- Geolocation Options
- Activity Recognition Options
- HTTP & Persistence Options
- Geofencing Options
- Application Options
- Logging & Debug Options
⚡ Events
🔹 Methods
- Philosophy of Operation
- Geofencing
- HTTP Features
- Android Headless Mode
- Location Data Schema
- Debugging
The following Options can all be provided to the SDK's TSConfig instance.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static String TAG = "MyApp";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Get a reference to the SDK
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
final TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Configure the SDK
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDebug(true) // Sound Fx / notifications during development
.setLogLevel(5) // Verbose logging during development
.setDesiredAccuracy(LocationRequest.PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY)
.setDistanceFilter(10F)
.setStopTimeout(1L)
.setHeartbeatInterval(60)
.setStopOnTerminate(false)
.setForegroundService(true)
.setStartOnBoot(true)
.setUrl("http://your.server.com/locations")
.commit();
// Listen events
bgGeo.onLocation(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation location) {
Log.i(TAG, "[location] " + location.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer code) {
Log.i(TAG, "[location] ERROR: " + code);
}
});
// Finally, signal #ready to the SDK.
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] success");
if (!config.getEnabled()) {
// Start tracking immediately (if not already).
bgGeo.start();
}
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
}| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
desiredAccuracy |
int |
PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY |
Specify the desired-accuracy of the geolocation system. |
distanceFilter |
float |
10 |
The minimum distance (measured in meters) a device must move horizontally before an update event is generated. |
locationUpdateInterval |
long |
1000 |
With distanceFilter: 0, Sets the desired interval for location updates, in milliseconds. distanceFilter > 0 |
fastestLocationUpdateInterval |
long |
10000 |
Explicitly set the fastest interval for location updates, in milliseconds. |
deferTime |
int |
0 |
Sets the maximum wait time in milliseconds for location updates to be delivered to your callback, when they will all be delivered in a batch. |
allowIdenticalLocations |
boolean |
false |
The Android SDK will ignore a received location when it is identical to the last location. Set true to override this behaviour and record every location, regardless if it is identical to the last location. |
stationaryRadius |
int |
25 |
When stopped, the minimum distance the device must move beyond the stationary location for aggressive background-tracking to engage. |
disableElasticity |
boolean |
false |
Set true to disable automatic speed-based #distanceFilter elasticity. eg: When device is moving at highway speeds, locations are returned at ~ 1 / km. |
elasticityMultiplier |
float |
1 |
Controls the scale of automatic speed-based distanceFilter elasticity. Increasing elasticityMultiplier will result in few location samples as speed increases. |
stopAfterElapsedMinutes |
int |
0 |
The SDK can optionally automatically stop tracking after some number of minutes elapses after the #start method was called. |
stopOnStationary |
boolean |
false |
The SDK can optionally automatically #stop tracking when the stopTimeout timer elapses. |
desiredOdometerAccuracy |
float |
100 |
Location accuracy threshold in meters for odometer calculations. |
useSignificantChangesOnly |
boolean |
false |
Defaults to false. Set true in order to disable constant background-tracking and record a loction only every 500-1000 meters. |
locationAuthorizationRequest |
String |
Always |
The desired iOS location-authorization request, either Always or WhenInUse. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
activityRecognitionInterval |
long |
10000 |
The desired time between activity detections. Larger values will result in fewer activity detections while improving battery life. A value of 0 will result in activity detections at the fastest possible rate. |
stopTimeout |
long |
5 |
The number of minutes to wait before turning off location-services after the ActivityRecognition System (ARS) detects the device is STILL |
minimumActivityRecognitionConfidence |
int |
75 |
Each activity-recognition-result returned by the API is tagged with a "confidence" level expressed as a %. You can set your desired confidence to trigger a state-change. |
disableStopDetection |
boolean |
false |
Disable accelerometer-based Stop-detection System. |
triggerActivities |
String |
These are the comma-delimited list of activity-names returned by the ActivityRecognition API which will trigger a state-change from stationary to moving. By default, the SDK will trigger on any of the moving-states. |
|
disableMotionActivityUpdates |
boolean |
false |
Disable iOS motion-activity updates (eg: "walking", "in_vehicle"). |
motionTriggerDelay |
long |
0 |
Optionally add a delay in milliseconds to trigger Android into the moving state when Motion API reports the device is moving (eg: on_foot, in_vehicle |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
url |
String |
"" |
Your server url where you wish to HTTP POST locations to |
httpTimeout |
int |
60000 |
HTTP request timeout in milliseconds. |
params |
JSONObject |
null |
Optional HTTP params sent along in HTTP request to above #url |
extras |
JSONObject |
null |
Optional meta-data to attach to each recorded location |
headers |
JSONObject |
null |
Optional HTTP headers sent along in HTTP request to above #url |
method |
String |
POST |
The HTTP method. Defaults to POST. Some servers require PUT. |
httpRootProperty |
String |
location |
The root property of the JSON data where location-data will be appended. |
locationTemplate |
String |
undefined |
Optional custom location data schema (eg: { "lat:<%= latitude %>, "lng":<%= longitude %> } |
geofenceTemplate |
String |
undefined |
Optional custom geofence data schema (eg: { "lat:<%= latitude %>, "lng":<%= longitude %>, "geofence":"<%= geofence.identifier %>:<%= geofence.action %>" } |
autoSync |
boolean |
true |
If you've enabeld HTTP feature by configuring an #url, the SDK will attempt to upload each location to your server as it is recorded. |
autoSyncThreshold |
int |
0 |
The minimum number of persisted records to trigger an #autoSync action. |
batchSync |
boolean |
false |
If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url, batchSync: true will POST all the locations currently stored in native SQLite datbase to your server in a single HTTP POST request. |
maxBatchSize |
int |
-1 |
If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url and batchSync: true, this parameter will limit the number of records attached to each batch. |
maxDaysToPersist |
int |
1 |
Maximum number of days to store a geolocation in SDK's SQLite database. |
maxRecordsToPersist |
int |
-1 |
Maximum number of records to persist in SDK's SQLite database. Defaults to -1 (no limit). To disable persisting locations, set this to 0 |
locationsOrderDirection |
String |
ASC |
Controls the order that locations are selected from the database (and synced to your server). Defaults to ascending (ASC), where oldest locations are synced first. Descending (DESC) syncs latest locations first. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
stopOnTerminate |
boolean |
true |
Set false to continue tracking after user teminates the app. |
startOnBoot |
boolean |
false |
Set to true to enable background-tracking after the device reboots. |
heartbeatInterval |
int |
60 |
Rate in seconds to fire heartbeat events. |
schedule |
ArrayList |
[] |
Defines a schedule to automatically start/stop tracking at configured times |
foregroundService |
Boolean |
false |
Set true to make the SDK mostly immune to OS termination due to memory pressure from other apps. |
enableHeadless |
boolean |
false |
Set to true to enable "Headless" mode when the user terminates the application. In this mode, you can respond to all the SDK's events in the native Android environment. For more information, see the wiki for Android Headless Mode |
notificationPriority |
int |
NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_DEFAULT |
Controls the priority of the foregroundService notification and notification-bar icon. |
notificationTitle |
String |
"Your App Name" | When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. Defaults to the application name |
notificationText |
String |
"Location service activated" | When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. |
notificationColor |
String |
null |
When running the service with foregroundService: true, controls the color of the persistent notification in the Notification Bar. |
notificationSmallIcon |
String |
Your App Icon | When running the service with foregroundService: true, controls your customize notification small icon. Defaults to your application icon. |
notificationLargeIcon |
String |
undefined |
When running the service with foregroundService: true, controls your customize notification large icon. Defaults to undefined. |
forceReloadOnMotionChange |
boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #motionchange event fires. |
forceReloadOnLocationChange |
Boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #location event fires. |
forceReloadOnGeofence |
boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #geofence event fires. |
forceReloadOnHeartbeat |
boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #heartbeat event fires. |
forceReloadOnSchedule |
boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever a schedule event fires. |
