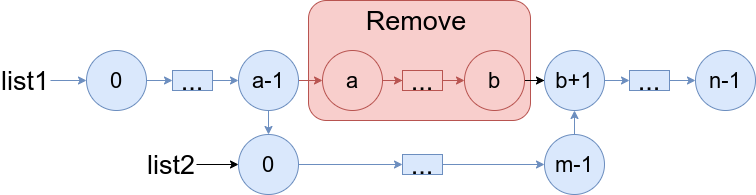
给你两个链表 list1 和 list2 ,它们包含的元素分别为 n 个和 m 个。
请你将 list1 中下标从 a 到 b 的全部节点都删除,并将list2 接在被删除节点的位置。
下图中蓝色边和节点展示了操作后的结果:
请你返回结果链表的头指针。
示例 1:
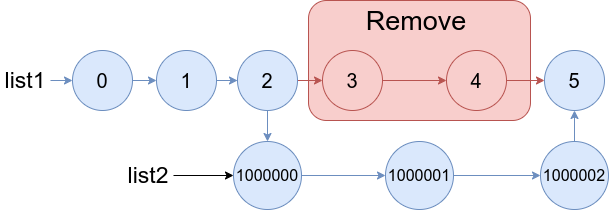
输入:list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002] 输出:[0,1,2,1000000,1000001,1000002,5] 解释:我们删除 list1 中下标为 3 和 4 的两个节点,并将 list2 接在该位置。上图中蓝色的边和节点为答案链表。
示例 2:
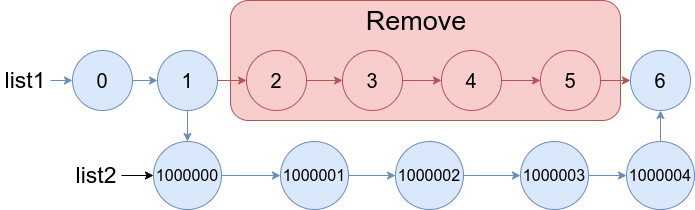
输入:list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6], a = 2, b = 5, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004] 输出:[0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6] 解释:上图中蓝色的边和节点为答案链表。
提示:
3 <= list1.length <= 1041 <= a <= b < list1.length - 11 <= list2.length <= 104
直接模拟题目中的操作即可。
在实现上,我们使用两个指针 list1 的头节点。
然后我们向后移动指针 list1 中第 list1 中第 next 指针指向链表 list2 的头节点,将链表 list2 的尾节点的 next 指针指向 next 指针指向的节点,即可完成题目要求。
时间复杂度 list1 和 list2 的长度。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeInBetween(
self, list1: ListNode, a: int, b: int, list2: ListNode
) -> ListNode:
p = q = list1
for _ in range(a - 1):
p = p.next
for _ in range(b):
q = q.next
p.next = list2
while p.next:
p = p.next
p.next = q.next
q.next = None
return list1/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p = list1, q = list1;
while (--a > 0) {
p = p.next;
}
while (b-- > 0) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = list2;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = q.next;
q.next = null;
return list1;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) {
auto p = list1, q = list1;
while (--a) {
p = p->next;
}
while (b--) {
q = q->next;
}
p->next = list2;
while (p->next) {
p = p->next;
}
p->next = q->next;
q->next = nullptr;
return list1;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func mergeInBetween(list1 *ListNode, a int, b int, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
p, q := list1, list1
for ; a > 1; a-- {
p = p.Next
}
for ; b > 0; b-- {
q = q.Next
}
p.Next = list2
for p.Next != nil {
p = p.Next
}
p.Next = q.Next
q.Next = nil
return list1
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function mergeInBetween(
list1: ListNode | null,
a: number,
b: number,
list2: ListNode | null,
): ListNode | null {
let p = list1;
let q = list1;
while (--a > 0) {
p = p.next;
}
while (b-- > 0) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = list2;
while (p.next) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = q.next;
q.next = null;
return list1;
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode MergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p = list1, q = list1;
while (--a > 0) {
p = p.next;
}
while (b-- > 0) {
q = q.next;
}
p.next = list2;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = q.next;
q.next = null;
return list1;
}
}