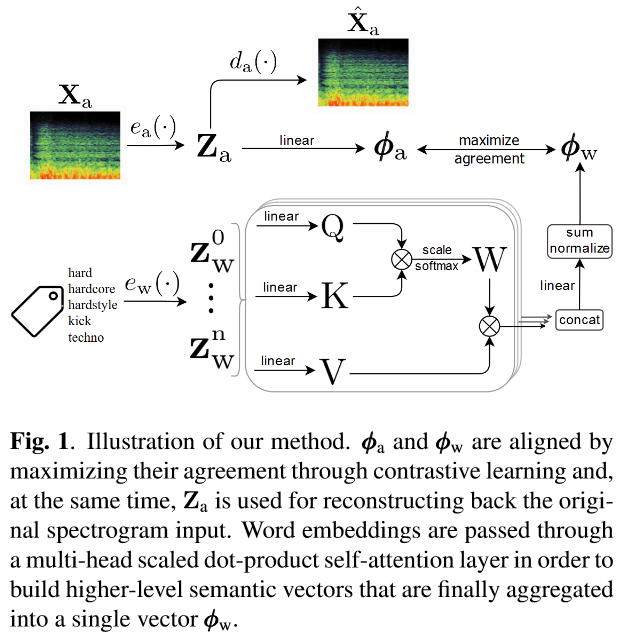
This is the repository for the method presented in the paper: "Learning Contextual Tag Embeddings for Cross-Modal Alignment of Audio and Tags" by X. Favory, K. Drossos, T. Virtanen, and X. Serra. (arXiv)
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you want to train the embeddings from scratch, you will need to download the dataset from this Zenodo page and place the hdf5 files in the hdf5_ds/ directory.
Then you can launch the training of an embedding model by running for instance:
python train_dual_ae.py 'configs/ae_w2v_128_self_c_4h.json'
The config file may be edited for instance to select which device to use for training ('cuda' or 'cpu').
If you want to re-compute the classification accuracies on the downstream tasks, you will need to:
-
download the three datasets:
-
place their content into the directory
data/as following:data └─── UrbanSound8K │ └─── audio │ └─── metadata └─── GTZAN │ └─── genres │ └─── test_filtered.txt │ └─── train_filtered.txt └─── nsynth └─── nsynth-train └─── audio_selected └─── nsynth-testkeeping existing sub-directories as they are for each dataset. However, for NSynth, you will have to manually create the audio_selected/ folder and put there the files that are listed in the values of the dictionary stored in
json/nsynth_selected_sounds_per_class.json. -
compute the embeddings with the pre-trained (or re-trained) embedding models runing the
encode.pyscript. This will store the embedding files into thedata/embedding/directory.
You can use the embedding models on your own data. You will need to create your own script, but the idea is simple. Here is a simple example to extract embedding chunks given an audio file:
from encode import return_loaded_model, extract_audio_embedding_chunks
from models_t1000_att import AudioEncoder
model = return_loaded_model(
lambda: AudioEncoder(128),
'saved_models/ae_w2v_128_selfatt_c_4h/audio_encoder_epoch_200.pt'
)
embedding, _ = extract_audio_embedding_chunks(model, '<path/to/audio/file>')