forceReloadOnBoot |
boolean |
false |
If the user reboots the device with the SDK configured for startOnBoot: true, your will app will launch when the device is rebooted. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
geofenceProximityRadius |
long |
1000 |
Radius in meters to query for geofences within proximity. |
geofenceInitialTriggerEntry |
boolean |
true |
Set false to disable triggering a geofence immediately if device is already inside it. |
geofenceModeHighAccuracy |
boolean |
false |
Runs #startGeofences with a foreground service (along with its corresponding persitent notification). This will make geofence triggering far more consistent at the expense of higher power usage. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
debug |
boolean |
false |
When enabled, the SDK will emit sounds & notifications for life-cycle events of background-geolocation |
logLevel |
int |
0 |
Sets the verbosity of the SDK's logs from OFF to VERBOSE |
logMaxDays |
int |
3 |
Maximum days to persist a log-entry in database. |
Event-listeners can be attached using the method #on{EventName}, supplying the Event Name in the following table.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Listen to location event:
bgGeo.onLocation(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[location] " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[location] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
}Event-listeners are removed with the method #removeListeners.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.removeListeners();| Event Name | Description |
|---|---|
location |
Fired whenever a new location is recorded. |
motionchange |
Fired when the device changes state between stationary and moving |
activitychange |
Fired when the activity-recognition system detects a change in detected-activity (still, on_foot, in_vehicle, on_bicycle, running) |
locationproviderchange |
Fired when a change in the state of the device's Location Services has been detected. eg: "GPS ON", "Wifi only". |
geofence |
Fired when a geofence crossing event occurs. |
geofenceschange |
Fired when the list of monitored geofences within #geofenceProximityRadius changed |
http |
Fired after a successful HTTP response. response object is provided with status and responseText. |
heartbeat |
Fired each #heartbeatInterval while the SDK is in the stationary state with. Your callback will be provided with a params {} containing the last known location {Object} |
schedule |
Fired when a schedule event occurs. Your callbackFn will be provided with the current state Object. |
powersavechange |
Fired when the state of the operating-system's "Power Saving" system changes. Your callbackFn will be provided with a Boolean showing whether "Power Saving" is enabled or disabled |
connectivitychange |
Fired when the state of the device's network connectivity changes (enabled -> disabled and vice-versa) |
enabledchange |
Fired when the SDK's enabled state changes. For example, executing #start and #stop will fire the enabledchange event. |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
ready |
TSCallback |
Signal to the SDK that your app is booted and ready. The supplied callback will be executed when the SDK is ready for tracking. |
start |
[TSCallback] |
Enable location & geofence tracking. This is the SDK's power ON button. |
stop |
[TSCallback] |
Disable location & geofence tracking. This is the SDK's power OFF button. |
getCurrentPosition |
TSCurrentPositionRequest |
Retrieves the current position using maximum power & accuracy by fetching a number of samples and returning the most accurate to your callbackFn. |
watchPosition |
TSWatchPositionRequest |
Start a stream of continuous location-updates. |
stopWatchPosition |
Halt #watchPosition updates. |
|
changePace |
boolean, [TSCallback] |
Toggles the SDK's state between stationary and moving. |
getOdometer |
The SDK constantly tracks distance travelled. Returns the current distance (meters) |
|
setOdometer |
Float, TSLocationCallback |
Set the odometer to any arbitrary value. NOTE setOdometer will perform a getCurrentPosition in order to record to exact location where odometer was set; as a result, the callback signatures are identical to those of getCurrentPosition. |
startSchedule |
If a schedule was configured, this method will initiate that schedule. |
|
stopSchedule |
This method will stop the Scheduler service. | |
removeListeners |
Remove all events-listeners registered with #on{EventName} method |
|
isPowerSaveMode |
Fetches the state of the operating-systems "Power Saving" mode, whether enabled or disabled |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
getLocations |
TSGetLocationsCallback |
Fetch all the locations currently stored in native SDK's SQLite database. Your callback will receive a List of locations. |
getCount |
Fetches count of SQLite locations table SELECT count(*) from locations |
|
destroyLocations |
[TSCallback] |
Delete all records in SDK's SQLite database |
sync |
[TSSyncCallback] |
If the SDK is configured for HTTP with an #url and #autoSync: false, this method will initiate POSTing the locations currently stored in the native SQLite database to your configured #url |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
startGeofences |
[TSCallback] |
Engages the geofences-only trackingMode. In this mode, no active location-tracking will occur -- only geofences will be monitored |
addGeofence |
TSGeofence, [TSCallback] |
Adds a geofence to be monitored by the native SDK. |
addGeofences |
List<TSGeofence>, [TSCallback] |
Adds a list geofences to be monitored by the native SDK. |
removeGeofence |
String, [TSCallback] |
Removes a geofence identified by the provided identifier |
removeGeofences |
[List<String>], [TSCallback] |
Removes geofences (all or by list of identifiers). |
getGeofences |
TSGetGeofencesCallback |
Fetch the list of monitored geofences. |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
getLog |
TSGetLogCallback |
Fetch the entire contents of the current log database as a String. |
destroyLog |
[TSCallback] |
Destroy the contents of the Log database. |
emailLog |
String, Activity,[TSCallback] |
Fetch the entire contents of Log database and email it to a recipient using the device's native email client. |
Specify the desired-accuracy ("priority") of the geolocation system. See Android API docs for available values.
int PRIORITY_BALANCED_POWER_ACCURACY Used with setPriority(int) to request "block" level accuracy. int PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY Used with setPriority(int) to request the most accurate locations available. int PRIORITY_LOW_POWER Used with setPriority(int) to request "city" level accuracy. int PRIORITY_NO_POWER Used with setPriority(int) to request the best accuracy possible with zero additional power consumption.
| Name | Location Providers | Description |
|---|---|---|
PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY |
GPS + Wifi + Cellular | Highest power; |
PRIORITY_BALANCED_POWER_ACCURACY |
Wifi + Cellular | Medium power; Medium accuracy; |
PRIORITY_LOW_POWER |
Wifi (low power) + Cellular | Lower power; No GPS |
PRIORITY_NO_POWER |
Cellular only | Lowest power; lowest accuracy |
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDesiredAccuracy(LocationRequest.PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY)
.commit();PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY use GPS. speed, heading and altitude are available only from GPS.
The minimum distance (measured in meters) a device must move horizontally before an update event is generated.
However, by default, distanceFilter is elastically auto-calculated by the SDK: When speed increases, distanceFilter increases; when speed decreases, so too does distanceFilter.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDistanceFilter(10f)
.commit();ℹ️ To disable this behaviour, configure disableElasticity: true
ℹ️ To control the scale of the automatic distanceFilter calculation, see elasticityMultiplier
distanceFilter is auto calculated by rounding speed to the nearest 5 m/s and adding distanceFilter meters for each 5 m/s increment.
For example, at biking speed of 7.7 m/s with a configured distanceFilter: 30:
rounded_speed = round(7.7, 5)
=> 10
multiplier = rounded_speed / 5
=> 10 / 5 = 2
adjusted_distance_filter = multiplier * distanceFilter
=> 2 * 30 = 60 meters
At highway speed of 27 m/s with a configured distanceFilter: 50:
rounded_speed = round(27, 5)
=> 30
multiplier = rounded_speed / 5
=> 30 / 5 = 6
adjusted_distance_filter = multiplier * distanceFilter * elasticityMultipiler
=> 6 * 50 = 300 meters
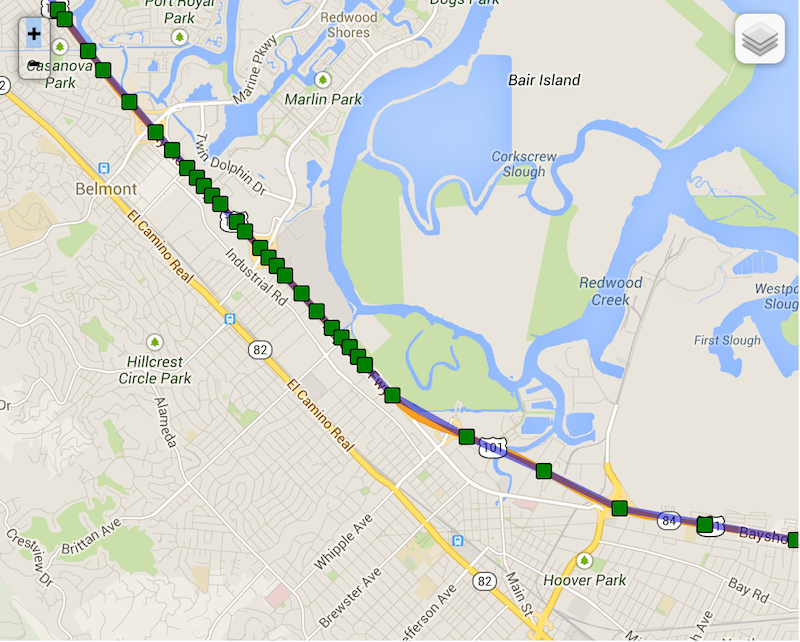
Note the following real example of background-geolocation on highway 101 towards San Francisco as the driver slows down as he runs into slower traffic (geolocations become compressed as distanceFilter decreases)
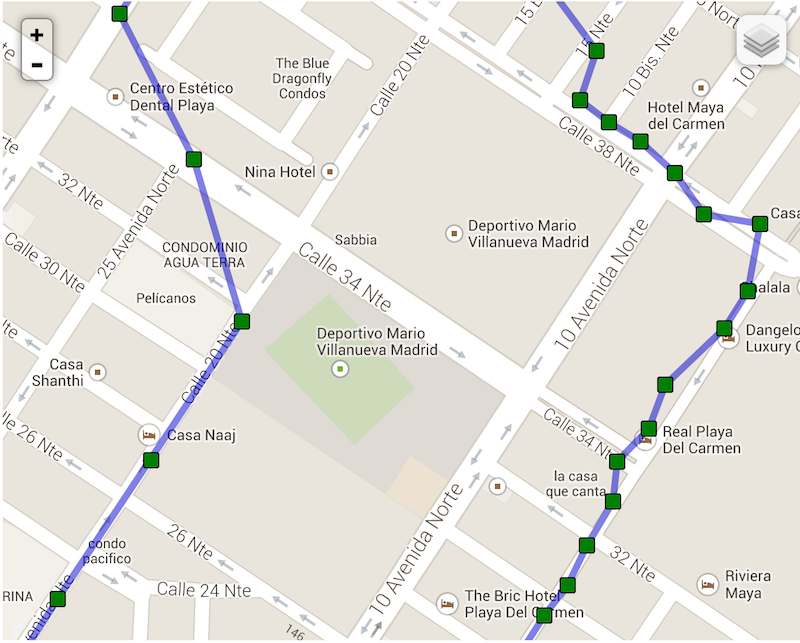
Compare now background-geolocation in the scope of a city. In this image, the left-hand track is from a cab-ride, while the right-hand track is walking speed.
locationUpdateInterval you must also configure distanceFilter: 0. distanceFilter overrides locationUpdateInterval.
Set the desired interval for active location updates, in milliseconds.
The location client will actively try to obtain location updates for your application at this interval, so it has a direct influence on the amount of power used by your application. Choose your interval wisely.
This interval is inexact. You may not receive updates at all (if no location sources are available), or you may receive them slower than requested. You may also receive them faster than requested (if other applications are requesting location at a faster interval).
