- 链表类总结
- 反转链表 (
easy三指针dummy节点) - 合并两个有序链表 (
easy双指针) - 删除排序链表中的重复元素 (
easy双指针) - 回文链表 (
easy反转链表) - 环形链表 (
easy双指针) - 环形链表II (
medium双指针) - 相交链表 (
easy) - 奇偶链表 (
mediumdummy节点) - 删除排序链表中的重复元素II (
medium双指针dummy节点) - 旋转链表 (
medium) - 两数相加 (
medium数学) - 删除链表的倒数第N个节点 (
medium) - 复制带随机指针的链表 (
medium)
- 反转链表 (
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶: 你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
设指针cur指向当前节点,反转指针的过程是改变当前节点的next指针指向当前节点前一个结点,所以同时需要保存前一个节点和下一个节点,设指针pre指向当前节点前一个节点,指针next指向当前节点下一个节点。cur指针最初指向链表首节点,next指向cur下一个节点,pre为空,改变当前节点的next结点指向pre指向的结点,每这样操作一次,三个指针同时前进,直到链表尾部为止。最后,返回反转后的链表表头指针。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* next = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
pre = None
cur = head
nex = None
while cur:
nex = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nex
return pre设一个dummy结点(头结点),它的next指针始终指向链表首节点。设cur指针指向当前节点,temp作为临时指针指向当前节点的下一个节点。那么翻转的过程就是:
- 令cur->next指向temp指向节点的下一个节点(
cur->next = temp->next) - 令temp->next指向链表当前的首节点(
temp->next = dummy->next) - 令dummy->next指向temp指向的结点(
dummy->next = temp)
重复这个过程,直到cur->next到达链表末尾为止,返回dummy->next就是反转后新链表的表头指针
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur->next)
{
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = temp->next;
temp->next = dummy->next;
dummy->next = temp;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
pre = None
cur = head
nex = None
while cur:
nex = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nex
return pre设第k+1层递归返回处理第k层结点k时,k以后的节点都已经反转。那么对于节点k,需要修改结点k+1的next指向节点k,以及节点k的next指向空
node(1) -> node(2) -> node(3) -> ... -> node(k) -> node(k+1) <- ... <- node(n-1) <- node(n)
node(k)->next->next = node(k);
node(k)->next = nullptr;最后,返回第一层递归就是逆序后的链表的头结点
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n) (
由于n层递归,而每层递归函数调用的栈帧会创建局部指针tmp)
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* tmp = head;
head = reverseList(tmp->next);
tmp->next->next = tmp;
tmp->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
tmp = head
head = self.reverseList(tmp.next)
tmp.next.next = tmp
tmp.next = None
return head
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
双指针法,维持两个指针l1,l2分别遍历两个链表,分两种情况处理:
- l1->val < l2->val ,那么合并的下一个节点是l1,同时l1前进一个节点
- l1->val >= l2->val , 那么合并的下一个节点时l2,同时l2前进一个节点
直到l1和l2有一个到达链表尾结束遍历,如果两个链表不等长,那此时肯定有一个链表没走完,将这个链表剩下没走完的那部分加到合并的新链表尾部即可
- 时间复杂度:O(m+n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(!l1 && !l2) return nullptr;
else if(!l1) return l2;
else if(!l2) return l1;
ListNode node(0),*head = &node;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
head->next = l1;
head = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
head->next = l2;
head = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1) head->next = l1;
if(l2) head->next = l2;
return node.next;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not l1:
return l2
if not l2:
return l1
if l1.val < l2.val:
res = l1
res.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2)
else:
res = l2
res.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next)
return res给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
示例 1:
输入: 1->1->2
输出: 1->2
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
输出: 1->2->3
双指针法:设置两个指针cur和pre遍历链表,cur指向当前节点,pre指向当前节点前一个节点,比较pre->val和cur->val的值:
- pre->val != cur->val,此时cur指向下一个不重复的节点,令pre的next指向cur指向的当前节点,这样就跳过了重复的节点,同时pre前进一步(
pre = pre->next); - pre->val == cur->val, 此时cur仍然指向重复的节点,cur继续前进直到找到不重复的节点
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(!head)
return nullptr;
ListNode* pre = head;
ListNode* cur = head->next;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val != pre->val)
{
pre->next = cur;
pre = pre->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(pre->next)
pre->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head:
return head
pre = head
cur = head.next
while cur:
if cur.val != pre.val:
pre.next = cur
pre = pre.next
cur = cur.next
pre.next = None
return head请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶: 你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
思路:要判断链表是否回文,可以分别从头和尾同时往中间遍历元素,比较遍历到的每个元素是否相等,直到链表中间。但是链表不同于数组,遍历只能从前往后而不能从后往前,所以需要调整链表,将链表的后半部分反转。
- 设两个指针遍历链表,一个快指针fast,一个慢指针slow,快指针一步走两个结点,慢指针一步走一个节点,直到快指针到达链表尾,此时慢指针到达链表的中间。
- 反转以slow指向的这个中间节点开始到链表尾之间的节点,详见反转链表。
- 接下来设置两个指针head和head1,从链表的头和尾同时向中间遍历,如果遍历的过程中出现head->val != head1->val,那么原链表就不是回文;否则,是回文。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if(!head)
return true;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(slow && fast->next && fast->next->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = slow->next;
ListNode* next = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
ListNode* head1 = pre;
while(head1 && head)
{
if(head1->val != head->val)
return false;
head1 = head1->next;
head = head->next;
}
return true;
}
};给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
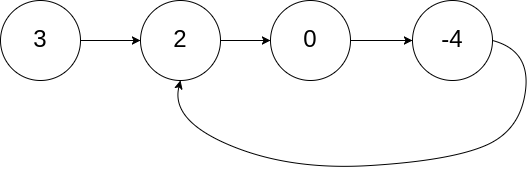
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
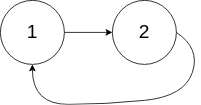
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
使用一个快指针和一个慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步。如果链表有环,两个指针一定会相遇,并且相遇的节点与头结点到环结点的距离相等;如果链表没有环,快指针会先到达链表尾。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(!head)
return false;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && slow)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if(fast)
fast = fast->next;
else
return false;
if(slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not head:
return False
if head.next:
p1 = head.next.next
p2 = head.next
else:
return False
while p1 != p2 and p1 :
p1 = p1.next
if p1:
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next
if not p1:
return False
return True给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:tail connects to node index 0
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:no cycle
解释:链表中没有环。
进阶:
你是否可以不用额外空间解决此题?
