一组公路连接 n 个城市,城市编号为从 0 到 n - 1 。 输入包含一个二维数组 highways ,其中 highways[i] = [city1i, city2i, tolli] 表示有一条连接城市 city1i 和 city2i 的双向公路,允许汽车缴纳值为 tolli 的费用从 city1i 前往 city2i 或 从 city2i 前往 city1i 。
另给你一个整数 discounts 表示你最多可以使用折扣的次数。你可以使用一次折扣使通过第 ith 条公路的费用降低至 tolli / 2(向下取整)。 最多只可使用 discounts 次折扣, 且 每条公路最多只可使用一次折扣 。
返回从城市0 前往城市 n - 1 的 最小费用 。如果不存在从城市0 前往城市 n - 1 的路径,返回 -1 。
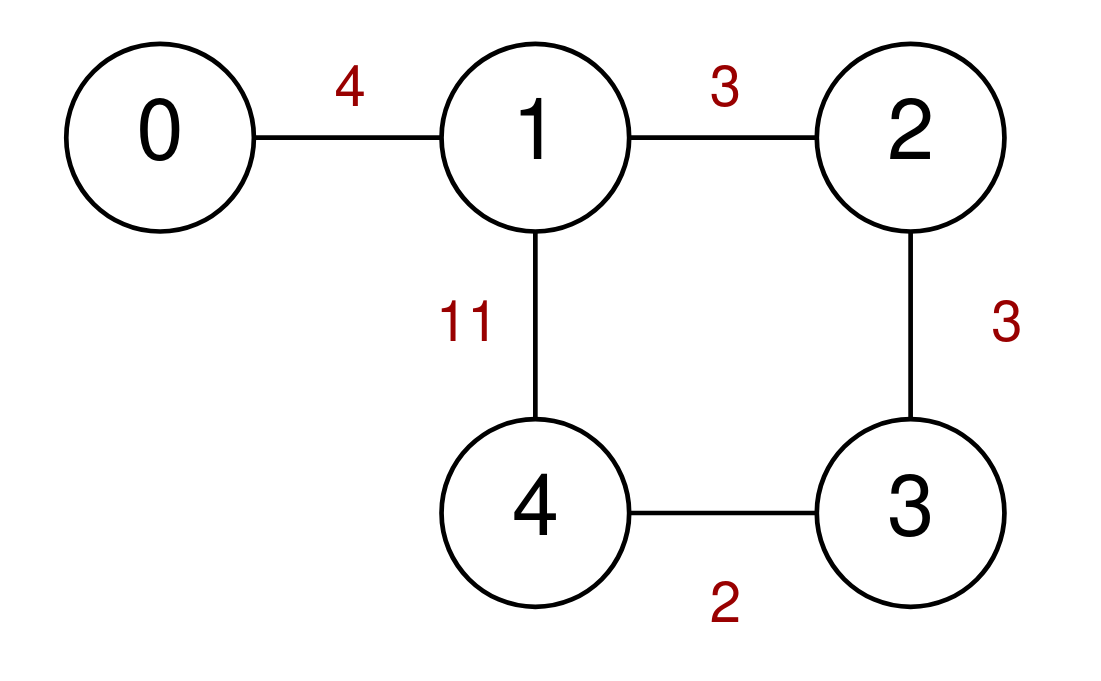
输入:n = 5, highways = [[0,1,4],[2,1,3],[1,4,11],[3,2,3],[3,4,2]], discounts = 1 输出:9 解释: 从 0 前往 1 ,需要费用为 4 。 从 1 前往 4 并使用一次折扣,需要费用为 11 / 2 = 5 。 从 0 前往 4 最小费用为 4 + 5 = 9 。
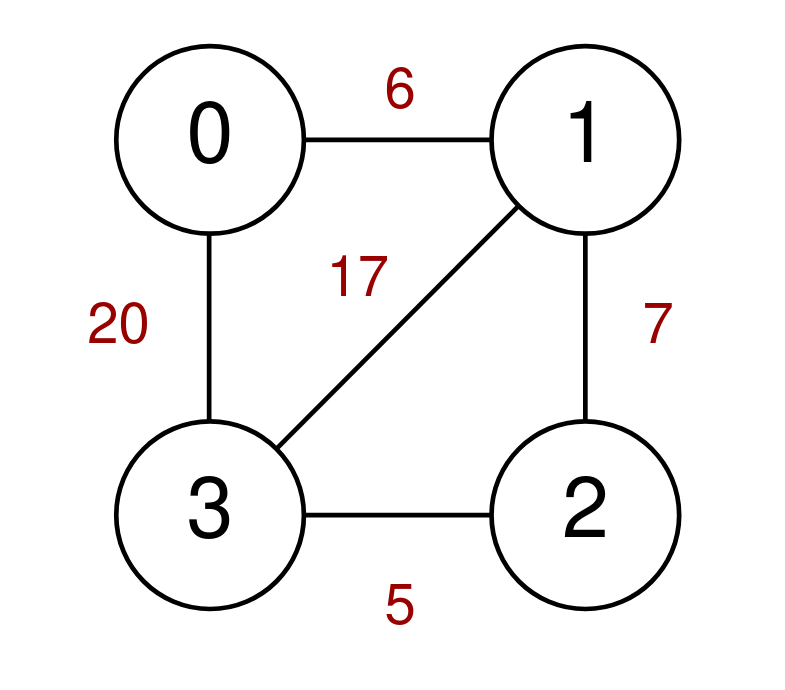
输入:n = 4, highways = [[1,3,17],[1,2,7],[3,2,5],[0,1,6],[3,0,20]], discounts = 20 输出:8 解释: 从 0 前往 1 并使用一次折扣,需要费用为 6 / 2 = 3 。 从 1 前往 2 并使用一次折扣,需要费用为 7 / 2 = 3 。 从 2 前往 3 并使用一次折扣,需要费用为 5 / 2 = 2 。 从 0 前往 3 最小费用为 3 + 3 + 2 = 8 。
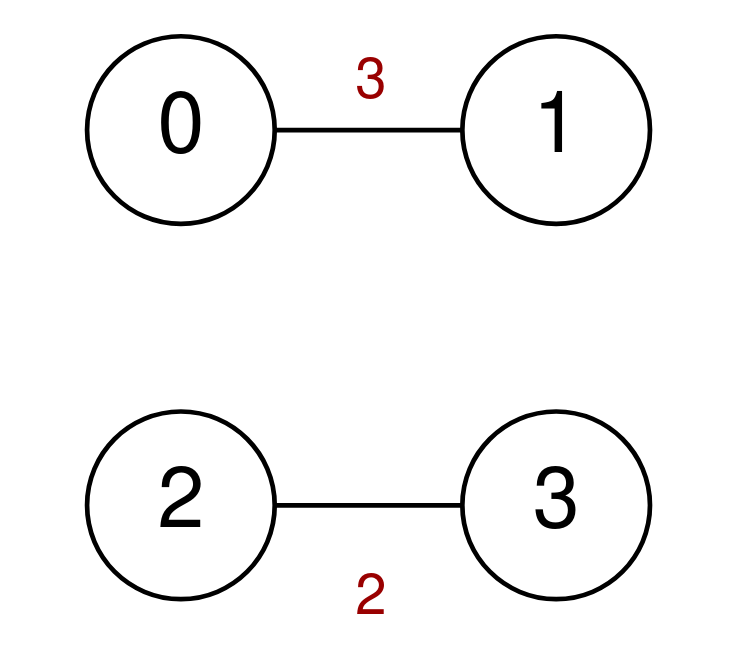
输入:n = 4, highways = [[0,1,3],[2,3,2]], discounts = 0 输出:-1 解释: 不存在从 0 前往 3 的路径,所以返回 -1 。
提示:
2 <= n <= 10001 <= highways.length <= 1000highways[i].length == 30 <= city1i, city2i <= n - 1city1i != city2i0 <= tolli <= 1050 <= discounts <= 500- 任意两个城市之间最多只有一条公路相连
本题属于带限制的单源最短路问题。
class Solution:
def minimumCost(self, n: int, highways: List[List[int]], discounts: int) -> int:
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b, c in highways:
g[a].append((b, c))
g[b].append((a, c))
q = [(0, 0, 0)]
dist = [[inf] * (discounts + 1) for _ in range(n)]
while q:
cost, i, k = heappop(q)
if k > discounts:
continue
if i == n - 1:
return cost
if dist[i][k] > cost:
dist[i][k] = cost
for j, v in g[i]:
heappush(q, (cost + v, j, k))
heappush(q, (cost + v // 2, j, k + 1))