Applications with only the coarse location permission may have their interval silently throttled.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setLocationUpdateInterval(5000L)
.setDistanceFilter(0F) // <-- Required to use locationUpdateInterval
.commit();Explicitly set the fastest interval for location updates, in milliseconds.
This controls the fastest rate at which your application will receive location updates, which might be faster than #locationUpdateInterval in some situations (for example, if other applications are triggering location updates).
This allows your application to passively acquire locations at a rate faster than it actively acquires locations, saving power.
Unlike #locationUpdateInterval, this parameter is exact. Your application will never receive updates faster than this value.
If you don't call this method, a fastest interval will be set to 30000 (30s).
An interval of 0 is allowed, but not recommended, since location updates may be extremely fast on future implementations.
If #fastestLocationUpdateInterval is set slower than #locationUpdateInterval, then your effective fastest interval is #locationUpdateInterval.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setFastestLocationUpdateInterval(1000L)
.commit();Defaults to 0 (no defer). Sets the maximum wait time in milliseconds for location updates. If you pass a value at least 2x larger than the interval specified with #locationUpdateInterval, then location delivery may be delayed and multiple locations can be delivered at once. Locations are determined at the #locationUpdateInterval rate, but can be delivered in batch after the interval you set in this method. This can consume less battery and give more accurate locations, depending on the device's hardware capabilities. You should set this value to be as large as possible for your needs if you don't need immediate location delivery.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDeferTime(60000L) // <-- delay location updates for 60 seconds
.commit();By default, the Android SDK will ignore a received location when it is identical to the last location. Set true to override this behaviour and record everylocation, regardless if it is identical to the last location.
In the logs, you will see a location being ignored:
TSLocationManager: ℹ️ IGNORED: same as last location
An identical location is often generated when changing state from stationary -> moving, where a single location is first requested (the motionchange location) before turning on regular location updates. Changing geolocation config params can also generate a duplicate location (eg: changing distanceFilter).
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setAllowIdenticalLocations(true)
.commit();Defaults to false. Set true to disable automatic, speed-based #distanceFilter elasticity.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDisableElasticity(true)
.commit();Controls the scale of automatic speed-based #distanceFilter elasticity. Increasing elasticityMultiplier will result in fewer location samples as speed increases. A value of 0 has the same effect as disableElasticity: true
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setElasticityMultiplier(2f)
.commit();When stopped, the minimum distance the device must move beyond the stationary location for aggressive background-tracking to engage.
Configuring stationaryRadius: 0 has NO EFFECT (in fact the SDK enforces a minimum stationaryRadius of 25).
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setStationaryRadius(25)
.commit();📘 For more information, see Philosophy of Operation
The SDK can optionally automatically stop tracking after some number of minutes elapses after the #start method was called.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setStopAfterElapsedMinutes(30)
.commit();
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
bgGeo.start(); // <-- SDK will automatically #stop itself after 30 minutes
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});The SDK can optionally automatically stop tracking when the stopTimeout timer elapses. For example, when the SDK first detects a motionchange into the "moving" state, the next time a motionchange event occurs into the "stationary" state, the SDK will have automatically called #stop upon itself.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setStopOnStationary(true)
.commit();stopOnStationary will only occur due to stopTimeout timer elapse. It will not occur by manually executing #changePace(true).
Specify an accuracy threshold in meters for odometer calculations. Defaults to 100. If a location arrives having accuracy > desiredOdometerAccuracy, that location will not be used to update the odometer. If you only want to calculate odometer from GPS locations, you could set desiredOdometerAccuracy: 10. This will prevent odometer updates when a device is moving around indoors, in a shopping mall, for example.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDesiredOdometerAccuracy(100F)
.commit();Defaults to false. Set true in order to disable constant background-tracking and record a location every ~500-1000 meters.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUseSignificantChangesOnly(true)
.commit();useSignificantChanges: false (Default)
>= API 29
The desired location-authorization request, either Always, WhenInUse or Any. locationAuthorizationRequest tells the SDK the mode it expects to be in.
Configuring Any will tell the plugin to operate in whichever mode the user selects, eight WhenInUse or Always.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setLocationAuthorizationRequest("Any")
.commit();WhenInUse will disable many of the plugin's features.
Defaults to 10000 (10 seconds). The desired time between activity detections. Larger values will result in fewer activity detections while improving battery life. A value of 0 will result in activity detections at the fastest possible rate.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setActivityRecognitionInterval(10000L)
.commit();Each activity-recognition-result returned by the API is tagged with a "confidence" level expressed as a %. You can set your desired confidence to trigger a motionchange event. Defaults to 75.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setMinimumActivityRecognitionConfidence(75)
.commit();When in the moving state, specifies the number of minutes to wait before turning off location-services and enter stationary state after the ActivityRecognition System detects the device is STILL (defaults to 5min). If you don't set a value, the SDK is eager to turn off the GPS ASAP. An example use-case for this configuration is to delay GPS OFF while in a car waiting at a traffic light.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setStopTimeout(5L)
.commit();📘 See Philosophy of Operation
Disables the accelerometer-based Stop-detection System. When disabled, you will no longer have control over #stopTimeout.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDisableStopDetection(false)
.commit();These are the comma-delimited list of activity-names returned by the ActivityRecognition API which will trigger a state-change from stationary to moving. By default, the SDK will trigger on any of the moving-states:
| Activity Name |
|---|
in_vehicle |
on_bicycle |
on_foot |
running |
walking |
If you wish, you can configure the SDK to only engage the moving state for vehicles by providing only "in_vehicle".
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
// Only trigger tracking for vehicles
.setTriggerActivities("in_vehicle")
.commit();
.
.
.
config.updateWithBuilder()
// Only trigger tracking for on_foot, walking and running
.setTriggerActivities("on_foot, walking, running")
.commit();Android 10+ now requires run-time permission from the user for "Physical Activity".
Traditionally, the background-geolocation Android SDK has relied heavily upon the Motion API for determining when to toggle location-services on/off based upon whether the device is moving vs stationary.
However, the Android SDK has a fallback "stationary geofence" mechanism just like iOS, the exit of which will cause the plugin to change to the moving state, toggle location-services and begin tracking. This will, of course, require the device moves a distance of typically 200-500 meters before tracking engages. With the Motion API authorized, the Android SDK typically requires just a few meters of movement for tracking to engage.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDisableMotionActivityUpdates(true)
.commit();Optionally add a delay in milliseconds to trigger Android into the moving state when Motion API reports the device is moving (eg: on_foot, in_vehicle)
This can help prevent false-positive motion-triggering when one moves about their home, for example. Only if the Motion API stays in the moving state for motionTriggerDelay milliseconds will the plugin trigger into the moving state and begin tracking the location.
If the Motion API returns to the still state before motionTriggerDelay times-out, the trigger to the moving state will be cancelled.
// Delay Android motion-triggering by 30000ms
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setMotionTriggerDelay(30000)
.commit();The following logcat shows an Android device detecting motion on_foot but returning to still before motionTriggerDelay expires, cancelling the transition to the moving state (see ⏰ Cancel OneShot: MOTION_TRIGGER_DELAY):
04-08 10:58:03.419 TSLocationManager: ╔═════════════════════════════════════════════
04-08 10:58:03.419 TSLocationManager: ║ Motion Transition Result
04-08 10:58:03.419 TSLocationManager: ╠═════════════════════════════════════════════
04-08 10:58:03.419 TSLocationManager: ╟─ 🔴 EXIT: still
04-08 10:58:03.419 TSLocationManager: ╟─ 🎾 ENTER: on_foot
04-08 10:58:03.419 TSLocationManager: ╚═════════════════════════════════════════════
04-08 10:58:03.416 TSLocationManager: ⏰ Scheduled OneShot: MOTION_TRIGGER_DELAY in 30000ms
.
. <motionTriggerDelay timer started>
.