方法详见环形链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(!head)
return nullptr;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(slow && fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if(fast)
fast = fast->next;
else
break;
if(slow == fast)
break;
}
if(!fast)
return nullptr;
slow = head;
while(slow && fast && slow != fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
在节点 c1 开始相交。
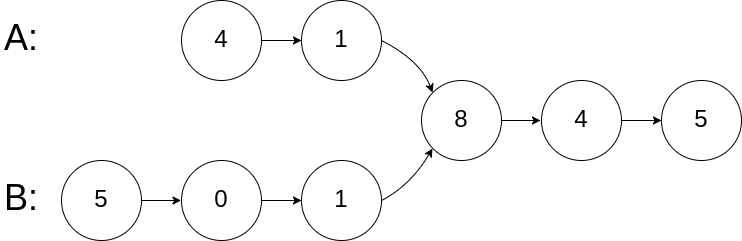
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
- 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
对于两个单链表,在它们起始相交节点之后的节点就是两个链表共有的,找到两个链表从后向前最后一个相同的结点就是相交的起始结点。但是由于链表只能从前往后遍历,设两个链表的长度分别为m和n,假设m>n,先让短的那个链表走m-n步,然后两个链表同时走,遇到的第一个相同的结点就是起始的相交节点。
- 时间复杂度:O(m+n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(!headA || !headB)
return nullptr;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
ListNode* p1 = headA;
ListNode* p2 = headB;
while(p1)
{
lenA++;
p1 = p1->next;
}
while(p2)
{
lenB++;
p2 = p2->next;
}
int k = lenA - lenB;
int cnt = abs(k);
if(k > 0)
{
while(cnt > 0)
{
headA = headA->next;
cnt--;
}
}
else
{
while(cnt > 0)
{
headB = headB->next;
cnt--;
}
}
while(headA && headB)
{
if(headA->val == headB->val && headA == headB)
return headA;
headA = headA->next;
headB = headB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};Python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
n1 = n2 = 0
p = headA
while p:
n1 += 1
p = p.next
p = headB
while p:
n2 += 1
p = p.next
p1 = p2 = None
if n1 > n2:
p1 = headA
p2 = headB
else:
p1 = headB
p2 = headA
for i in range(abs(n1 - n2)):
p1 = p1.next
while p1 and p2 and p1 != p2:
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next
return p1给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
说明:
- 应当保持奇数节点和偶数节点的相对顺序。
- 链表的第一个节点视为奇数节点,第二个节点视为偶数节点,以此类推。
将原链表分为两个链表分别存放奇数位置和偶数位置的节点,然后将一个链表接到另一个链表的尾部。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head)
return nullptr;
ListNode head1(0),head2(0);//头结点
ListNode* cur1 = &head1;
ListNode* cur2 = &head2;
ListNode* cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while(cur)
{
if((cnt&0x1) == 0)
{
cur1->next = cur;
cur1 = cur;
}
else{
cur2->next = cur;
cur2 = cur;
}
cnt++;
cur = cur->next;
}
if(cur2) cur2->next = nullptr;
cur1->next = head2.next;
return head1.next;
}
};给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5
输出: 1->2->5
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->1->2->3
输出: 2->3
由于要删除所有重复的节点,处理情况相比于删除排序链表中的重复元素复杂一些,基本思路还是双指针法,由于链表开头可能就是重复节点,设置一个头结点dummy,然后设置一个慢指针pre = dummy,一个快指针 cur = head。cur指针遍历链表,对于cur节点分两种情况处理:
- cur节点和下一个节点值相等:向后移动,直到cur值不等于下一节点或者下一节点为nullptr
pre->next = cur->next; //令pre指向下一个可能不重复的节点
cur = cur->next; //cur前进一步- cur结点和下一节点不相等,令pre前进一步
pre = pre->next; //找到下一个不重复的节点
cur = cur->next; //cur前进一步以上处理一直循环到cur为空指针结束,
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
ListNode node(0),*dummy = &node;
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummy,*cur = head;
while(cur && cur->next)
{
if(cur->val == cur->next->val)
{
int a = cur->val;
while(cur->next && cur->next->val == a)
cur = cur->next;
pre->next = cur->next;
}
else
{
pre = pre->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return node.next;
}
};递归处理,思路同方法1
- 时间复杂度O(n)
- 空间复杂度O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(!head)
return nullptr;
ListNode* p = head;
if(p->next && p->val == p->next->val)
{
int tmp = p->val;
while(p && p->val == tmp)
p = p->next;
return deleteDuplicates(p);
}
else{
p->next = deleteDuplicates(p->next);
}
return p;
}
};给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
输出: 2->0->1->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL
向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL
向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
设链表长度len,将链表右移k个位置相当于将链表的最后step(step = k%len)个节点移到链表头部。*
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head)
return nullptr;
int len = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
len++;
cur = cur->next;
}
int step = k%len;
if(step == 0)
return head;
cur = head;
int cnt = 1;