return -1class Solution {
public int minimumCost(int n, int[][] highways, int discounts) {
List<int[]>[] g = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (var e : highways) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1], c = e[2];
g[a].add(new int[] {b, c});
g[b].add(new int[] {a, c});
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
q.offer(new int[] {0, 0, 0});
int[][] dist = new int[n][discounts + 1];
for (var e : dist) {
Arrays.fill(e, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var p = q.poll();
int cost = p[0], i = p[1], k = p[2];
if (k > discounts || dist[i][k] <= cost) {
continue;
}
if (i == n - 1) {
return cost;
}
dist[i][k] = cost;
for (int[] nxt : g[i]) {
int j = nxt[0], v = nxt[1];
q.offer(new int[] {cost + v, j, k});
q.offer(new int[] {cost + v / 2, j, k + 1});
}
}
return -1;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumCost(int n, vector<vector<int>>& highways, int discounts) {
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n);
for (auto& e : highways) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1], c = e[2];
g[a].push_back({b, c});
g[b].push_back({a, c});
}
priority_queue<tuple<int, int, int>, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>, greater<tuple<int, int, int>>> q;
q.push({0, 0, 0});
vector<vector<int>> dist(n, vector<int>(discounts + 1, INT_MAX));
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [cost, i, k] = q.top();
q.pop();
if (k > discounts || dist[i][k] <= cost) continue;
if (i == n - 1) return cost;
dist[i][k] = cost;
for (auto [j, v] : g[i]) {
q.push({cost + v, j, k});
q.push({cost + v / 2, j, k + 1});
}
}
return -1;
}
};