04-08 10:58:19.385 TSLocationManager: ╔═════════════════════════════════════════════
04-08 10:58:19.385 TSLocationManager: ║ Motion Transition Result
04-08 10:58:19.385 TSLocationManager: ╠═════════════════════════════════════════════
04-08 10:58:19.385 TSLocationManager: ╟─ 🔴 EXIT: on_foot
04-08 10:58:19.385 TSLocationManager: ╟─ 🎾 ENTER: still
04-08 10:58:19.385 TSLocationManager: ╚═════════════════════════════════════════════
04-08 10:58:19.381 TSLocationManager: [c.t.l.s.TSScheduleManager cancelOneShot]
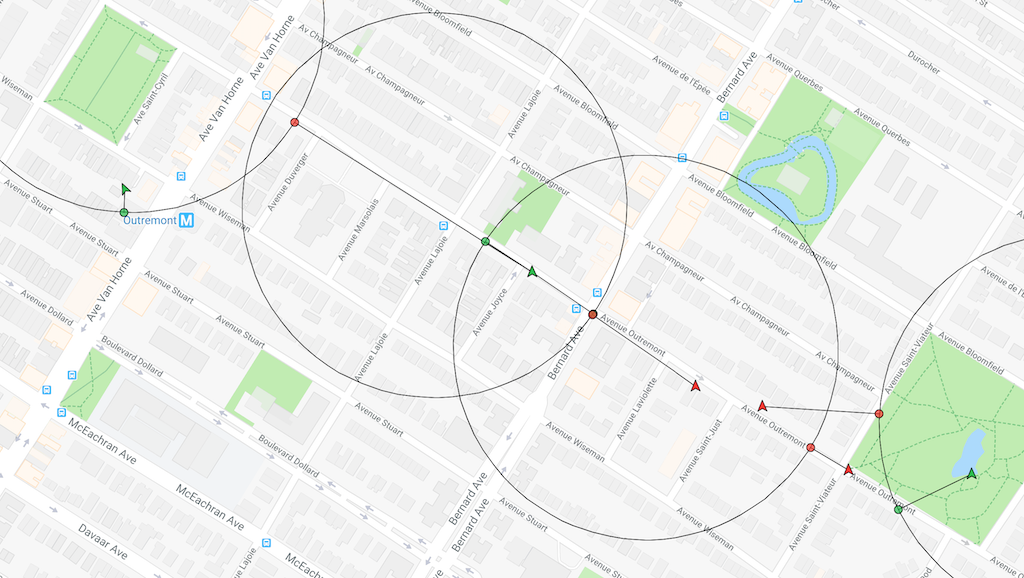
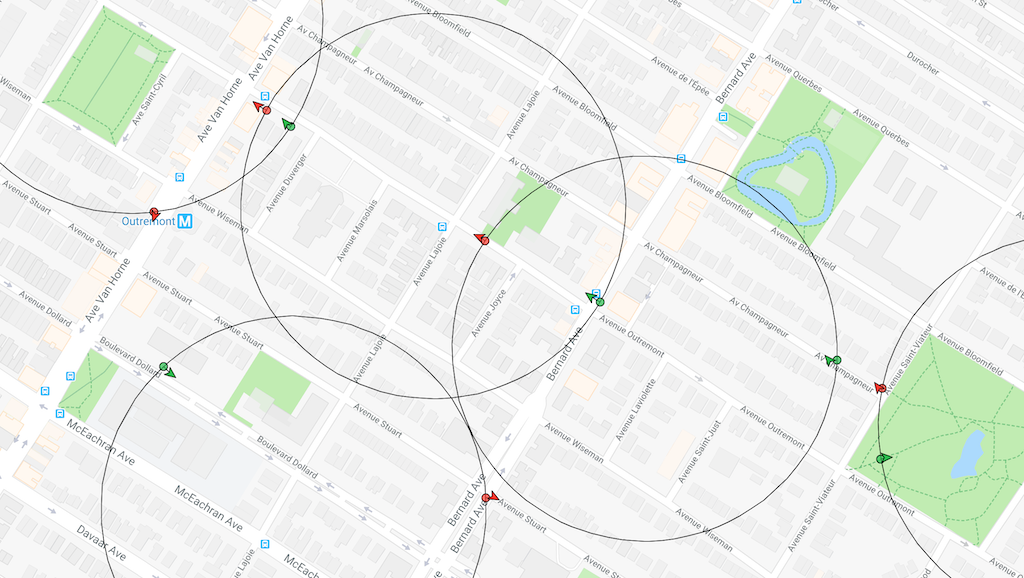
04-08 10:58:19.381 TSLocationManager: ⏰ Cancel OneShot: MOTION_TRIGGER_DELAY <-- timer cancelledDefaults to 1000 meters. @see releated event geofenceschange. When using Geofences, the SDK activates only thoses in proximity (the maximim geofences allowed to be simultaneously monitored is limited by the platform, where iOS allows only 20 and Android. However, the SDK allows you to create as many geofences as you wish (thousands even). It stores these in its database and uses spatial queries to determine which 20 or 100 geofences to activate.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setGeofenceProximityRadius(1000L)
.commit();📺 View animation of this behaviour
Defaults to true. Set false to disable triggering a geofence immediately if device is already inside it.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setGeofenceInitialTriggerEntry(true)
.commit();[Android only] Enable high-accuracy for geofence-only mode (See [[BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences]]).
Defaults to false. Runs Android's [[BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences]] with a foreground service (along with its corresponding persistent [[Notification]].
Configuring geofenceModeHighAccuracy: true will make Android geofence triggering far more responsive. In this mode, the usual config options to control location-services will be applied:
desiredAccuracylocationUpdateIntervaldistanceFilterdeferTime
With the default geofenceModeHighAccuracy: false, a device will have to move farther into a geofence before the ENTER event fires and farther out of a geofence before the EXIT event fires.
The more aggressive you configure the location-update params above (at the cost of power consumption), the more responsive will be your geofence-triggering.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setGeofenceModeHighAccuracy(true)
.commit();
BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences();geofenceModeHighAccuracy: false (Default) — Transition events are delayed.
geofenceModeHighAccuracy: true — Transition events are nearly instantaneous.
Your server url where you wish to HTTP POST location data to.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Compose optional HTTP #params attached to each HTTP request
JSONObject params = new JSONObject();
try {
params.put("user_id", 123);
params.put("route_id", 456);
} catch (JSONException e) {
}
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setAutoSync(true)
.setParams(params)
.setHeader("X-FOO", "foo")
.setHeader("X-BAR", "bar")
.commit();📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
stopOnTerminate: false, since your MainActivity will terminate — only the SDK's native Android background service will continue to operate, recording locations and uploading to your server. The SDK's native HTTP service is better at this task your own manual HTTP requests, since the SDK will automatically retry on server failure.
HTTP request timeout in milliseconds. The http callback will execute when an HTTP timeout occurs with an error code of 408. Defaults to 60000 ms (1 minute).
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setHttpTimeout(60000)
.commit();
bgGeo.onHttp(new TSHttpResponseCallback() {
@Override
public void onHttpResponse(HttpResponse response) {
Log.i(TAG, "- Http Response: " + response.status);
}
});The HTTP method to use when creating an HTTP request to your configured #url. Defaults to POST. Valid values are POST, PUT and OPTIONS.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setMethod("POST")
.commit();Optional HTTP params sent along in each HTTP request.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Compose optional HTTP #params attached to each HTTP request
JSONObject params = new JSONObject();
try {
params.put("user_id", 1234);
params.put("device_id", "abc123");
} catch (JSONException e) {
}
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setParams(params)
.commit();The HTTP request JSON will be structured as follows:
POST /locations
{
"location": {
"coords": {
"latitude": 45.51927004945047,
"longitude": -73.61650072045029
.
.
.
}
},
"user_id": 1234,
"device_id": 'abc123'
}Optional HTTP params sent along in HTTP request to above #url.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Compose optional HTTP #params attached to each HTTP request
JSONObject headers = new JSONObject();
try {
headers.put("X-FOO", "foo");
headers.put("X-BAR", "bar");
} catch (JSONException e) {
}
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setHeaders(headers)
.commit();ℹ️ Note: You can also use the TSConfig method setHeader repeatedly to add headers instead of composing a JSONObject:
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setHeader("X-FOO", "foo")
.setHeader("X-BAR", "bar")
.commit();The root property of the JSON data where location-data will be placed in the HTTP request data.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setHttpRootProperty("rootProperty")
.commit();📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
The HTTP request JSON will be structured as follows:
{
"rootProperty":{ // <--------
"coords": {
"latitude":23.232323,
"longitude":37.373737
}
}
}
You may also specify the character httpRootProperty:"." to place your data in the root of the JSON:
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setHttpRootProperty(".")
.commit();The HTTP request JSON will be structured as follows:
{
"coords": {
"latitude":23.232323,
"longitude":37.373737
}
}Optional custom template for rendering location JSON request data in HTTP requests. Evaulate variables in your locationTemplate using Ruby erb-style tags:
<%= variable_name %>📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setLocationTemplate("{\"lat\":<%= latitude %>,\"lng\":<%= longitude %>,\"event\":\"<%= event %>\",isMoving:<%= isMoving %>}")
.commit();
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setLocationTemplate("[<%=latitude%>, <%=longitude%>, \"<%=event%>\", <%=is_moving%>]")
.commit();#extras, these key-value pairs will be merged directly onto your location data. Eg:
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Compose optional HTTP #extras attached to each HTTP request
JSONObject extras = new JSONObject();
try {
extras.put("foo", "bar");
} catch (JSONException e) {
}
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setHttpRootProperty("data")
.setLocationTemplate("{\"lat\":<%= latitude %>,\"lng\":<%= longitude %>}")
.setExtras(extras)
.commit();Will result in JSON:
{
"data": { // <-- httpRootProperty
"lat":23.23232323,
"lng":37.37373737,
"foo":"bar" // <-- appended extras
}
}
Template Tags
| Tag | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
latitude |
Float |
|
longitude |
Float |
|
speed |
Float |
Meters |
heading |
Float |
Degress |
accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
altitude |
Float |
Meters |
altitude_accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
timestamp |
String |
ISO-8601 |
uuid |
String |
Unique ID |
event |
String |
`motionchange |
odometer |
Float |
Meters |
activity.type |
String |
`still |
activity.confidence |
Integer |
0-100% |
battery.level |
Float |
0-100% |
battery.is_charging |
Boolean |
Is device plugged in? |
Optional custom template for rendering geofence JSON request data in HTTP requests. The geofenceTemplate is similar to #locationTemplate with the addition of two extra geofence.* tags.
Evaulate variables in your geofenceTemplate using Ruby erb-style tags:
<%= variable_name %>📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setGeofenceTemplate("{\"lat\":<%= latitude %>,\"lng\":<%= longitude %>, \"geofence\":\"<%= geofence.identifier %>:<%= geofence.action %>\"}")
.commit();Template Tags
The tag-list is identical to #locationTemplate with the addition of geofence.identifier and geofence.action.
| Tag | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
geofence.identifier |
String |
Which geofence? |
geofence.action |
String |
`ENTER |
latitude |
Float |
|
longitude |
Float |
|
speed |
Float |
Meters |
heading |
Float |
Degress |
accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
altitude |
Float |
Meters |
altitude_accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
timestamp |
String |
ISO-8601 |
uuid |
String |
Unique ID |
event |
String |
`motionchange |
odometer |
Float |
Meters |
activity.type |
String |
`still |
activity.confidence |
Integer |
0-100% |
battery.level |
Float |
0-100% |
battery.is_charging |
Boolean |
Is device plugged in? |
Default is false. If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url, batchSync: false will POST all the locations currently stored in native SQLite datbase to your server in a single HTTP POST request. With batchSync: false, an HTTP POST request will be initiated for each location in database.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setBatchSync(true)
.commit();If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url with batchSync: true, this parameter will limit the number of records attached to each batch request. If the current number of records exceeds the maxBatchSize, multiple HTTP requests will be generated until the location queue is empty.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setBatchSync(true)
.setMaxBatchSize(100)
.commit();Default is true. If you've enabeld HTTP feature by configuring an #url, the SDK will attempt to HTTP POST each location to your server as it is recorded. If you set autoSync: NO, it's up to you to manually execute the #sync method to initate the HTTP POST (NOTE The SDK will continue to persist every recorded location in the SQLite database until you execute #sync).