while(cnt != len - step)
{
cur = cur->next;
cnt++;
}
ListNode* head1 = cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
cur = head1;
while(cur->next)
cur = cur->next;
cur->next = head;
return head1;
}
};给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
按照十进制加法的进位方法来操作链表,注意特殊情况
-
时间复杂度:O(m + n)
-
空间复杂度:O(max(m,n))
-
递归代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* recursion(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2,int carry)
{
if(carry == 0)
{
if(!l1 && !l2) return nullptr;
if(!l1 && l2) return l2;
if(l1 && !l2) return l1;
}
ListNode* res = new ListNode(0);
if(l1 && l2)
{
int sum = l1->val + l2->val + carry;
res->val = sum%10;
carry = sum/10;
res->next = recursion(l1->next,l2->next,carry);
}
else if(!l1 && l2)
{
int sum = l2->val + carry;
res->val = sum % 10;
carry = sum / 10;
res->next = recursion(nullptr,l2->next,carry);
}
else if(l1 && !l2)
{
int sum = l1->val + carry;
res->val = sum % 10;
carry = sum / 10;
res->next = recursion(l1->next,nullptr,carry);
}
else
{
res->val = carry;
res->next = nullptr;
}
return res;
}
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
return recursion(l1,l2,0);
}
};- 非递归代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(!l1 && !l2) return nullptr;
int carry = 0;
ListNode node(-1),*cur = &node;
while(l1 || l2)
{
if(l1 && l2)
{
int sum = l1->val + l2->val + carry;
cur->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
carry = sum / 10;
l1 = l1->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else
{
if(carry == 0)
{
cur->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
break;
}
else
{
int sum = (l1 ? l1->val : l2->val) + carry;
cur->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
carry = sum / 10;
if(l1) l1 = l1->next;
if(l2) l2 = l2->next;
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(carry > 0) cur->next = new ListNode(carry);
return node.next;
}
};给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
说明:
给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
在真实的面试中遇到过这道题?
参考剑指Offer 第二版 面试题22: 链表中倒数第k个节点
- C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if (!head) return head;
ListNode node(0), *pre = &node;
pre->next = head;
ListNode *slow = pre, *fast = pre;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (fast) {
fast = fast->next;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (!fast) return nullptr;
while (slow->next && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return node.next;
}
};给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的深度拷贝。
参考剑指Offer 第二版 面试题35:复杂链表的复制
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* struct RandomListNode {
* int label;
* RandomListNode *next, *random;
* RandomListNode(int x) : label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
RandomListNode *copyRandomList(RandomListNode *head) {
if(!head)
return head;
RandomListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
RandomListNode* node = new RandomListNode(cur->label);
node->next = cur->next;
cur->next = node;
cur = node->next;
}
RandomListNode* cur1 = head;
while(cur1)
{
if(cur1->next && cur1->label == cur1->next->label)
{
if(cur1->random)
cur1->next->random = cur1->random->next;
}
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
RandomListNode node(0),*head1 = &node;
RandomListNode node1(0),*head2 = &node;
RandomListNode* cur2 = head;
int cnt = 0;
while(cur2)
{
if((cnt & 0x1) == 1)
{
head1->next = cur2;
head1 = cur2;
}
else{
head2->next = cur2;
head2 = cur2;
}
cnt++;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
head1->next = nullptr;
head2->next = nullptr;
head = node1.next;
return node.next;
}
};哈希表
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> mp;
Node* cur = head;
Node node(0);
Node* dummy = &node;
while (cur) {
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->val);
dummy->next = tmp;
dummy = dummy->next;
mp.insert({cur, tmp});
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur) {
mp[cur]->random = mp[cur->random];
cur = cur->next;
}
return node.next;
}
};