 的有效行程,因此返回-1。
提示:
2 <= n <= 151 <= highways.length <= 50highways[i].length == 30 <= city1i, city2i <= n - 1city1i != city2i0 <= tolli <= 1001 <= k <= 50-
没有重复的高速公路。
我们注意到,题目要求正好经过
另外,我们也可以发现,城市数量
我们用
考虑
其中
求出
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def maximumCost(self, n: int, highways: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int:
if k >= n:
return -1
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b, cost in highways:
g[a].append((b, cost))
g[b].append((a, cost))
f = [[-inf] * n for _ in range(1 << n)]
for i in range(n):
f[1 << i][i] = 0
ans = -1
for i in range(1 << n):
for j in range(n):
if i >> j & 1:
for h, cost in g[j]:
if i >> h & 1:
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i ^ (1 << j)][h] + cost)
if i.bit_count() == k + 1:
ans = max(ans, f[i][j])
return ansclass Solution {
public int maximumCost(int n, int[][] highways, int k) {
if (k >= n) {
return -1;
}
List<int[]>[] g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, h -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] h : highways) {
int a = h[0], b = h[1], cost = h[2];
g[a].add(new int[] {b, cost});
g[b].add(new int[] {a, cost});
}
int[][] f = new int[1 << n][n];
for (int[] e : f) {
Arrays.fill(e, -(1 << 30));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
f[1 << i][i] = 0;
}
int ans = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((i >> j & 1) == 1) {
for (var e : g[j]) {
int h = e[0], cost = e[1];
if ((i >> h & 1) == 1) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i][j], f[i ^ (1 << j)][h] + cost);
}
}
}
if (Integer.bitCount(i) == k + 1) {
ans = Math.max(ans, f[i][j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maximumCost(int n, vector<vector<int>>& highways, int k) {
if (k >= n) {
return -1;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> g[n];
for (auto& h : highways) {
int a = h[0], b = h[1], cost = h[2];
g[a].emplace_back(b, cost);
g[b].emplace_back(a, cost);
}
int f[1 << n][n];
memset(f, -0x3f, sizeof(f));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
f[1 << i][i] = 0;
}
int ans = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i >> j & 1) {
for (auto& [h, cost] : g[j]) {
if (i >> h & 1) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i ^ (1 << j)][h] + cost);
}
}
}
if (__builtin_popcount(i) == k + 1) {
ans = max(ans, f[i][j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func maximumCost(n int, highways [][]int, k int) int {
if k >= n {
return -1
}
g := make([][][2]int, n)
for _, h := range highways {
a, b, cost := h[0], h[1], h[2]
g[a] = append(g[a], [2]int{b, cost})
g[b] = append(g[b], [2]int{a, cost})
}
f := make([][]int, 1<<n)
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range f[i] {
f[i][j] = -(1 << 30)
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
f[1<<i][i] = 0
}
ans := -1
for i := 0; i < 1<<n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if i>>j&1 == 1 {
for _, e := range g[j] {
h, cost := e[0], e[1]
if i>>h&1 == 1 {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i^(1<<j)][h]+cost)
}
}
}
if bits.OnesCount(uint(i)) == k+1 {
ans = max(ans, f[i][j])
}
}
}
return ans
}function maximumCost(n: number, highways: number[][], k: number): number {
if (k >= n) {
return -1;
}
const g: [number, number][][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b, cost] of highways) {
g[a].push([b, cost]);
g[b].push([a, cost]);
}
const f: number[][] = Array(1 << n)
.fill(0)
.map(() => Array(n).fill(-(1 << 30)));
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
f[1 << i][i] = 0;
}
let ans = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < 1 << n; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((i >> j) & 1) {
for (const [h, cost] of g[j]) {
if ((i >> h) & 1) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i][j], f[i ^ (1 << j)][h] + cost);
}
}
}
if (bitCount(i) === k + 1) {
ans = Math.max(ans, f[i][j]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
function bitCount(i: number): number {
i = i - ((i >>> 1) & 0x55555555);
i = (i & 0x33333333) + ((i >>> 2) & 0x33333333);
i = (i + (i >>> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
i = i + (i >>> 8);
i = i + (i >>> 16);
return i & 0x3f;
}