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setAutoSync(true)
.commit();The minimum number of persisted records to trigger an autoSync action. If you configure a value greater-than 0, the SDK will wait until that many locations are recorded before executing HTTP requests to your server through your configured #url.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setAutoSyncThreshold(5) // <-- queue 5 locations before performing HTTP
.commit();ℹ️ The SDK will ignore autoSyncThreshold when a motionchange event occurs and automatically upload all queued locations.
Optional arbitrary key/value {} to attach to each recorded location
Eg: Every recorded location will have the following extras appended:
📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Compose optional HTTP #extras attached to each HTTP request
JSONObject extras = new JSONObject();
try {
extras.put("route_id", 1234);
} catch (JSONException e) {
}
// Compose optional HTTP #params attached to each HTTP request
JSONObject params = new JSONObject();
try {
params.put("device_id", "abc123");
} catch (JSONException e) {
}
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setUrl("http://my-server.com/locations")
.setExtras(extras)
.setParams(params)
.commit();The HTTP request JSON will be composed as follows:
- POST /locations
{
"device_id": "abc123" // <-- params appended to root of JSON
"location": {
"coords": {
"latitude": 45.51927004945047,
"longitude": -73.61650072045029,
.
.
.
},
"extras": { // <-- extras appended to *each* location
"route_id": 1234
}
}
}Maximum number of days to store a geolocation in SDK's SQLite database when your server fails to respond with HTTP 200 OK. The SDK will continue attempting to sync with your server until maxDaysToPersist when it will give up and remove the location from the database.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setMaxDaysToPersist(5) // <-- persist locations for up to 5 days
.commit();Maximum number of records to persist in SDK's SQLite database. Default -1
means no limit.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setMaxRecordsToPersist(10000) // <-- persist maximum 10000 records
.commit();ℹ️ Records are automatically deleted from the SDK's SQLite database when your server returns and HTTP success response (eg: 200).
Controls the order that locations are selected from the database (and synced to your server). Defaults to ascending (ASC), where oldest locations are synced first. Descending (DESC) syncs latest locations first.|
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setLocationsOrderDirection("ASC")
.commit();Defaults to true. When the user terminates the app, the SDK will stop tracking. Set this to false to continue tracking after application terminate.
If you do configure stopOnTerminate: false, your application's MainActivity will terminate at that time. Only the Android background-service remains running. If you've configured the SDK with an #url, the HTTP service will continue upload locations to your server.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setStopOnTerminate(false)
.commit();Defaults to false. Set true to engage background-tracking after the device reboots.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setStartOnBoot(true)
.commit();Controls the rate (in seconds) the heartbeat event will fire. The SDK will not provide any updated locations to your heartbeat event-handler, since it will provide only the last-known location. If you wish for an updated location in your heartbeat callback, it's up to you to request one with #getCurrentPosition.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setHeartbeatInterval(60)
.commit();
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onHeartbeat(new TSHeartbeatCallback() {
@Override
public void onHeartbeat(HeartbeatEvent heartbeatEvent) {
TSLocation location = heartbeatEvent.getLocation();
Log.i(TAG, "[heartbeat] last known location: " + location.toJson());
}
});Provides an automated schedule for the SDK to start/stop tracking at pre-defined times. The format is cron-like:
"{DAY(s)} {START_TIME}-{END_TIME}"The START_TIME, END_TIME are in 24h format. The DAY param corresponds to the Locale.US, such that Sunday=1; Saturday=7). You may configure a single day (eg: 1), a comma-separated list-of-days (eg: 2,4,6) or a range (eg: 2-6), eg:
// Compose schedule
ArrayList<String> schedule = new ArrayList<>();
schedule.add("1 17:30-21:00"); // Sunday: 5:30pm-9:00pm)
schedule.add("2-6 9:00-17:00"); // Mon-Fri: 9:00am to 5:00pm)
schedule.add("2,4,6 20:00-00:00"); // Mon, Web, Fri: 8pm to midnight (next day)
schedule.add("7 10:00-19:00"); // Sat: 10am-7pm
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setSchedule(schedule)
.commit();
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Listen to schedule event
bgGeo.onSchedule(new TSScheduleCallback() {
@Override
public void onSchedule(ScheduleEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "[schedule] tracking is enabled? " + event.getEnabled());
}
});
// Finally, signal #ready and #startSchedule
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] success");
bgGeo.startSchedule();
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
.
.
.
// Later when you want to stop the Scheduler (eg: user logout)
bgGeo.stopSchedule();
// Note: if SDK is currently tracking, stopSchedule does NOT stop tracking.
// It will only stop the schedule from executing.
if (config.getEnabled()) {
bgGeo.stop();
}The schedule can also be configured with a literal start date of the form:
"yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm-HH:mm"
eg:
// Compose schedule
ArrayList<String> schedule = new ArrayList<>();
schedule.add("2018-01-01 09:00-17:00");
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setSchedule(schedule)
.commit();Or two literal dates to specify both a start and stop date (note the format here is a bit ugly):
"yyyy-mm-dd-HH:mm yyyy-mm-dd-HH:mm"
"2018-01-01-09:00 2019-01-01-17:00" // <-- track for 1 year
Defaults to false. When the Android OS is under memory pressure from other applications (eg: a phone call), the OS can and will free up memory by terminating other processes and scheduling them for re-launch when memory becomes available. If you find your tracking being terminated unexpectedly, this is why.
If you set this option to true, the SDK will run its Android service in the foreground, supplying the ongoing notification to be shown to the user while in this state. Running as a foreground-service makes the tracking-service much more inmmune to OS killing it due to memory/battery pressure. By default services are background, meaning that if the system needs to kill them to reclaim more memory (such as to display a large page in a web browser).
ℹ️ See related config options notificationTitle, notificationText & notificationColor
📘 For more information, see the Android Service docs.
Set to true to enable "Headless" mode when the user terminates the application where you've configured stopOnTerminate: false. In this mode, you can respond to all the SDK's events in the native Android environment. For more information, see the wiki for Android Headless Mode.
ℹ️ "Headless" mode is an alternartive to using the forceReloadOnXXX configuration options below.
When the user terminates your Android app with BackgroundGeolocation configured with stopOnTerminate: false, the foreground MainActivity will terminate — only the SDK's background-service is running, "headless", in this case. The background service will continue tracking the location. However, the background-service can optionally re-launch your MainActivity.
To "force reload" your application, set any of the following options to true:
Launch your app whenever the #motionchange event fires.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setForceReloadOnMotionChange(true)
.commit();Launch your app whenever the #location event fires.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setForceReloadOnLocationChange(true)
.commit();Launch your app whenever the #geofence event fires.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setForceReloadOnGeofence(true)
.commit();Launch your app whenever the #heartbeat event fires.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setForceReloadOnHeartbeat(true)
.commit();Launch your app whenever a schedule event fires.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setForceReloadOnSchedule(true)
.commit();If the user reboots the device with the SDK configured for startOnBoot: true, your will app will launch when the device is rebooted.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setForceReloadOnBoot(true)
.commit();When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will control the priority of that notification as well as the position of the notificaiton-bar icon.
ℹ️ To completely hide the icon in the notification-bar, use NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MIN (:warning: It is no longer possible to hide the notification-bar icon in Android O)
The following notificationPriority values defined as constants on the NotificationCompat object:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
PRIORITY_DEFAULT |
Notification weighted to top of list; notification-bar icon weighted left |
PRIORITY_HIGH |
Notification strongly weighted to top of list; notification-bar icon strongly weighted to left |
PRIORITY_LOW |
Notification weighted to bottom of list; notification-bar icon weighted right |
PRIORITY_MAX |
Same as PRIORITY_HIGH |
PRIORITY_MIN |
Notification strongly weighted to bottom of list; notification-bar icon hidden |
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setNotificationPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_MIN)
.commit();When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will configure the title of that notification. Defaults to the application name.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setNotificationTitle("My Application Name")
.setNotificationText("Location tracking engaged")
.setNotificationColor("#FF0000")
.commit();When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will configure the text of that notification. Defaults to "Location service activated".
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setNotificationTitle("My Application Name")
.setNotificationText("Location tracking engaged")
.setNotificationColor("#FF0000")
.commit();When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will configure the color of the notification icon (API >= 21).Supported formats are:
#RRGGBB#AARRGGBB
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setNotificationTitle("My Application Name")
.setNotificationText("Location tracking engaged")
.setNotificationColor("#FF0000")
.commit();When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This allows you customize that icon. Defaults to your application icon. NOTE You must specify the type (drawable|mipmap) of resource you wish to use in the following format:
{type}/icon_name,
.png)
eg:
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
// 1. drawable
.setNotificationSmallIcon("drawable/my_custom_notification_small_icon")
// Or 2. MipMap
.setNotificationSmallIcon("mipmap/my_custom_notification_small_icon")
.commit();When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This allows you customize that icon. Defaults to undefined. NOTE You must specify the type (drawable|mipmap) of resource you wish to use in the following format:
.png)
{type}/icon_name,
eg:
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
// 1. drawable
.setNotificationSmallIcon("drawable/my_custom_notification_large_icon")
// Or 2. MipMap
.setNotificationSmallIcon("mipmap/my_custom_notification_large_icon")
.commit();Defaults to false. When set to true, the SDK will emit debugging sounds and notifications for life-cycle events of background-geolocation!
