Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
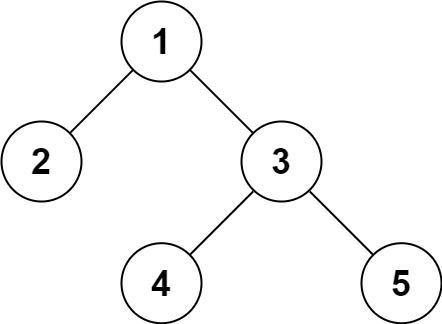
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5] Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
"""Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
if root is None:
return ''
res = []
def preorder(root):
if root is None:
res.append("#,")
return
res.append(str(root.val) + ",")
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
preorder(root)
return ''.join(res)
def deserialize(self, data):
"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not data:
return None
vals = data.split(',')
def inner():
first = vals.pop(0)
if first == '#':
return None
return TreeNode(int(first), inner(), inner())
return inner()
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# ser = Codec()
# deser = Codec()
# ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root))/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
private static final String NULL = "#";
private static final String SEP = ",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
preorder(root, sb);
return sb.toString();
}
private void preorder(TreeNode root, StringBuilder sb) {
if (root == null) {
sb.append(NULL + SEP);
return;
}
sb.append(root.val + SEP);
preorder(root.left, sb);
preorder(root.right, sb);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data == null || "".equals(data)) {
return null;
}
List<String> vals = new LinkedList<>();
for (String x : data.split(SEP)) {
vals.add(x);
}
return deserialize(vals);
}
private TreeNode deserialize(List<String> vals) {
String first = vals.remove(0);
if (NULL.equals(first)) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(first));
root.left = deserialize(vals);
root.right = deserialize(vals);
return root;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser = new Codec();
// Codec deser = new Codec();
// TreeNode ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return "";
string s = "";
preorder(root, s);
return s;
}
void preorder(TreeNode* root, string& s) {
if (!root)
s += "# ";
else {
s += to_string(root->val) + " ";
preorder(root->left, s);
preorder(root->right, s);
}
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if (data == "") return nullptr;
stringstream ss(data);
return deserialize(ss);
}
TreeNode* deserialize(stringstream& ss) {
string first;
ss >> first;
if (first == "#") return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(first));
root->left = deserialize(ss);
root->right = deserialize(ss);
return root;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser, deser;
// TreeNode* ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
/*
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*/
function serialize(root: TreeNode | null): string {
return JSON.stringify(root);
}
/*
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*/
function deserialize(data: string): TreeNode | null {
return JSON.parse(data);
}
/**
* Your functions will be called as such:
* deserialize(serialize(root));
*/// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
struct Codec {}
/**
* `&self` means the method takes an immutable reference.
* If you need a mutable reference, change it to `&mut self` instead.
*/
impl Codec {
fn new() -> Self {
Codec {}
}
fn serialize(&self, root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> String {
if root.is_none() {
return String::from("#");
}
let mut node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut();
let left = node.left.take();
let right = node.right.take();
format!("{},{},{}", self.serialize(right), self.serialize(left), node.val)
}
fn deserialize(&self, data: String) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if data.len() == 1 {
return None;
}
Self::renew(&mut data.split(",").collect())
}
fn renew(vals: &mut Vec<&str>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let val = vals.pop().unwrap_or("#");
if val == "#" {
return None;
}
Some(
Rc::new(
RefCell::new(TreeNode {
val: val.parse().unwrap(),
left: Self::renew(vals),
right: Self::renew(vals),
})
)
)
}
}/**
* Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
* let obj = Codec::new();
* let data: String = obj.serialize(strs);
* let ans: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> = obj.deserialize(data);
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {string}
*/
var serialize = function (root) {
return rserialize(root, '');
};
/**
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*
* @param {string} data
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var deserialize = function (data) {
const dataArray = data.split(',');
return rdeserialize(dataArray);
};
const rserialize = (root, str) => {
if (root === null) {
str += '#,';
} else {
str += root.val + '' + ',';
str = rserialize(root.left, str);
str = rserialize(root.right, str);
}
return str;
};
const rdeserialize = dataList => {
if (dataList[0] === '#') {
dataList.shift();
return null;
}
const root = new TreeNode(parseInt(dataList[0]));
dataList.shift();
root.left = rdeserialize(dataList);
root.right = rdeserialize(dataList);
return root;
};
/**
* Your functions will be called as such:
* deserialize(serialize(root));
*//**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
/*
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*/
function serialize(root: TreeNode | null): string {
if (root == null) {
return '#';
}
const { val, left, right } = root;
return `${val},${serialize(left)},${serialize(right)}`;
}
/*
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*/
function deserialize(data: string): TreeNode | null {
const n = data.length;
if (n === 1) {
return null;
}
const vals = data.split(',').reverse();
const renew = () => {
const val = vals.pop();
if (val == null || val === '#') {
return null;
}
return new TreeNode(Number(val), renew(), renew());
};
return renew();
}
/**
* Your functions will be called as such:
* deserialize(serialize(root));
*/