You are given a rectangular cake of size h x w and two arrays of integers horizontalCuts and verticalCuts where:
horizontalCuts[i]is the distance from the top of the rectangular cake to theithhorizontal cut and similarly, andverticalCuts[j]is the distance from the left of the rectangular cake to thejthvertical cut.
Return the maximum area of a piece of cake after you cut at each horizontal and vertical position provided in the arrays horizontalCuts and verticalCuts. Since the answer can be a large number, return this modulo 109 + 7.
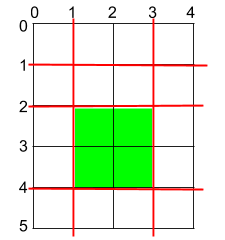
Example 1:
Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [1,2,4], verticalCuts = [1,3] Output: 4 Explanation: The figure above represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green piece of cake has the maximum area.
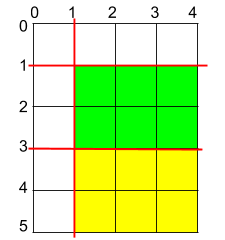
Example 2:
Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3,1], verticalCuts = [1] Output: 6 Explanation: The figure above represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green and yellow pieces of cake have the maximum area.
Example 3:
Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3], verticalCuts = [3] Output: 9
Constraints:
2 <= h, w <= 1091 <= horizontalCuts.length <= min(h - 1, 105)1 <= verticalCuts.length <= min(w - 1, 105)1 <= horizontalCuts[i] < h1 <= verticalCuts[i] < w- All the elements in
horizontalCutsare distinct. - All the elements in
verticalCutsare distinct.
We first sort horizontalCuts and verticalCuts separately, and then traverse both arrays to calculate the maximum difference between adjacent elements. We denote these maximum differences as
Note that we need to consider the boundary cases, i.e., the first and last elements of horizontalCuts and verticalCuts.
The time complexity is horizontalCuts and verticalCuts, respectively. The space complexity is
class Solution:
def maxArea(
self, h: int, w: int, horizontalCuts: List[int], verticalCuts: List[int]
) -> int:
horizontalCuts.extend([0, h])
verticalCuts.extend([0, w])
horizontalCuts.sort()
verticalCuts.sort()
x = max(b - a for a, b in pairwise(horizontalCuts))
y = max(b - a for a, b in pairwise(verticalCuts))
return (x * y) % (10**9 + 7)class Solution {
public int maxArea(int h, int w, int[] horizontalCuts, int[] verticalCuts) {
final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
Arrays.sort(horizontalCuts);
Arrays.sort(verticalCuts);
int m = horizontalCuts.length;
int n = verticalCuts.length;
long x = Math.max(horizontalCuts[0], h - horizontalCuts[m - 1]);
long y = Math.max(verticalCuts[0], w - verticalCuts[n - 1]);
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
x = Math.max(x, horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
y = Math.max(y, verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]);
}
return (int) ((x * y) % mod);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(int h, int w, vector<int>& horizontalCuts, vector<int>& verticalCuts) {
horizontalCuts.push_back(0);
horizontalCuts.push_back(h);
verticalCuts.push_back(0);
verticalCuts.push_back(w);
sort(horizontalCuts.begin(), horizontalCuts.end());
sort(verticalCuts.begin(), verticalCuts.end());
int x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < horizontalCuts.size(); ++i) {
x = max(x, horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < verticalCuts.size(); ++i) {
y = max(y, verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]);
}
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
return (1ll * x * y) % mod;
}
};func maxArea(h int, w int, horizontalCuts []int, verticalCuts []int) int {
horizontalCuts = append(horizontalCuts, []int{0, h}...)
verticalCuts = append(verticalCuts, []int{0, w}...)
sort.Ints(horizontalCuts)
sort.Ints(verticalCuts)
x, y := 0, 0
const mod int = 1e9 + 7
for i := 1; i < len(horizontalCuts); i++ {
x = max(x, horizontalCuts[i]-horizontalCuts[i-1])
}
for i := 1; i < len(verticalCuts); i++ {
y = max(y, verticalCuts[i]-verticalCuts[i-1])
}
return (x * y) % mod
}function maxArea(h: number, w: number, horizontalCuts: number[], verticalCuts: number[]): number {
const mod = 1e9 + 7;
horizontalCuts.push(0, h);
verticalCuts.push(0, w);
horizontalCuts.sort((a, b) => a - b);
verticalCuts.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let [x, y] = [0, 0];
for (let i = 1; i < horizontalCuts.length; i++) {
x = Math.max(x, horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]);
}
for (let i = 1; i < verticalCuts.length; i++) {
y = Math.max(y, verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]);
}
return Number((BigInt(x) * BigInt(y)) % BigInt(mod));
}impl Solution {
pub fn max_area(
h: i32,
w: i32,
mut horizontal_cuts: Vec<i32>,
mut vertical_cuts: Vec<i32>
) -> i32 {
const MOD: i64 = 1_000_000_007;
horizontal_cuts.sort();
vertical_cuts.sort();
let m = horizontal_cuts.len();
let n = vertical_cuts.len();
let mut x = i64::max(
horizontal_cuts[0] as i64,
(h as i64) - (horizontal_cuts[m - 1] as i64)
);
let mut y = i64::max(vertical_cuts[0] as i64, (w as i64) - (vertical_cuts[n - 1] as i64));
for i in 1..m {
x = i64::max(x, (horizontal_cuts[i] as i64) - (horizontal_cuts[i - 1] as i64));
}
for i in 1..n {
y = i64::max(y, (vertical_cuts[i] as i64) - (vertical_cuts[i - 1] as i64));
}
((x * y) % MOD) as i32
}
}