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDebug(true)
.commit();📘 See Debugging Sounds
BackgroundGeolocation contains powerful logging features. By default, the SDK boots with a value of LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE, storing 3 days worth of logs (configurable with logMaxDays) in its SQLite database.
The following log-levels are defined as constants on the BackgroundGeolocation object:
| logLevel | Description |
|---|---|
0 |
Logging disabled |
1 |
Only log errors |
2 |
Only log warnings & errors |
3 |
Log Info, Warnings & errors |
4 |
Log debug, info, warnings & errors |
5 |
Log everything |
Eg:
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setLogLevel(5) // <-- Log everything
.commit();ℹ️ To retrieve the SDK's logs, see getLog & emailLog.
logLevel appropriately (eg: 1)
Maximum number of days to persist a log-entry in database. Defaults to 3 days.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setLogMaxDays(3)
.commit();Fired whenever a location is recorded.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onLocation(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Location location = tsLocation.getLocation();
boolean isMoving = tsLocation.getIsMoving();
DetectedActivity activity = tsLocation.getDetectedActivity();
Log.i(TAG, "[location] - " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[location] error: " + error);
}
});Your onLocation callback will be executed with the following signature whenever a new location is recorded:
@param {TSLocation} location The Location data
ℹ️ When performing a motionchange or getCurrentPosition, the SDK requests multiple location samples in order to record the most accurate location possible. These samples are not persisted to the database but they will be provided to your location listener, for your convenience, since it can take some seconds for the best possible location to arrive. For example, you might use these samples to progressively update the user's position on a map. You can detect these samples in your callbackFn via location.sample === true. If you're manually POSTing location to your server, you should ignore these locations.
| Code | Error |
|---|---|
| 0 | Location unknown |
| 1 | Location permission denied |
| 2 | Network error |
| 408 | Location timeout |
Fired whenever the device changes state between moving and stationary.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onMotionChange(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[motionchange] - " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[motionchange] error: " + error);
}
});Your onLocation callback will be executed each time the device has changed-state between MOVING or STATIONARY.
| Code | Error |
|---|---|
| 0 | Location unknown |
| 1 | Location permission denied |
| 2 | Network error |
| 408 | Location timeout |
Your onActivityChange callback will be executed each time the activity-recognition system receives an event (still, on_foot, in_vehicle, on_bicycle, running).
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onActivityChange(new TSActivityChangeCallback() {
@Override
public void onActivityChange(ActivityChangeEvent event) {
DetectedActivity activity = event.getDetectedActivity();
Log.i(TAG, "[activitychange] " + activity);
}
});Your onLocationProviderChange callback will be executed when a change in the state of the device's Location Services has been detected. eg: "GPS ON", "Wifi only".
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onLocationProviderChange(new TSLocationProviderChangeCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocationProviderChange(LocationProviderChangeEvent event) {
boolean enabled = event.isEnabled();
boolean gpsOn = event.isGPSEnabled();
boolean wifiOn = event.isNetworkEnabled();
boolean authorized = event.isPermissionGranted();
Log.i(TAG, "[locationproviderchange] " + event.toJson());
}
});Adds a geofence event-listener. Your supplied onGeofence callback will be executed when any monitored geofence crossing occurs, provided with a GeofenceEvent parameter.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onGeofence(new TSGeofenceCallback() {
@Override
public void onGeofence(GeofenceEvent event) {
TSLocation tsLocation = event.getLocation();
Location location = tsLocation.getLocation();
TSGeofence tsGeofence = event.getGeofence();
GeofencingEvent geofencingEvent = event.getGeofencingEvent();
Log.i(TAG, "[geofence] " + event.toJson());
}
});Fired when the list of monitored-geofences changed. The SDK contains powerful geofencing features that allow you to monitor any number of circular geofences you wish (thousands even), in spite of limits imposed by the native platform APIs (20 for iOS; 100 for Android).
The SDK achieves this by storing your geofences in its database, using a geospatial query to determine those geofences in proximity (@see config geofenceProximityRadius), activating only those geofences closest to the device's current location (according to limit imposed by the corresponding platform).
When the device is determined to be moving, the SDK periodically queries for geofences in proximity (eg. every minute) using the latest recorded location. This geospatial query is very fast, even with tens-of-thousands geofences in the database.
It's when this list of monitored geofences changes, the SDK will fire the geofenceschange event.
📘 For more information, see Geofencing Guide
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onGeofencesChange(new TSGeofencesChangeCallback() {
@Override
public void onGeofencesChange(GeofencesChangeEvent event) {
ArrayList<TSGeofence> on = event.getActivatedGeofences();
ArrayList<String> off = event.getDeactivatedGeofences();
Log.i(TAG, "[geofenceschange] " + event.toJson());
}
});This GeofencesChangeEvent provides only the changed geofences, those which just activated or de-activated.
When all geofences have been removed, the event object will provide an empty List for both activated and deactivated geofences.
The TSHttpResponseCallback will be executed for each HTTP request (success or failure).
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onHttp(new TSHttpResponseCallback() {
@Override
public void onHttpResponse(HttpResponse response) {
int status = response.getStatus();
int responseText = response.getResponseText();
boolean success = response.isSuccess();
Log.i(TAG, "[http] " + status + ", responseText: " + responseText);
}
});The TSHeartbeatCallback will be executed for each #heartbeatInterval while the device is in stationary state. The HeartbeatEvent provides access to the last known location -- this is not the current location. The heartbeat event will not request a new location. If you want a new location in the heartbeat event, use the #getCurrentPosition method.
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onHeartbeat(new TSHeartbeatCallback() {
@Override
public void onHeartbeat(HeartbeatEvent event) {
TSLocation lastKnownLocation = event.getLocation();
Log.i(TAG, "[heartbeat] " + event.toJson());
}
});The TSScheduleCallback will be executed each time a schedule event fires.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
// Configure schedule: every day from 9am-5pm.
ArrayList<String> schedule = new ArrayList<>();
schedule.add("1-7 09:00-17:00");
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setSchedule(schedule)
.commit();
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Listen to schedule event
bgGeo.onSchedule(new TSScheduleCallback() {
@Override
public void onSchedule(ScheduleEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "[schedule] tracking is enabled? " + event.getEnabled());
}
});
// Finally, signal #ready and #startSchedule
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] success");
bgGeo.startSchedule();
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});Fired when the state of the operating-system's "Power Saving" mode changes. Your callback will be provided with a Boolean parameter signalling whether "Power Saving" is enabled or disabled. Power Saving mode can throttle certain services in the background, such as HTTP requests or GPS.
ℹ️ You can manually request the current-state of "Power Saving" mode with the method #isPowerSaveMode.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onPowerSaveChange(new TSPowerSaveChangeCallback() {
@Override
public void onPowerSaveChange(Boolean isPowerSaveMode) {
Log.i(TAG, "[powersavechange] is power save mode? " + isPowerSaveMode);
}
});Fired when the state of the device's network-connectivity changes (enabled -> disabled and vice-versa). By default, the SDK will automatically fire a connectivitychange event with the current state network-connectivity whenever the #start method is executed.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onConnectivityChange(new TSConnectivityChangeCallback() {
@Override
public void onConnectivityChange(ConnectivityChangeEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "[connectivitychange] has network connection? " + event.hasConnection());
}
});Fired when the SDK's enabled state changes. For example, executing #start and #stop will cause the enabledchange event to fire. This event is primarily desigend for use with the configuration option [stopAfterElapsedMinutes], which automatically executes the SDK's #stop method.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.onEnabledChange(new TSEnabledChangeCallback() {
@Override
public void onEnabledChange(boolean enabled) {
enabledchange
Log.i(TAG, "[enabledchnage] is enabled? " + enabled);
}
});The #ready method is your first point-of-contact with the SDK. You must execute the #ready method each time your application boots. The supplied TSCallback will be executed when the SDK is ready for tracking.
ℹ️ BackgroundGeolocation persists its enabled state between application terminate or device reboot and #ready will automatically #start tracking if it finds enabled == true.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static String TAG = "MyApp";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setDebug(true)
.setLogLevel(5) // Verbose logging
.setDesiredAccuracy(LocationRequest.PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY)
.setDistanceFilter(50f)
.setForegroundService(true)
.setUrl("http://your.server.com/locations")
.commit();
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Listen to events:
bgGeo.onLocation(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override public void onLocation(TSLocation location) {
Log.i(TAG, "[event] - location: " + location.toJson());
}
@Override public void onError(Integer code) {
Log.i(TAG, "[event] - location error: " + code);
}
});
// Finally, signal #ready to the SDK.
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "- configure success");
// The SDK persists its enabled state.
// #ready will automatically execute #start if already enabled.
if (!config.getEnabled()) {
bgGeo.start(); // <-- start tracking.
}
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "- configure FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
}Enable location tracking. This is the SDK's power ON button. The SDK will initially start into its stationary state, fetching an initial location before turning off location services and firing the motionchange event.
private CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener createEnableSwitchListener() {
return new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isMoving) {
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
mBtnChangePace.setEnabled(isMoving);
// #start / #stop BackgroundGeolocation
if (isMoving) {
bgGeo.start();
// Or with optional callback
bgGeo.start(new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[start] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[start] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
} else {
bgGeo.stop();
}
}
};
}Note: The SDK persists its enabled state between restarts / reboots and will automatically #start itself after executing the #ready method.
📘 For more information, see Philosophy of Operation
Disable location tracking. This is the SDK's power OFF button.
private CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener createEnableSwitchListener() {
return new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isMoving) {
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
mBtnChangePace.setEnabled(isMoving);
// #start / #stop BackgroundGeolocation
if (isMoving) {
bgGeo.start();
} else {
bgGeo.stop();
// Or with optional callback
bgGeo.stop(new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[stop] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[stop] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
}
};
}schedule, #stop will not halt the Scheduler. You must explicitly stop the Scheduler as well:
Retrieves the current position. This method instructs the SDK to fetch exactly one location using maximum power & accuracy. The SDK will persist the fetched location to its SQLite database just as any other location in addition to POSTing to your configured #url (if you've enabled the HTTP features).
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static String TAG = "MyApp";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
View.OnClickListener listener = new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override public void onClick(View view) {
// Build position request.
TSCurrentPositionRequest request = new TSCurrentPositionRequest.Builder(getApplicationContext())
.setPersist(true) // <-- yes, persist to database
.setSamples(3) // <-- fetch 3 location samples and return highest accuracy
.setCallback(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[current position] success: " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[current position] failure: " + error);
}
})
.build();
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
bgGeo.getCurrentPosition(request);
}
};
}
}ℹ️ While the callback block will receive only one location, the SDK does request multiple location samples in order to record the most accurate location possible. These samples are not persisted to the database but they will be provided to your location event-listener, for your convenience, since it can take some seconds for the best possible location to arrive. For example, you might use these samples to progressively update the user's position on a map. You can detect these samples in your location onLocation callback via location.sample. If you're manually POSTing location to your server, you should ignore these locations.
If a location failed to be retrieved, the onError callback will be executed and provided with an int error with one of the following error-codes:
| Code | Error |
|---|---|
| 0 | Location unknown |
| 1 | Location permission denied |
| 2 | Network error |
| 408 | Location timeout |
Start a stream of continuous location-updates. The SDK will persist the fetched location to its SQLite database just as any other location in addition to POSTing to your configured #url (if you've enabled the HTTP features).
#watchPosition is not reccommended for long term monitoring in the background — It's primarily designed for use in the foreground only. You might use it for fast-updates of the user's current position on the map, for example.
#watchPosition will continue to run in the background, preventing OS from suspending your application. Take care to listen to suspend event and call #stopWatchPosition if you don't want your app to keep running (TODO make this configurable).
TSWatchPositionRequest request = new TSWatchPositionRequest.Builder()
.setPersist(true) // <-- persist each location to SDK database.
.setInterval(5000L) // <-- record location every 5s.
.setCallback(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[watchposition] " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[watchposition error: " + error);
}
})
.build();
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
bgGeo.watchPosition(request);ℹ️ Also see #stopWatchPosition
Halt #watchPosition updates.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
bgGeo.stopWatchPosition();Manually Toggles the SDK motion state between stationary and moving. When enabled is set to true, the SDK will engage location-services and begin aggressively tracking the device's location immediately, bypassing stationary monitoring. If you were making a "Jogging" application, this would be your [Start Workout] button to immediately begin location-tracking. Send false to turn off location-services and return the SDK to the stationary state.
Executing #changePace will cause the motionchange event to be fired.
@param {boolean} Set true to manually turn on location-services and enter tracking state. Set false to manually enter stationary state.
View.OnClickListener listener new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override public void onClick(View view) {
// Toggle BackgroundGeolocation ON or OFF.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
boolean isMoving = !config.getIsMoving();
bgGeo.changePace(isMoving);
// Or with optional callback
bgGeo.changePace(isMoving, new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[changePace] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[changePace] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
};Retrieves the current value of the odometer in meters. The value of the odometer is persisted between application boots / device restarts. Note: odometer is available from TSConfig -- not BackgroundGeolocation.
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
Float odometer = config.getOdometer();Set the odometer to any arbitrary value. NOTE setOdometer will perform a getCurrentPosition in order to record the exact reference location where odometer was set.
@param {TSLocationCallback} (Optional) callback executed when reference location is successfully retrieved (or failure).
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.setOdometer(0F, new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[setOdometer] success");
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer integer) {
Log.i(TAG, "[setOdometer] failed to retreive reference location");
}
});If a #schedule was configured, this method will initiate that schedule. The SDK will automatically be started or stopped according to the configured #schedule.
// Compose schedule
ArrayList<String> schedule = new ArrayList<>();
schedule.add("1 17:30-21:00"); // Sunday: 5:30pm-9:00pm)
schedule.add("2-6 9:00-17:00"); // Mon-Fri: 9:00am to 5:00pm)
schedule.add("2,4,6 20:00-00:00"); // Mon, Web, Fri: 8pm to midnight (next day)
schedule.add("7 10:00-19:00"); // Sat: 10am-7pm
TSConfig config = TSConfig.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
config.updateWithBuilder()
.setSchedule(schedule)
.commit();
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Listen to schedule event
bgGeo.onSchedule(new TSScheduleCallback() {
@Override
public void onSchedule(ScheduleEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "[schedule] tracking is enabled? " + event.getEnabled());
}
});
// Finally, signal #ready and #startSchedule
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] success");
bgGeo.startSchedule(); // <-- start the scheduler.
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});This method will stop the Scheduler service.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.stopSchedule();#stopSchedule will not execute #stop if the SDK is currently enabled. You must explicitly execute #stop.
Fetches the state of the operating-systems "Power Saving" mode, whether enabled or disabled. Power Saving mode can throttle certain services in the background, such as HTTP requests or GPS.
ℹ️ You can listen to changes in the state of "Power Saving" mode with the event #powersavechange.
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
boolean isPowerSaveMode = bgGeo.isPowerSaveMode();Remove all event-listeners registered with #onEventName method. You're free to add more listeners again after executing #removeListeners.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.removeListeners();Fetch all the locations currently stored in native SDK's SQLite database. Your TSGetLocationsCallback will receive an List of locations
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.getLocations(new TSGetLocationsCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<LocationModel> list) {
for (LocationModel record : list) {
JSONObject json = (JSONObject) record.getJson();
Log.i(TAG, "[getLocations] record: " + json.toString());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[getLocations] failure: " + error);
}
});Fetches count of SQLite locations table SELECT count(*) from locations.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
int count = bgGeo.getCount();Remove all records in SDK's SQLite database.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.destroyLocations();
// Or with optional Callback
bgGeo.destroyLocations(new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[destroyLocations] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[destroyLocations] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});Remove a single record from the SDK's SQLite database by Location.uuid.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
bgGeo.destroyLocation(tsLocation.getUUID());
// Or with optional Callback
bgGeo.destroyLocation(tsLocation.getUUID(), new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[destroyLocation] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[destroyLocation] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});If the SDK is configured for HTTP with an #url and autoSync: false, this method will initiate POSTing the locations currently stored in the native SQLite database to your configured #url. When your HTTP server returns a response of 200 OK, that record(s) in the database will be DELETED.
If you configured batchSync: true, all the locations will be sent to your server in a single HTTP POST request, otherwise the SDK will create execute an HTTP post for each location in the database (REST-style). Your TSSyncCallback#onSuccess will be executed and provided with a List of all the locations from the SQLite database. If you configured the SDK for HTTP (by configuring an #url, your TSSyncCallback#onSuccess will be executed after the HTTP request(s) have completed. If the SDK failed to sync to your server (possibly because of no network connection), the TSSyncCallback#onFailure will be called with an errorMessage. If you are not using the HTTP features, sync will delete all records from its SQLite datbase. Eg:
Your callback will be provided with the following params
@param {TSSyncCallback} (Optional) Callback to receive successfully synced location records from datbase.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.sync(new TSSyncCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<LocationModel> list) {
Log.i(TAG, "[sync] success: " + list);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[sync] failure: " + error);
}
});
// You may optionally provide no callback if you're configured an #url with
// autoSync: false and simply wish to initiate the SDK's HTTP service.
bgGeo.sync();📘 For more information, see HTTP Guide
Engages the geofences-only trackingMode. In this mode, no active location-tracking will occur -- only geofences will be monitored. To stop monitoring "geofences" trackingMode, simply use the usual #stop method.
@param {TSCallback} (Optional) Callback to signal success / failure to start geofence-only tracking.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static String TAG = "MyApp";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Create a Geofence.
TSGeofence geofence = new TSGeofence.Builder()
.setIdentifier("Office")
.setLatitude(37.234234)
.setLongitude(47.2856623)
.setRadius(200)
.setNotifyOnEntry(true)
.setNotifyOnExit(true)
.build();
bgGeo.addGeofence(geofence);
// Finally, signal #ready to the SDK and #startGeofences
bgGeo.ready(new TSCallback() {
@Override public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] success");
bgGeo.startGeofences();
}
@Override public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[ready] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
}
Adds a geofence to be monitored by the native SDK. If a geofence already exists with the configured identifier, the previous one will be deleted before the new one is inserted.
The SDK persists each added geofence into into a SQLite database. The will exist there and automatically be monitored until you #removeGeofence.
@param {TSGeofence} geofence to monitor.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
// Optional geofence extras.
JSONObject extras = new JSONObject();
try {
extras.put("job_id", 1234);
} catch (JSONException e) {}
// Create a Geofence.
TSGeofence geofence = new TSGeofence.Builder()
.setIdentifier("Office")
.setLatitude(37.234234)
.setLongitude(47.2856623)
.setRadius(200)
.setNotifyOnEntry(true)
.setNotifyOnExit(true)
.setExtras(extras)
.build();
// Add it.
bgGeo.addGeofence(geofence);
// You may optionally supply a TSCallback to be notified of insert errors
bgGeo.addGeofence(geofence, new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[addGeofence] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[addGeofence] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});ℹ️ When adding a list-of-geofences, it's about 10 faster* to use #addGeofences instead.
📘 See Geofencing Guide for more information.
Adds a list of geofences to be monitored by the native SDK. If a geofence already exists with the configured identifier, the previous one will be deleted before the new one is inserted.
@param {List<TSGeofence>} List of TSGeofence to monitor
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
TSGeofence office = new TSGeofence.Builder()
.setIdentifier("Office")
.setLatitude(37.234234)
.setLongitude(47.2856623)
.setRadius(200)
.setNotifyOnEntry(true)
.setNotifyOnExit(true)
.build();
TSGeofence home = new TSGeofence.Builder()
.setIdentifier("Home")
.setLatitude(37.5723811)
.setLongitude(46.2396901)
.setRadius(200)
.setNotifyOnEntry(true)
.setNotifyOnExit(true)
.build();
List<TSGeofence> geofences = new ArrayList<>();
geofences.add(office);
geofences.add(home);
// Add geofences
bgGeo.addGeofences(geofences);
// You may optionally supply a TSCallback to be notified insert errors
bgGeo.addGeofences(geofences, new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[addGeofences] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[addGeofences] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});Removes a geofence having the given {String} identifier.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.removeGeofence("Home");
// With optional Callback
bgGeo.removeGeofence("Home", new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[removeGeofence] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String s) {
Log.i(TAG, "[removeGeofence] FAILURE");
}
});Stop monitoring geofences and destroy them from database.
@param {List<String>} (Optional) List of geofences to remove by identifier. All geofences will be removed if omitted.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.removeGeofences();
// With optional Callback
bgGeo.removeGeofences(new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[removeGeofence] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String s) {
Log.i(TAG, "[removeGeofence] FAILURE");
}
});BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
List<String> identifiers = new ArrayList<>();
identifiers.add("Home");
identifiers.add("Office");
bgGeo.removeGeofences(identifiers);
// With optional Callback
bgGeo.removeGeofences(identifiers, new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[removeGeofences] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String s) {
Log.i(TAG, "[removeGeofences] FAILURE");
}
});Fetch the list of monitored geofences from SDK database. Your TSGetGeofencesCallback will be provided a List<TSGeofence>:
@param {TSGetGeofencesCallback} Callback to receive List<TSGeofence> from the database.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.getGeofences(new TSGetGeofencesCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<TSGeofence> geofences) {
for (TSGeofence geofence : geofences) {
Log.i(TAG, "[getGeofences] " + geofence.toJson());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String s) {
Log.i(TAG, "[getGeofences] FAILURE");
}
});Fetches the entire contents of the current circular-log and return it to the provided callback. The SDK persists its logs in a SQLite database. Logs are controlled by the configuration options logLevel and logMaxDays. See also emailLog
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.getLog(new TSGetLogCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(String log) {
Log.i(TAG, log);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[getLog] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});Fetch the entire contents of the current circular log and email it to a recipient using the device's native email client.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static String TAG = "MyApp";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.emailLog("[email protected]", this, new TSEmailLogCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[emailLog] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[emailLog] FAILURE: " + error);
}
});
}
}Destory the entire contents of Log database.
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
bgGeo.destroyLog();
// Or with optional callback
bgGeo.destroyLog(new TSCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "[destroyLog] success");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(String error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[destroyLog] failure: " + error);
}
});| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Location |
getLocation |
Fetch native Location instance |
String |
getTimestamp |
Returns the ISO-8601 formatted UTC timestamp |
String |
getUUID |
Returns the uuid of the location |
String |
getEvent |
Returns associated event for this location (eg: motionchange, providerchange, geofence) |
boolean |
getIsMoving |
true when the location was recorded while device is in moving state |
double |
getBatteryLevel |
The battery-level at the time the location was recorded. |
boolean |
getBatteryIsCharging |
true if location was recorded while device was plugged into power. |
JSONObject |
getExtras |
The optional extras object appended to this location. |
DetectedActivity |
getDetectedActivity |
The associated DetectedActivity at the time the location was recorded. |
TSGeofence |
getGeofence |
Returns cooresponding TSGeofence instance if this location was recorded due to a geofence event |
String |
getGeofenceAction |
Returns the geofence action (ENTER,EXIT,DWELL) if the location was due to a geofence event |
String |
getGeofenceIdentifier |
Returns the geofence identifier if the location was recorded due to a geofence event. |
JSONObject |
toJson |
Renders the location-data to JSONObject. |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
DetectedActivity |
getDetectedActivity |
The associated DetectedActivity. |
String |
getActivityName |
String representation of motion activity (still, on_foot, in_vehicle, running, on_bicycle). |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
boolean |
isGPSEnabled |
true when GPS is enabled. |
boolean |
isNetworkEnabled |
true when Wifi geolocation is enabled. |
boolean |
isEnabled |
true when location-services is enabled. |
boolean |
isPermissionGranted |
true when user has authorized location permission. |
JSONObject |
toJson |
Render the event as a JSONObject. |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
TSGeofence |
getGeofence |
Returns the associated TSGeofence instance responsible for the geofence event. |
GeofencingEvent |
getGeofencingEvent |
Returns raw Android GeofencingEvent. |
TSLocation |
getLocation |
Returns the corresponding TSLocation instance where the geofence was triggered. |
JSONObject |
toJson |
Render the event as a JSONObject. |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
List<TSGeofence> |
getActivatedGeofences |
Returns the list of newly activated TSGeofence instances now being monitored. |
List<String> |
getDeactivatedGeofences |
Returns the list of geofence identifiers for those geofences which have stopped being monitored (likely due to being out-of-range of geofenceProximityRadius). |
JSONObject |
toJson |
Render the event as a JSONObject. |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
int |
getStatus |
Returns the HTTP response status code. |
String |
getResponseText |
Returns the raw HTTP response text. |
boolean |
isSuccess |
true when HTTP status respresents successful response (eg: 200, 201, 204). |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
TSLocation |
getLocation |
Returns the last known location. |
JSONObject |
toJson |
Render the event as a JSONObject |
| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
boolean |
hasConnecction |
Returns true if a network connection is available. |
Builds a TSCurrentPositionRequest:
TSCurrentPositionRequest request = new TSCurrentPositionRequest.Builder()
.setPersist(true)
.setCallback(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[current position] success: " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[current position] failure: " + error);
}
})
.setSamples(3)
.setExtras(extras)
.build();| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Builder |
setTimeout(int) |
Sets the timeout for location failure in seconds. |
Builder |
setPersist(boolean) |
Whether to persist the recorded location to SDK's database. Default is true when SDK is enabled. |
Builder |
setSamples(int) |
Number of location samples to record before returning the most accurate. Defaults to 3. |
Builder |
setDesiredAccuracy(int) |
If a location sample arrives having accuracy <= desiredAccuracy, the SDK will immediately stop sampling and return that location. |
Builder |
setExtras(JSONObject) |
Append arbitrary JSONObject to the persisted location. |
Builder |
setCallback(TSLocationCallback) |
Sets the TSLocationCallback for receiving the final location (or error). |
Builder |
setMaximumAge(Long) |
If a value > 0 is provided, the SDK can optionally return the last known location if that location-age is <= maximumAge instead of turning on location-services. |
TSCurrentPositionRequest |
build |
Builds the TSCurrentPositionRequest |
Builds a TSWatchPositionRequest instance:
TSWatchPositionRequest request = new TSWatchPositionRequest.Builder()
.setPersist(true)
.setInterval(5000L)
.setCallback(new TSLocationCallback() {
@Override
public void onLocation(TSLocation tsLocation) {
Log.i(TAG, "[watch position] success: " + tsLocation.toJson());
}
@Override
public void onError(Integer error) {
Log.i(TAG, "[watch position] failure: " + error);
}
})
.build();| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Builder |
setInterval(int) |
Sets sample rate to record locations. |
Builder |
setTimeout(int) |
Sets the timeout for location failure in seconds. |
Builder |
setPersist(boolean) |
Whether to persist the recorded location to SDK's database. Default is true when SDK is enabled. |
Builder |
setExtras(JSONObject) |
Append arbitrary JSONObject to the persisted location. |
Builder |
setCallback(TSLocationCallback) |
Sets the TSLocationCallback for receiving the final location (or error). |
TSWatchPositionRequest |
build |
Builds the TSWatchPositionRequest |
Builds a TSGeofence instance:
BackgroundGeolocation bgGeo = BackgroundGeolocation.getInstance(getApplicationContext(), getIntent());
TSGeofence geofence = new TSGeofence.Builder()
.setIdentifier("Office")
.setLatitude(37.234234)
.setLongitude(47.2856623)
.setRadius(200)
.setNotifyOnEntry(true)
.setNotifyOnExit(true)
.setNotifyOnDwell(true)
.setLoiteringDelay(30000)
.build();
bgGeo.addGeofence(geofence);| Return | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Builder |
setIdentifier(String) |
Unique identifier |
Builder |
setLatitude(double) |
Latitude of geofence center position. |
Builder |
setLongitude(double) |
Longitude of geofence center position. |
Builder |
setRadius(float) |
Radius of circular geofence in meters. Minimum reliable radius is 150 meters. |
Builder |
setNotifyOnEntry(boolean) |
Set true to enable enter transition. |
Builder |
setNotifyOnExit(boolean) |
Set true to enable exit transition. |
Builder |
setNotifyOnDwell(boolean) |
Set true to enable dwell transition. You must configure corresponding loiteringDelay |
Builder |
setLoiteringDelay(int) |
Time in milliseconds that device must loiter within a geofence before dwell transition fires. |
Builder |
setExtras(JSONObject) |
Attach arbitrary key/values to geofence event when posted to server. |